Elasticity of Supply 2013
... of canister have switched their production processes quickly to meet the high demand for fuel containers? If capital and labour resources are occupationally mobile then the elasticity of supply for a product is higher than if capital equipment and labour cannot be switched and the production process ...
... of canister have switched their production processes quickly to meet the high demand for fuel containers? If capital and labour resources are occupationally mobile then the elasticity of supply for a product is higher than if capital equipment and labour cannot be switched and the production process ...
Lecture 9
... of workers whose skills are not demanded, who lack sufficient skill to obtain employment, or who cannot move to locations where jobs are available. ► The demand for the good or the service produced is important ► Need to be retrained or move ► More likely to be long-term Alomar_111_9 ...
... of workers whose skills are not demanded, who lack sufficient skill to obtain employment, or who cannot move to locations where jobs are available. ► The demand for the good or the service produced is important ► Need to be retrained or move ► More likely to be long-term Alomar_111_9 ...
The Role of Profit
... • Started with an industry where economic profits were being made. This attracted new firms and, as a result, price decreased and the output of existing firms decreased. This continued until economic profit was zero. Price was then equal to minimum average total cost. (See graph) ...
... • Started with an industry where economic profits were being made. This attracted new firms and, as a result, price decreased and the output of existing firms decreased. This continued until economic profit was zero. Price was then equal to minimum average total cost. (See graph) ...
AP Macroeconomics, Chapter 7 (Consumers, Producers, and the
... Suppose a technological advance reduces the cost of making computers. (8) a. Draw a supply-and-demand diagram to show what happens to price, quantity, consumer surplus, and producer surplus in the market for computers. b. Computers and adding machines are substitutes. Use a supply-and-demand diagram ...
... Suppose a technological advance reduces the cost of making computers. (8) a. Draw a supply-and-demand diagram to show what happens to price, quantity, consumer surplus, and producer surplus in the market for computers. b. Computers and adding machines are substitutes. Use a supply-and-demand diagram ...
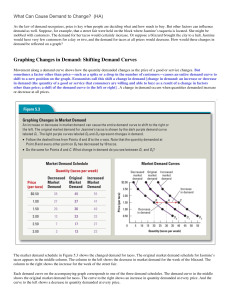
Graphing Changes in Demand: Shifting Demand Curves
... consumer incomes or tastes] that can cause a change in demand for a good or service. We will consider each demand shifter as if it were independent of all the rest—ceteris paribus. But in fact, as any economist will tell you, everything is interconnected. Changes in income. Generally, an increase in ...
... consumer incomes or tastes] that can cause a change in demand for a good or service. We will consider each demand shifter as if it were independent of all the rest—ceteris paribus. But in fact, as any economist will tell you, everything is interconnected. Changes in income. Generally, an increase in ...
Week 7
... The rate of change of revenue with respect to the number of employees is called the marginal-revenue product. It approximates the change in revenue that results when a manufacturer hires an extra employee. Example 5: (Example 8 in Section 11.5) A manufacturer determines that m employees will produce ...
... The rate of change of revenue with respect to the number of employees is called the marginal-revenue product. It approximates the change in revenue that results when a manufacturer hires an extra employee. Example 5: (Example 8 in Section 11.5) A manufacturer determines that m employees will produce ...
Some Basic Stuff on Empirical Work
... Some Basic Stuff on Empirical Work • Clearly we need to account for demand shifters i.e. other variables that may shift the demand function. For example, population (N), prices of related goods (Pr) and income (M) may explain the shifts in demand in different points in time (D1, D2, and D3). • So s ...
... Some Basic Stuff on Empirical Work • Clearly we need to account for demand shifters i.e. other variables that may shift the demand function. For example, population (N), prices of related goods (Pr) and income (M) may explain the shifts in demand in different points in time (D1, D2, and D3). • So s ...
Week 3
... their use accordingly. Since lubricating oil is a complement to fuel, less of it will be demanded as the usage of cars declines. Car engines present more complex problem. If they are complements, fewer of them will be demanded as the demand for cars decreases. On the other hand, if people substitute ...
... their use accordingly. Since lubricating oil is a complement to fuel, less of it will be demanded as the usage of cars declines. Car engines present more complex problem. If they are complements, fewer of them will be demanded as the demand for cars decreases. On the other hand, if people substitute ...
Graphing Changes in Demand: Shifting Demand Curves
... demand for a good or service; examples include changes in consumer incomes or tastes] that can cause a change in demand for a good or service. We will consider each demand shifter as if it were independent of all the rest—ceteris paribus. But in fact, as any economist will tell you, everything is in ...
... demand for a good or service; examples include changes in consumer incomes or tastes] that can cause a change in demand for a good or service. We will consider each demand shifter as if it were independent of all the rest—ceteris paribus. But in fact, as any economist will tell you, everything is in ...
