Eisenmenger`s Syndrome
... the pulmonary (lung) arteries is high, causing an increased resistance to blood flow in the lungs. The syndrome can occur as a complication of ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect or persistent ductus arteriosus but can be associated with any congenital disease. It is often accompanied by ...
... the pulmonary (lung) arteries is high, causing an increased resistance to blood flow in the lungs. The syndrome can occur as a complication of ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect or persistent ductus arteriosus but can be associated with any congenital disease. It is often accompanied by ...
Chromosomal Disorders
... – Abnormal facies (flattened face and occiput, large tongue, small ears, epicanthal folds) – Congenital heart disease (40%)—AV canal – GI abnormalities (5%)—duodenal stenosis – Leukemia (10 to 20 x increased risk) – Ear infections – Thyroid problems – Premature aging (cataracts, Alzheimer Disease) • ...
... – Abnormal facies (flattened face and occiput, large tongue, small ears, epicanthal folds) – Congenital heart disease (40%)—AV canal – GI abnormalities (5%)—duodenal stenosis – Leukemia (10 to 20 x increased risk) – Ear infections – Thyroid problems – Premature aging (cataracts, Alzheimer Disease) • ...
Genetic Disorders Project
... It is autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive or sex linked (x-linked)? Does it affect more girls than boys or vice-versa? Does it affect a certain race in greater proportion? What is the frequency in the population? Slide 5 Symptoms/ Effects Age at which the symptoms begin Slide 6 Pro ...
... It is autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive or sex linked (x-linked)? Does it affect more girls than boys or vice-versa? Does it affect a certain race in greater proportion? What is the frequency in the population? Slide 5 Symptoms/ Effects Age at which the symptoms begin Slide 6 Pro ...
Tricamy 21 (Down Syndrome)
... •Smaller head than average •Abnormally shaped head •Never fully reach their average adult height ...
... •Smaller head than average •Abnormally shaped head •Never fully reach their average adult height ...
7. Oswaldo Hasb n - Cri-du-Chat
... mostly revolving around the length of the deletion in chromosome 5 as well as where the deletion occurs on the chromosome. The deletion occurs most often as a random event during the formation of reproductive cells (eggs or sperm) or in early fetal development. Only about 10 percent of people with C ...
... mostly revolving around the length of the deletion in chromosome 5 as well as where the deletion occurs on the chromosome. The deletion occurs most often as a random event during the formation of reproductive cells (eggs or sperm) or in early fetal development. Only about 10 percent of people with C ...
Slide ()
... Ehlers-Danlos syndrome This syndrome is actually a collection of six major genetic types with the common features of hyperextensible skin and joints, easy bruising, defective wound healing, and blood vessel fragility. Distinct abnormalities in collagen synthesis have been identified in some of the v ...
... Ehlers-Danlos syndrome This syndrome is actually a collection of six major genetic types with the common features of hyperextensible skin and joints, easy bruising, defective wound healing, and blood vessel fragility. Distinct abnormalities in collagen synthesis have been identified in some of the v ...
Mutations and Disorders worksheet-ANS
... MUSCUALR DYSTROPHY Sex linked recessive disorder in which the protein dystrophin is defective ...
... MUSCUALR DYSTROPHY Sex linked recessive disorder in which the protein dystrophin is defective ...
Genetic Disorder Poster Project
... Down Syndrome: mental retardation, short, heart defects, mild facial defects. Edwards Syndrome: baby’s ability to grow and develop appropriately is delayed or impaired. Undersized features, heart defects, organ malformation. Gaucher Disease: lacking enzyme to breakdown a fat: enlargement of organs, ...
... Down Syndrome: mental retardation, short, heart defects, mild facial defects. Edwards Syndrome: baby’s ability to grow and develop appropriately is delayed or impaired. Undersized features, heart defects, organ malformation. Gaucher Disease: lacking enzyme to breakdown a fat: enlargement of organs, ...
Cystic Fibrosis “65 Roses”
... ruptures in the walls of major arteries can occur, spine may curve, eye lens may dislocate. • Unusually long limbs, and is believed to have affected Abraham Lincoln. ...
... ruptures in the walls of major arteries can occur, spine may curve, eye lens may dislocate. • Unusually long limbs, and is believed to have affected Abraham Lincoln. ...
What is Phelan-McDermid Syndrome?
... reattaches to another chromosome. A ring chromosome is caused when the two ends of a chromosome fuse together, creating a circle. ...
... reattaches to another chromosome. A ring chromosome is caused when the two ends of a chromosome fuse together, creating a circle. ...
Pedigrees and Karyotypes What is a pedigree? How do you read a
... • Where can I get one? – Genetic counseling centers. ...
... • Where can I get one? – Genetic counseling centers. ...
Kate is born with features that do not look quite normal. Her eyes are
... The etiology behind Kate’s condition is a genetic abnormality known as trisomy 21. Each cell in our body normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. Down syndrome occurs when chromosome 21 receives a third chromosome. This extra genetic information on chromosome 21 causes all of the abnormalities ass ...
... The etiology behind Kate’s condition is a genetic abnormality known as trisomy 21. Each cell in our body normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. Down syndrome occurs when chromosome 21 receives a third chromosome. This extra genetic information on chromosome 21 causes all of the abnormalities ass ...
ONE GENE, TWO DISEASES: SCN5A AND ITS ROLE IN LONG QT
... Sudden cardiac death (SCD) is one of the leading causes of mortality globally and accounted for 24.1% of deaths in Singapore in 2008. Cardiac arrhythmias such as the Long QT (LQTS) and Brugada syndrome cause deaths in young individuals with structurally normal hearts. Cardiac arrhythmias include the ...
