See an abridged list of rulers in Mesopotamia
... • ca. 3500–3000 B.C. Cities emerge throughout the region, with the largest concentration in the south. These cities are centered around monumental mud-brick temples set on high platforms. At the largest city, Uruk, walls and massive columns of some buildings are decorated with mosaics of colored sto ...
... • ca. 3500–3000 B.C. Cities emerge throughout the region, with the largest concentration in the south. These cities are centered around monumental mud-brick temples set on high platforms. At the largest city, Uruk, walls and massive columns of some buildings are decorated with mosaics of colored sto ...
Sumer and Akkad
... The Sumerian location was located in the Southern parts of Mesopotamia between the Tigris and Euphrates river. in the area that later became Babylonia and is now southern Iraq from around Baghdad to the Persian . Sumerians were non-semitic peoples and spoke a language isolate. ...
... The Sumerian location was located in the Southern parts of Mesopotamia between the Tigris and Euphrates river. in the area that later became Babylonia and is now southern Iraq from around Baghdad to the Persian . Sumerians were non-semitic peoples and spoke a language isolate. ...
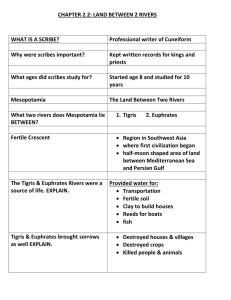
1. Mesopotamia literally means “between the rivers”. (p.117) 2. What
... 3. Cuneiform involved using styluses to make wedged- shaped symbols on clay tablets. (p.127) 4. What was the world’s first civilization that developed in Mesopotamia (p.122)? Sumer 5. What role did silt play in the development of Mesopotamia (p.117)? Made land ideal for farming 6. Hammurabi was most ...
... 3. Cuneiform involved using styluses to make wedged- shaped symbols on clay tablets. (p.127) 4. What was the world’s first civilization that developed in Mesopotamia (p.122)? Sumer 5. What role did silt play in the development of Mesopotamia (p.117)? Made land ideal for farming 6. Hammurabi was most ...
Lecture outline
... a. Fertile land, but irratic floodings The rise of the city-state and the city’s relationship to the country Justification of kingship (god-like, or half/ 2/3 divine) 3. Human relationship to nature From the description of the gods (often in animal or natural form) From the relationship of g ...
... a. Fertile land, but irratic floodings The rise of the city-state and the city’s relationship to the country Justification of kingship (god-like, or half/ 2/3 divine) 3. Human relationship to nature From the description of the gods (often in animal or natural form) From the relationship of g ...
sswhhl08na_bio101020..
... over Sumerian territory. The city of Akkad was located north of Sumer along the Euphrates River. As ruler of Akkad, Sargon formed the world’s first permanent army. It is thought that at this time, Sargon named himself Sharrum-kin, which translates to “the rightful king” in Akkadian. Sargon might hav ...
... over Sumerian territory. The city of Akkad was located north of Sumer along the Euphrates River. As ruler of Akkad, Sargon formed the world’s first permanent army. It is thought that at this time, Sargon named himself Sharrum-kin, which translates to “the rightful king” in Akkadian. Sargon might hav ...
Learning Center Documents
... strikingly similar to those found in the Judeo-Christian Book of Genesis. Sumerian society was made up of several classes, including kings, priests, nobles, and government officials in the upper part; traders, artisans, and farmers in the middle; and slaves in the lowest part. Slaves were usually pr ...
... strikingly similar to those found in the Judeo-Christian Book of Genesis. Sumerian society was made up of several classes, including kings, priests, nobles, and government officials in the upper part; traders, artisans, and farmers in the middle; and slaves in the lowest part. Slaves were usually pr ...
