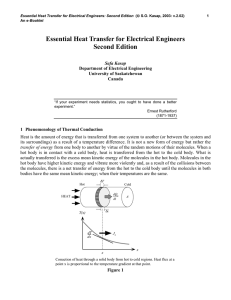
Latent Heat of Vaporisation of Liquid Nitrogen
... by 1.28kJmol-1 and shows a discrepancy with equation (4), where decreasing the power from 10W to 5.15 W, a factor of 0.515, should result in the gradients in figure 5, being smaller by a factor of 0.515 to those in figure 3, so that L remains constant. Possible sources of systematic error that were ...
... by 1.28kJmol-1 and shows a discrepancy with equation (4), where decreasing the power from 10W to 5.15 W, a factor of 0.515, should result in the gradients in figure 5, being smaller by a factor of 0.515 to those in figure 3, so that L remains constant. Possible sources of systematic error that were ...
Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Question Bank
... a) gills b) book gills c) book lungs d) tracheal system 38. Sensory structures found in arthropods are a) Anternnae b) Eye (simple & compound) c) statocysts 39. 1) Honey bee or apis 2) Bombyx or silkworm 40. Vectors are those animals which carries diseases causing germs in them example : mosquito (a ...
... a) gills b) book gills c) book lungs d) tracheal system 38. Sensory structures found in arthropods are a) Anternnae b) Eye (simple & compound) c) statocysts 39. 1) Honey bee or apis 2) Bombyx or silkworm 40. Vectors are those animals which carries diseases causing germs in them example : mosquito (a ...
Chapter 18
... a. Celsius degrees. b. Kelvins. c. Fahrenheit degrees. d. (a) or (b) above. e. (a), (b) or (c) above. ANS: b 62. Real heat engines are less efficient than Carnot engines because a. they operate irreversibly. b. they complete a cycle in a relatively brief time interval. c. they do not have the cold r ...
... a. Celsius degrees. b. Kelvins. c. Fahrenheit degrees. d. (a) or (b) above. e. (a), (b) or (c) above. ANS: b 62. Real heat engines are less efficient than Carnot engines because a. they operate irreversibly. b. they complete a cycle in a relatively brief time interval. c. they do not have the cold r ...
Passive and Active Solar Heating Systems
... strategy, when the outside a i r i s very cold and heat losses from the building are large, comparatively warm water in storage may go unused for a time while the a u x i l i a r y supply i s meeting the large load demand. However, stored solar heat w i l l be called upon when the load i s less seve ...
... strategy, when the outside a i r i s very cold and heat losses from the building are large, comparatively warm water in storage may go unused for a time while the a u x i l i a r y supply i s meeting the large load demand. However, stored solar heat w i l l be called upon when the load i s less seve ...
Thermodynamics
... take an infinite amount of time for the process to finish, perfectly reversible processes are impossible. However, if the system undergoing the changes responds much faster than the applied change, the deviation from reversibility may be negligible. In some cases, it is important to distinguish bet ...
... take an infinite amount of time for the process to finish, perfectly reversible processes are impossible. However, if the system undergoing the changes responds much faster than the applied change, the deviation from reversibility may be negligible. In some cases, it is important to distinguish bet ...
C044
... generation of heat. Due to the high heat fluxes generated by modem chips and the ever increasing density of electronic components on circuit boards it was estimated in the early 1980s that there would be a need to dissipate as much as 100 W/cm 2 by the end of the decade Prior to 1981, the highest co ...
... generation of heat. Due to the high heat fluxes generated by modem chips and the ever increasing density of electronic components on circuit boards it was estimated in the early 1980s that there would be a need to dissipate as much as 100 W/cm 2 by the end of the decade Prior to 1981, the highest co ...
Dynamic Modeling and Control Strategies for a
... Based on an existing micro-CSP (concentrating solar power) plant, the dynamic model is implemented in the Modelica modeling language. Detailed steady-state component models, which are implemented in EES and validated to data where available, form the basis for the dynamic components. The dynamic mod ...
... Based on an existing micro-CSP (concentrating solar power) plant, the dynamic model is implemented in the Modelica modeling language. Detailed steady-state component models, which are implemented in EES and validated to data where available, form the basis for the dynamic components. The dynamic mod ...
Fabric and ventilation heat loss
... recommended U-values for building elements in some European countries at April 2007 • Task. For the same temperature difference between inside and outside - identify the country which should have the smallest overall heat loss from its buildings. Identify the country that should have the largest. ...
... recommended U-values for building elements in some European countries at April 2007 • Task. For the same temperature difference between inside and outside - identify the country which should have the smallest overall heat loss from its buildings. Identify the country that should have the largest. ...
Thermodynamics and Kinetics
... Enthalpy changes are not the only factors that determine whether a process is spontaneous. Most spontaneous reactions are exothermic, but there are many that are not exothermic, however, reactions can be both spontaneous and highly endothermic. ...
... Enthalpy changes are not the only factors that determine whether a process is spontaneous. Most spontaneous reactions are exothermic, but there are many that are not exothermic, however, reactions can be both spontaneous and highly endothermic. ...
Heat review sheet
... Convection – Rising of hot air and falling of cold air. Heat – Movement of thermal energy of from one place to another. Medium – Something through which heat moves. Insulator – An object through which heat cannot pass (example – cork). Radiation – Heat energy traveling through space/air (heat from t ...
... Convection – Rising of hot air and falling of cold air. Heat – Movement of thermal energy of from one place to another. Medium – Something through which heat moves. Insulator – An object through which heat cannot pass (example – cork). Radiation – Heat energy traveling through space/air (heat from t ...
Entropy
... value, because teh mole fractions are less than one, and ln of a number less than one will be negative. ...
... value, because teh mole fractions are less than one, and ln of a number less than one will be negative. ...
Paper Title (use style: paper title)
... succeeding review. It is a well-known fact that while ambient temperatures are subjected to diurnal, seasonal and annual fluctuations, temperatures of the soil beyond a certain depth remain virtually constant. Though these variations do occur, amplitudes of fluctuations in the deep soil temperatures ...
... succeeding review. It is a well-known fact that while ambient temperatures are subjected to diurnal, seasonal and annual fluctuations, temperatures of the soil beyond a certain depth remain virtually constant. Though these variations do occur, amplitudes of fluctuations in the deep soil temperatures ...
Chapter Two The Thermodynamic Laws
... reservoir and produce a net amount of work." This was shown to be equivalent to the statement of Clausius. (2.3.2). Statements of the second law (2.3.2.1). Thermal reservoir Thermal reservoir, characterized by its temperature, is a reservoir of infinite heat capacity. Thermal reservoir can play the ...
... reservoir and produce a net amount of work." This was shown to be equivalent to the statement of Clausius. (2.3.2). Statements of the second law (2.3.2.1). Thermal reservoir Thermal reservoir, characterized by its temperature, is a reservoir of infinite heat capacity. Thermal reservoir can play the ...