... Sudden cardiac death (SCD) is one of the leading causes of mortality globally and accounted for 24.1% of deaths in Singapore in 2008. Cardiac arrhythmias such as the Long QT (LQTS) and Brugada syndrome cause deaths in young individuals with structurally normal hearts. Cardiac arrhythmias include the ...
Name - Hightower Trail
... Know what a carrier is. Be able to draw/interpret one. 15. What causes genetic disorders? Are all mutations harmful? 16. What are hemophilia, cystic fibrosis, Kleinfelters’ syndrome, Turner’s syndrome, and Down syndrome? 17. What causes colorblindness? Are males or females more likely to have it? 18 ...
... Know what a carrier is. Be able to draw/interpret one. 15. What causes genetic disorders? Are all mutations harmful? 16. What are hemophilia, cystic fibrosis, Kleinfelters’ syndrome, Turner’s syndrome, and Down syndrome? 17. What causes colorblindness? Are males or females more likely to have it? 18 ...
Document
... Teenage Mothers May suffer from poverty and prenatal care Children may exhibit learning and behavior problems at schools Both preterm and low birth weight babies were twice as common in preteen mothers ...
... Teenage Mothers May suffer from poverty and prenatal care Children may exhibit learning and behavior problems at schools Both preterm and low birth weight babies were twice as common in preteen mothers ...
Due Date: Genetic Mutations Project As you have learned in class
... recessive?) What are the chances of getting this mutation? Is it because of a specific gene mutation? Or does it chromosomal? What are the sings/symptoms? How is it diagnosed? What types of treatment there are for those with this mutation? How can we help those affected? Include a suggested list of ...
... recessive?) What are the chances of getting this mutation? Is it because of a specific gene mutation? Or does it chromosomal? What are the sings/symptoms? How is it diagnosed? What types of treatment there are for those with this mutation? How can we help those affected? Include a suggested list of ...
Human Genetic Disorders
... syndrome will be born with 45 chromosomes in each cell rather than 46. The missing chromosome is an X chromosome. The affected person is always female ...
... syndrome will be born with 45 chromosomes in each cell rather than 46. The missing chromosome is an X chromosome. The affected person is always female ...
ppt
... Amniocentesis: • Fluid surrounding the fetus is drawn out by needle • Fetal cells are collected and grown in a lab. • Chromosomes can be then Karyotyped ...
... Amniocentesis: • Fluid surrounding the fetus is drawn out by needle • Fetal cells are collected and grown in a lab. • Chromosomes can be then Karyotyped ...
Human Heredity Notes
... females who lack ovaries & sex characteristics; short & sterile 2. Klinefelter Syndrome - XXY taller, longer limbs, sterile, some exhibit mental retardation 3. XYY male – 1 in every 1000; normal, fertile, taller than average How to Study: take sample cells from fetus & photograph metaphase chrom ...
... females who lack ovaries & sex characteristics; short & sterile 2. Klinefelter Syndrome - XXY taller, longer limbs, sterile, some exhibit mental retardation 3. XYY male – 1 in every 1000; normal, fertile, taller than average How to Study: take sample cells from fetus & photograph metaphase chrom ...
Genetic disorder/testing PPT
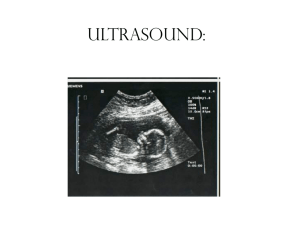
... Using sound waves to look at physical features of the developing fetus including size, anatomy, number of appendages/parts, sex, and heartbeat. ...
... Using sound waves to look at physical features of the developing fetus including size, anatomy, number of appendages/parts, sex, and heartbeat. ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... • Trisomy 21: Downs Syndrome • Trisomy 18: Edwards syndrome • Trisomy 13: Patau syndrome • XXY: Klinefelter's syndrome ...
... • Trisomy 21: Downs Syndrome • Trisomy 18: Edwards syndrome • Trisomy 13: Patau syndrome • XXY: Klinefelter's syndrome ...
Down syndrome

Down syndrome (DS or DNS) or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is typically associated with physical growth delays, characteristic facial features, and mild to moderate intellectual disability. The average IQ of a young adult with Down syndrome is 50, equivalent to the mental age of an 8- or 9-year-old child, but this varies widely.Down syndrome can be identified during pregnancy by prenatal screening followed by diagnostic testing, or after birth by direct observation and genetic testing. Since the introduction of screening, pregnancies with the diagnosis are often terminated. Regular screening for health problems common in Down syndrome is recommended throughout the person's life.Education and proper care have been shown to improve quality of life. Some children with Down syndrome are educated in typical school classes, while others require more specialized education. Some individuals with Down syndrome graduate from high school and a few attend post-secondary education. In adulthood, about 20% in the United States do paid work in some capacity with many requiring a sheltered work environment. Support in financial and legal matters is often needed. Life expectancy is around 50 to 60 years in the developed world with proper health care.Down syndrome is one of the most common chromosome abnormalities in humans, occurring in about one per 1000 babies born each year. In 2013 it resulted in 36,000 deaths down from 43,000 deaths in 1990. It is named after John Langdon Down, the British doctor who fully described the syndrome in 1866. Some aspects of the condition were described earlier by Jean-Étienne Dominique Esquirol in 1838 and Édouard Séguin in 1844. The genetic cause of Down syndrome—an extra copy of chromosome 21—was identified by French researchers in 1959.