Ch 30. - Cloudfront.net
... is to the left (below) the full-benefit demand curve Dt. As a result, the equilibrium output Qe is less than the optimal output Qo. ...
... is to the left (below) the full-benefit demand curve Dt. As a result, the equilibrium output Qe is less than the optimal output Qo. ...
1 - people.vcu.edu
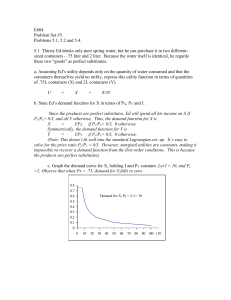
... Graphically, then, the demand curve would consist of a vertical line. At any price ratio where X was consumed, every increase or decrease in Px would have enough income added or subtracted to leave consumption at exactly the same point. The only change occurs when Px rises enough to cause a shift to ...
... Graphically, then, the demand curve would consist of a vertical line. At any price ratio where X was consumed, every increase or decrease in Px would have enough income added or subtracted to leave consumption at exactly the same point. The only change occurs when Px rises enough to cause a shift to ...
File
... • The Income Effect: A change in the price of a product changes a consumer’s real income (purchasing power) and thus the quantity of the product purchased. In other words, you are richer if a price drops and vice versa. • The Substitution Effect: Things become a better or worse “deal.” When the pric ...
... • The Income Effect: A change in the price of a product changes a consumer’s real income (purchasing power) and thus the quantity of the product purchased. In other words, you are richer if a price drops and vice versa. • The Substitution Effect: Things become a better or worse “deal.” When the pric ...
The_Importance_of_Elasticity_of_Supply.pdf
... Barriers to entry – e.g. Patents or high cost of advertising could make it hard for new firms to enter the market Raw materials – If raw materials are readily available, it will be relatively easy to expand production Inventory – Businesses with plenty of stock can increase supply easily. Time – Man ...
... Barriers to entry – e.g. Patents or high cost of advertising could make it hard for new firms to enter the market Raw materials – If raw materials are readily available, it will be relatively easy to expand production Inventory – Businesses with plenty of stock can increase supply easily. Time – Man ...
Econ161SQ8(Money and Inflation)
... The adjustment process: i.At the initial value of money of 1/P1, people are now holding more money than they desire to hold (that is, the supply of money exceeds the demand for money at 1/P1). ii. The public attempts to reduce their excess holdings by either spending on goods and services or by lend ...
... The adjustment process: i.At the initial value of money of 1/P1, people are now holding more money than they desire to hold (that is, the supply of money exceeds the demand for money at 1/P1). ii. The public attempts to reduce their excess holdings by either spending on goods and services or by lend ...
Ch 4
... one must determine what is essential and what is not. - If there are few substitutions for goods then the product is less elastic - Life saving medicine is inelastic However, if there are ample substitutions for a product then the product is more elastic ...
... one must determine what is essential and what is not. - If there are few substitutions for goods then the product is less elastic - Life saving medicine is inelastic However, if there are ample substitutions for a product then the product is more elastic ...
Consumer-Driven Demand and Operations Management
... functions of price and product attributes (e.g., quality, style trends, etc.). However, these new sophisticated selling techniques—examples are mixed sales channels, portals, group buying, and auctions, each of which is enabled by information technologies, the Internet, or both—are changing and expa ...
... functions of price and product attributes (e.g., quality, style trends, etc.). However, these new sophisticated selling techniques—examples are mixed sales channels, portals, group buying, and auctions, each of which is enabled by information technologies, the Internet, or both—are changing and expa ...
Money - Gaian Economics
... investment capital. The inadequate supply of money that remains condemns certain areas to a permanently low level of economic activity. ...
... investment capital. The inadequate supply of money that remains condemns certain areas to a permanently low level of economic activity. ...
Chapter 5 Quiz
... Correct Answers are marked with an “*”. 1. Demand is said to be elastic if a. the price of the good responds substantially to changes in demand. b. demand shifts substantially when income or the expected future price of the good changes. c. buyers do not respond much to changes in the price of the g ...
... Correct Answers are marked with an “*”. 1. Demand is said to be elastic if a. the price of the good responds substantially to changes in demand. b. demand shifts substantially when income or the expected future price of the good changes. c. buyers do not respond much to changes in the price of the g ...
ECO 154/254
... under conditions of governmental noninterference, or laissez-faire, and free trade. In Smith's view, the production and exchange of goods can be stimulated, and a consequent rise in the general standard of living attained, only through the efficient operations of private industrial and commercial en ...
... under conditions of governmental noninterference, or laissez-faire, and free trade. In Smith's view, the production and exchange of goods can be stimulated, and a consequent rise in the general standard of living attained, only through the efficient operations of private industrial and commercial en ...
Chapter 4, Section 3
... A measure of responsiveness that tells us how a dependent variable such as quantity responds to a change in an independent variable such as price. ...
... A measure of responsiveness that tells us how a dependent variable such as quantity responds to a change in an independent variable such as price. ...
