Chapter Two The Thermodynamic Laws
... reservoir and produce a net amount of work." This was shown to be equivalent to the statement of Clausius. (2.3.2). Statements of the second law (2.3.2.1). Thermal reservoir Thermal reservoir, characterized by its temperature, is a reservoir of infinite heat capacity. Thermal reservoir can play the ...
... reservoir and produce a net amount of work." This was shown to be equivalent to the statement of Clausius. (2.3.2). Statements of the second law (2.3.2.1). Thermal reservoir Thermal reservoir, characterized by its temperature, is a reservoir of infinite heat capacity. Thermal reservoir can play the ...
finite volume analysis of convective heat transfer augmentation from
... Razzaq Al-Doori[2] An experimental study was conducted to investigate the enhancement of natural convection heat transfer from the rectangular fins by circular perforations. They showed that the heat ...
... Razzaq Al-Doori[2] An experimental study was conducted to investigate the enhancement of natural convection heat transfer from the rectangular fins by circular perforations. They showed that the heat ...
Full Text
... bound by infinite vertical plates. They considered the temperature of the plate is oscillating with time about a nonzero constant. However, Pop9 solved the problem of transient free convection in porous medium adjacent to a vertical semi-infinite flat plate with a steep increase in wall temperature ...
... bound by infinite vertical plates. They considered the temperature of the plate is oscillating with time about a nonzero constant. However, Pop9 solved the problem of transient free convection in porous medium adjacent to a vertical semi-infinite flat plate with a steep increase in wall temperature ...
Towards a microscopic description of the free
... Very recently, we showed that configuration-spacenetworks can be used to map the free-energy landscape of bulk water at ambient conditions.3 In this case, microstates are defined by hydrogen-bond connectivity patterns including the first and second solvation shells of a given water molecule (see Fig ...
... Very recently, we showed that configuration-spacenetworks can be used to map the free-energy landscape of bulk water at ambient conditions.3 In this case, microstates are defined by hydrogen-bond connectivity patterns including the first and second solvation shells of a given water molecule (see Fig ...
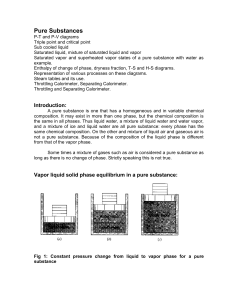
Pure Substances
... cylinder contains one kg of ice at –200C and one bar. When heat is transferred to the ice the pressure remains constant the specific volume increases slightly and the temperature increases until it reaches 0 0C, at which point the ice melts and temperature remains constant. This state is called satu ...
... cylinder contains one kg of ice at –200C and one bar. When heat is transferred to the ice the pressure remains constant the specific volume increases slightly and the temperature increases until it reaches 0 0C, at which point the ice melts and temperature remains constant. This state is called satu ...
972649 Quasi-Isothermal Expansion Engines for Liquid Nitrogen
... injection is adjusted so that the final pressure is always 0.11 MPa. For the range of injection pressures shown the isothermal work increases monotonically with increasing pressure, whereas the adiabatic cycle is only weakly dependent on peak cycle pressure above 4 MPa. The inclusion of pump work re ...
... injection is adjusted so that the final pressure is always 0.11 MPa. For the range of injection pressures shown the isothermal work increases monotonically with increasing pressure, whereas the adiabatic cycle is only weakly dependent on peak cycle pressure above 4 MPa. The inclusion of pump work re ...
1 CHAPTER 17 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS 17.1 Equilibrium
... The heat of reaction is the heat required to effect the reaction, or the heat produced by the reaction – some authors use one definition, others use the other. Here we shall define the heat of reaction as the heat required to effect the reaction, so that it is positive for endothermic reactions and ...
... The heat of reaction is the heat required to effect the reaction, or the heat produced by the reaction – some authors use one definition, others use the other. Here we shall define the heat of reaction as the heat required to effect the reaction, so that it is positive for endothermic reactions and ...
