Electrical Safety
... The wire has a quite low melting point. As current flows through the wire it heats up. If too large a current flows it melts, thus breaking the circuit Use appropriate fuse size/rating ...
... The wire has a quite low melting point. As current flows through the wire it heats up. If too large a current flows it melts, thus breaking the circuit Use appropriate fuse size/rating ...
LonWorks PLCA-22 Power Line Communications Analyzer User`s
... current limits of the PLT-22 transceiver and booster amplifier are electronically controlled so that any load, including a short circuit, may be driven indefinitely without damage to the transceiver. The PLCA-22 analyzer supports 1.7,3.5,7, and 1OV p-p signal output levels at both 1A and 2A current ...
... current limits of the PLT-22 transceiver and booster amplifier are electronically controlled so that any load, including a short circuit, may be driven indefinitely without damage to the transceiver. The PLCA-22 analyzer supports 1.7,3.5,7, and 1OV p-p signal output levels at both 1A and 2A current ...
Heavy-Duty Truck Sytems Chapter 09
... • The vehicle cranking circuit functions to crank the engine until it can operate under its own power. • A cranking circuit is managed by a control circuit that uses low current to switch and energize a highcurrent starter motor circuit. • A starter motor converts the electrical energy of the vehicl ...
... • The vehicle cranking circuit functions to crank the engine until it can operate under its own power. • A cranking circuit is managed by a control circuit that uses low current to switch and energize a highcurrent starter motor circuit. • A starter motor converts the electrical energy of the vehicl ...
Obliteration of Harmonics on a VSI Fed Induction Motor Drive
... Sri Ramakrishna Institute of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India. ...
... Sri Ramakrishna Institute of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India. ...
Unit 2 - GVPCEW
... to be measured is transformed directly, with a suitable mechanism, into an electrical signal (current, voltage and frequency). The production of these signals is based upon electrical effects which may be resistive, inductive, capacitive etc. in nature. The input versus output energy relationship ta ...
... to be measured is transformed directly, with a suitable mechanism, into an electrical signal (current, voltage and frequency). The production of these signals is based upon electrical effects which may be resistive, inductive, capacitive etc. in nature. The input versus output energy relationship ta ...
Comparison of energy efficiency determination methods for the
... Fig. 2 compares the efficiency of a 1.1 kW induction motor derived from four international standards, namely, the IEEE Std. 112, IEC 60034-2-1 (direct method), JEC 37 and the GOST 25941-83. The direct method IEC 60034-2-1 and IEEE Std. 112 result in the lowest efficiency. The difference comes from t ...
... Fig. 2 compares the efficiency of a 1.1 kW induction motor derived from four international standards, namely, the IEEE Std. 112, IEC 60034-2-1 (direct method), JEC 37 and the GOST 25941-83. The direct method IEC 60034-2-1 and IEEE Std. 112 result in the lowest efficiency. The difference comes from t ...
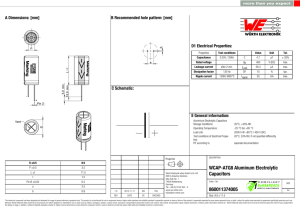
860011374005 Datasheet
... Moreover Würth Elektronik eiSos GmbH & Co KG products are neither designed nor intended for use in areas such as military, aerospace, aviation, nuclear control, submarine, transportation (automotive control, train control, ship control), transportation signal, disaster prevention, medical, public in ...
... Moreover Würth Elektronik eiSos GmbH & Co KG products are neither designed nor intended for use in areas such as military, aerospace, aviation, nuclear control, submarine, transportation (automotive control, train control, ship control), transportation signal, disaster prevention, medical, public in ...
Occupational Licensing -Electrical Work Licence Classes
... wired electrical equipment in such a manner so as to comply with all relevant standards. Reconnected electrical equipment shall be situated in the same location as previously disconnected electrical equipment. Reconnection of an electrical circuit but excludes electrical work; a) where voltages exis ...
... wired electrical equipment in such a manner so as to comply with all relevant standards. Reconnected electrical equipment shall be situated in the same location as previously disconnected electrical equipment. Reconnection of an electrical circuit but excludes electrical work; a) where voltages exis ...
Grounding and Bonding
... When designed and installed following the appropriate codes, specifications, and safety practices, the grounding and bonding network components create a system that effectively safeguards personnel, property, and equipment The most common hazard in grounding and bonding networks is electric shock, w ...
... When designed and installed following the appropriate codes, specifications, and safety practices, the grounding and bonding network components create a system that effectively safeguards personnel, property, and equipment The most common hazard in grounding and bonding networks is electric shock, w ...
Presentation Slides
... Transfers signals to alarm (activate/deactivate). Sends signals to the indoor display unit for user visibility (power on, low battery, alarm activated). ...
... Transfers signals to alarm (activate/deactivate). Sends signals to the indoor display unit for user visibility (power on, low battery, alarm activated). ...
Electromagnetic compatibility

Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the branch of electrical sciences which studies the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy with reference to the unwanted effects (electromagnetic interference, or EMI) that such energy may induce. The goal of EMC is the correct operation, in the same electromagnetic environment, of different equipment which use electromagnetic phenomena, and the avoidance of any interference effects.In order to achieve this, EMC pursues two different kinds of issues. Emission issues are related to the unwanted generation of electromagnetic energy by some source, and to the countermeasures which should be taken in order to reduce such generation and to avoid the escape of any remaining energies into the external environment. Susceptibility or immunity issues, in contrast, refer to the correct operation of electrical equipment, referred to as the victim, in the presence of unplanned electromagnetic disturbances.Interference mitigation and hence electromagnetic compatibility is achieved by addressing both emission and susceptibility issues, i.e., quieting the sources of interference and hardening the potential victims. The coupling path between source and victim may also be separately addressed to increase its attenuation.