Slide 1
... THE DECLINE IN THE PRICE LEVEL REDUCES NOMINAL WAGES, WHICH THEN SHIFTS AGGREGATE SUPPLY TO THE RIGHT. THE PRICE LEVEL DECLINES AND OUTPUT RETURNS TO FULL EMPLOYMENT. -THIS IS THE MOST CONTROVERSIAL APPLICATION OF THE EXTENDED AD-AS MODEL. THE KEY POINT OF DISPUTE IS HOW LONG IT WOULD TAKE IN THE RE ...
... THE DECLINE IN THE PRICE LEVEL REDUCES NOMINAL WAGES, WHICH THEN SHIFTS AGGREGATE SUPPLY TO THE RIGHT. THE PRICE LEVEL DECLINES AND OUTPUT RETURNS TO FULL EMPLOYMENT. -THIS IS THE MOST CONTROVERSIAL APPLICATION OF THE EXTENDED AD-AS MODEL. THE KEY POINT OF DISPUTE IS HOW LONG IT WOULD TAKE IN THE RE ...
Marginal costs and benefits
... S tells us the dollars worth of other goods and services that firms must forgo to produce one more pizza. That is, the S shows the seller’s cost of producing each unit of pizza. ...
... S tells us the dollars worth of other goods and services that firms must forgo to produce one more pizza. That is, the S shows the seller’s cost of producing each unit of pizza. ...
... The purpose of this project is to develop such a model for the supply of lettuce in the UK bagged salad market, based on research undertaken at HRI to look at the value system and supply chain for delivering lettuce to the UK pre-pack market. The project will entail a staged process, starting out wi ...
Product and Process Design
... fixed costs are estimated to be $500,000. Your product sells for $100 and costs you $50 to manufacture. What is the breakeven point? If you sell 15,000 units, what will be ...
... fixed costs are estimated to be $500,000. Your product sells for $100 and costs you $50 to manufacture. What is the breakeven point? If you sell 15,000 units, what will be ...
Money and its Functions Текст взят из: English for Economists
... of payment. In modern economies, fiat money is supplemented by IOU (I owe you) money. IOU money is a medium of exchange based on the debt of a private firm or individual. A bank deposit is IOU money because it is a debt of the bank. When you have a bank deposit the bank owes you money. Bank deposits ...
... of payment. In modern economies, fiat money is supplemented by IOU (I owe you) money. IOU money is a medium of exchange based on the debt of a private firm or individual. A bank deposit is IOU money because it is a debt of the bank. When you have a bank deposit the bank owes you money. Bank deposits ...
The Circular Flow Model
... Shows the economic transactions that occur between households, firms and other sectors in the economy. ...
... Shows the economic transactions that occur between households, firms and other sectors in the economy. ...
Willingness to Pay, MB and Consumer Surplus
... game. Let’s note that the $50 you are willing to spend could be spent on something else. In economics we tend to say if you spend the $50 on the ticket then the game is at least as valuable, and maybe more valuable, to you then what you would have used the $50 for in the alternative case. In other w ...
... game. Let’s note that the $50 you are willing to spend could be spent on something else. In economics we tend to say if you spend the $50 on the ticket then the game is at least as valuable, and maybe more valuable, to you then what you would have used the $50 for in the alternative case. In other w ...
Price Elasticity (Fig 5.6)
... 1 - week advance purchase, Saturday night stay 3 - week advance purchase, Saturday night stay 3-week advance purchase, Saturday night stay, $100 for changes Specified flights, book on Internet, no ...
... 1 - week advance purchase, Saturday night stay 3 - week advance purchase, Saturday night stay 3-week advance purchase, Saturday night stay, $100 for changes Specified flights, book on Internet, no ...
Supply & Demand
... A change of the curve (right or left) indicates an across the board change in supply ...
... A change of the curve (right or left) indicates an across the board change in supply ...
Ch. 21 Demand and Supply
... Subsidy—gov’t payment to an individual or business for certain actions; encourage producers to enter or even stay in the market; taxes and subsidies change production costs ...
... Subsidy—gov’t payment to an individual or business for certain actions; encourage producers to enter or even stay in the market; taxes and subsidies change production costs ...
PROBLEM SET 3 SOLUTIONS 14.02 Introductory Macroeconomics March 16, 2005
... I. Answer each as True, False, or Uncertain, providing some explanation for your choice. 1. The aggregate demand curve is downward sloping because people demand fewer goods at higher prices. FALSE. The AD curve is downward sloping because an increase in prices reduces real money supply, which induce ...
... I. Answer each as True, False, or Uncertain, providing some explanation for your choice. 1. The aggregate demand curve is downward sloping because people demand fewer goods at higher prices. FALSE. The AD curve is downward sloping because an increase in prices reduces real money supply, which induce ...
09-Elasticities
... change in opposite direction – Thus, Higher price → lower spending Lower price → higher spending ...
... change in opposite direction – Thus, Higher price → lower spending Lower price → higher spending ...