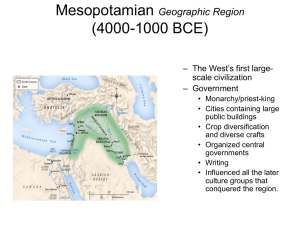
Mesopotamia, c. 4000-1000 B.C.E. (Bronze Age)
... discovered that there was a marked increase in the sea levels about 6,000 years ago as the last ice age ended. The melting ice drained to the oceans causing the sea level to rise more than ten feet in one century. ...
... discovered that there was a marked increase in the sea levels about 6,000 years ago as the last ice age ended. The melting ice drained to the oceans causing the sea level to rise more than ten feet in one century. ...
Mesopotamia
... Temple and rituals to their own dominant God of a shared pantheon. The region and peoples came to be the Sumerian civilization. The King of Akkadia, Sargon The Great united Sumeria through warfare into the world’s first empire 2370 BC ...
... Temple and rituals to their own dominant God of a shared pantheon. The region and peoples came to be the Sumerian civilization. The King of Akkadia, Sargon The Great united Sumeria through warfare into the world’s first empire 2370 BC ...
Mesopotamia: Sumerians Notes
... __________________________________ = Sumerian system of writing ...
... __________________________________ = Sumerian system of writing ...
MesopotamiaPPT
... • As wars became more frequent the warriors ruled for longer periods of time • Eventually they became rulers for life • These rulers usually passed their power on to their sons. • A series of rulers from a single family is called a dynasty. Gudea of Lagash (c. 2140 BC) ...
... • As wars became more frequent the warriors ruled for longer periods of time • Eventually they became rulers for life • These rulers usually passed their power on to their sons. • A series of rulers from a single family is called a dynasty. Gudea of Lagash (c. 2140 BC) ...
Lesson 2: Mesopotamia Vocabulary
... sounds. This new form of writing was called cuneiform. People used writing to keep records, tell stories, write letters, and set down laws. ...
... sounds. This new form of writing was called cuneiform. People used writing to keep records, tell stories, write letters, and set down laws. ...
Empires in Mesopotamia - White Plains Public Schools
... Migration and Empire. Between 3000 B.C. and 2000 B.C. two major groups of people began to migrate within western Asia. One group spoke Semitic languages, the other Indo-European languages. The first of these were Semitic-speaking pastoral nomads who began migrating into Mesopotamia from Arabia and S ...
... Migration and Empire. Between 3000 B.C. and 2000 B.C. two major groups of people began to migrate within western Asia. One group spoke Semitic languages, the other Indo-European languages. The first of these were Semitic-speaking pastoral nomads who began migrating into Mesopotamia from Arabia and S ...
Slide 1
... 282 laws, written by scribes on 12 tablets. Unlike earlier laws, it was written in Akkadian, the daily language of Babylon, and could therefore be read by any literate person in the city. ...
... 282 laws, written by scribes on 12 tablets. Unlike earlier laws, it was written in Akkadian, the daily language of Babylon, and could therefore be read by any literate person in the city. ...
Akkadian Empire

The Akkadian Empire /əˈkeɪdiən/ was an ancient Semitic empire centered in the city of Akkad /ˈækæd/ and its surrounding region, also called Akkad in ancient Mesopotamia. The empire united all the indigenous Akkadian-speaking Semites and the Sumerian speakers under one rule. The Akkadian Empire controlled Mesopotamia, the Levant, and parts of Iran.During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Semitic Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism. Akkadian gradually replaced Sumerian as a spoken language somewhere between the 3rd and the 2nd millennia BC (the exact dating being a matter of debate).The Akkadian Empire reached its political peak between the 24th and 22nd centuries BC, following the conquests by its founder Sargon of Akkad (2334–2279 BC). Under Sargon and his successors, Akkadian language was briefly imposed on neighboring conquered states such as Elam. Akkad is sometimes regarded as the first empire in history, though there are earlier Sumerian claimants.After the fall of the Akkadian Empire, the Akkadian people of Mesopotamia eventually coalesced into two major Akkadian speaking nations: Assyria in the north, and, a few centuries later, Babylonia in the south.