Mathematical Principles of the Theory of Wealth
... Let us not forget that, strictly speaking, the principle just enunciated admits of exceptions, because a continuous function may have interruptions of continuity in some points of its course ; but just as friction wears down roughnesses and softens outlines, so the wear of commerce tends to suppress ...
... Let us not forget that, strictly speaking, the principle just enunciated admits of exceptions, because a continuous function may have interruptions of continuity in some points of its course ; but just as friction wears down roughnesses and softens outlines, so the wear of commerce tends to suppress ...
Int. trade 4- answers
... decreased sales of domestically produced goods lower costs of production for businesses using imported inputs (paragraph o) improvements in efficiency and allocation of resources caused by the reduction of the deadweight loss arising from the lower tariffs increased FDI increased exports. Impacts on ...
... decreased sales of domestically produced goods lower costs of production for businesses using imported inputs (paragraph o) improvements in efficiency and allocation of resources caused by the reduction of the deadweight loss arising from the lower tariffs increased FDI increased exports. Impacts on ...
Think of all the words connected to unemployment and fill in as
... company moves its work to another country. No similar work is available locally ...
... company moves its work to another country. No similar work is available locally ...
JEAN-BAPTISTE SAY AND THE LAW OF MARKETS
... Maynard Keynes later erroneously attributed to Jean-Baptiste Say”. Others, such as Jacob Hollander and TE Gregory (1928: lxxx), Chipman (1965) and Stigler (1965) argue that James Mill published something closer to the version of Say’s law now commonly accepted in his 1807 Commerce Defended, thereby ...
... Maynard Keynes later erroneously attributed to Jean-Baptiste Say”. Others, such as Jacob Hollander and TE Gregory (1928: lxxx), Chipman (1965) and Stigler (1965) argue that James Mill published something closer to the version of Say’s law now commonly accepted in his 1807 Commerce Defended, thereby ...
Capitalism and Free Enterprise - McGraw
... Businesses want to make money. That desire will lead them to make products that people need and want. People will give their money to the businesses that supply those needs and wants. In a similar fashion, people compete to sell their labor and employers compete to purchase it. The result is an effi ...
... Businesses want to make money. That desire will lead them to make products that people need and want. People will give their money to the businesses that supply those needs and wants. In a similar fashion, people compete to sell their labor and employers compete to purchase it. The result is an effi ...
Suggested Solutions to Assignment 2 (Optional)
... Using both the liquidity preference framework and the supply and demand for bonds framework, explain why interest rates are pro-cyclical (rising when the economy is expanding and falling during recessions). In the loanable funds (the supply and demand for bonds) framework, when the economy booms, th ...
... Using both the liquidity preference framework and the supply and demand for bonds framework, explain why interest rates are pro-cyclical (rising when the economy is expanding and falling during recessions). In the loanable funds (the supply and demand for bonds) framework, when the economy booms, th ...
Supply and Demand
... -Perfect Competition: a large number of small firms (businesses), each of which sells an identical or homogeneous product to a large number of buyers. -both consumers and producers have perfect or accurate knowledge about the market -no buyer in the market gets or expects to get preferential treatme ...
... -Perfect Competition: a large number of small firms (businesses), each of which sells an identical or homogeneous product to a large number of buyers. -both consumers and producers have perfect or accurate knowledge about the market -no buyer in the market gets or expects to get preferential treatme ...
Deriving the Demand Curve Review: A demand curve is a graph
... and the quantity demanded of that good, all other things being equal. The demand curve for a good is derived by finding the consumer’s optimal combination at various prices. Using the example of snacks and toys, find the consumers optimal choice when the price of the toy is $3. Under the goods space ...
... and the quantity demanded of that good, all other things being equal. The demand curve for a good is derived by finding the consumer’s optimal combination at various prices. Using the example of snacks and toys, find the consumers optimal choice when the price of the toy is $3. Under the goods space ...
Thinking Like an Economist
... interest rates to increase. The income gains from a higher minimum wage are worth more than any slight reduction in employment. Provincial governments should be allowed to collect from tobacco companies the costs of treating smoking-related illnesses among the ...
... interest rates to increase. The income gains from a higher minimum wage are worth more than any slight reduction in employment. Provincial governments should be allowed to collect from tobacco companies the costs of treating smoking-related illnesses among the ...
Chapter 7 Consumer Surplus - addendum
... 2. Free markets allocate the demand for goods to the sellers who can produce them at the least cost Only produce if you are paid as much (or more) than product costs to make (MC) ...
... 2. Free markets allocate the demand for goods to the sellers who can produce them at the least cost Only produce if you are paid as much (or more) than product costs to make (MC) ...
Demand
... Determinants of Demand Exercise • Now make a list of all 5 determinants of demand. Indented below each determinant write a scenario that would increase or decrease the demand for coke. Then state whether it increased or decreased and which new curve the demand curve would shift to…D2 or D3. Reset t ...
... Determinants of Demand Exercise • Now make a list of all 5 determinants of demand. Indented below each determinant write a scenario that would increase or decrease the demand for coke. Then state whether it increased or decreased and which new curve the demand curve would shift to…D2 or D3. Reset t ...