K - Rapid Learning Center
... (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 3. For the following picture, the first flask is 1.00 L and is at 180 mm Hg. The second flask is 1.00 L and is at 342 mm Hg. The third flask is 2.00 L and is at 188 mm Hg. What is the final pressure of the total system wh ...
... (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 3. For the following picture, the first flask is 1.00 L and is at 180 mm Hg. The second flask is 1.00 L and is at 342 mm Hg. The third flask is 2.00 L and is at 188 mm Hg. What is the final pressure of the total system wh ...
Chondrites as samples of differentiated planetesimals
... silicate melting temperatures, the metal liquid may be unable to segregate into a core until the silicates are partially molten. Previous studies differ on whether core segregation occurs near 950 °C, at the iron alloy eutectic, or in the range 1170 to 1570 °C, between the solidus and liquidus of th ...
... silicate melting temperatures, the metal liquid may be unable to segregate into a core until the silicates are partially molten. Previous studies differ on whether core segregation occurs near 950 °C, at the iron alloy eutectic, or in the range 1170 to 1570 °C, between the solidus and liquidus of th ...
h07rn-f lineax - Cables Plus Tas
... appliances and for building sites. The cable may be rated 0,6/1 kV where the installation has built-in protection and for motors in lifting appliances - machine tools - etc. This cable can be used in refrigerating installations. ...
... appliances and for building sites. The cable may be rated 0,6/1 kV where the installation has built-in protection and for motors in lifting appliances - machine tools - etc. This cable can be used in refrigerating installations. ...
Chapter 3. Thermodynamics and Electrochemical Kinetics
... are to produce heat or to do work, which could be either electrical or mechanical in form. The source of energy is fuel, in which the energy is bound in chemical form. Devices such as fuel cells and heat engines release the energy by chemical reactions, converting it into electricity or heat. Electr ...
... are to produce heat or to do work, which could be either electrical or mechanical in form. The source of energy is fuel, in which the energy is bound in chemical form. Devices such as fuel cells and heat engines release the energy by chemical reactions, converting it into electricity or heat. Electr ...
Temperature-Profile Methods for Estimating Thermally
... Temperature-profile methods have been originally employed to estimate ambient percolation fluxes in vadose environments, using measured deviations from the conduction-only geothermal gradient to evaluate the rate of convective heat transport with the percolating water (e.g, Bredehoeft and Papadopolo ...
... Temperature-profile methods have been originally employed to estimate ambient percolation fluxes in vadose environments, using measured deviations from the conduction-only geothermal gradient to evaluate the rate of convective heat transport with the percolating water (e.g, Bredehoeft and Papadopolo ...
Processing of milk-Cooling-Pasteurization
... due to oscillation of molecules generate heat. The high temperature produced in are of high water concentration transfer heat to other areas of food not absorbing microwave energy so well. Microwave absorption is inversely proportional to the penetration depth as a function of water content, salt co ...
... due to oscillation of molecules generate heat. The high temperature produced in are of high water concentration transfer heat to other areas of food not absorbing microwave energy so well. Microwave absorption is inversely proportional to the penetration depth as a function of water content, salt co ...
Second Law of Thermodynamics
... In all these cases, systems evolve to a state of less disorder and lower entropy, apparently violating the second law of thermodynamics. Could we, then, consider them as processes occurring in systems that are not isolated? ANSWER: True False ...
... In all these cases, systems evolve to a state of less disorder and lower entropy, apparently violating the second law of thermodynamics. Could we, then, consider them as processes occurring in systems that are not isolated? ANSWER: True False ...
Complete Paper
... no electrical supply, need no controller or pump, easy to install, can withstand mild sub-zero temperature, is reliable and long-lasting since there are no moving parts, scalable (several collectors can be connected in parallel to increase hot water supply), is easy to build and operate, no fuel cos ...
... no electrical supply, need no controller or pump, easy to install, can withstand mild sub-zero temperature, is reliable and long-lasting since there are no moving parts, scalable (several collectors can be connected in parallel to increase hot water supply), is easy to build and operate, no fuel cos ...