heat and temperature
... can measure the latter, we could ask ourselves how bodies are heated. Is the increase in temperature proportional to the energy which we supply in the form of heat? In the following visual we deal with these questions. We have a substance which is heated by a heater the power of which, in W, we can ...
... can measure the latter, we could ask ourselves how bodies are heated. Is the increase in temperature proportional to the energy which we supply in the form of heat? In the following visual we deal with these questions. We have a substance which is heated by a heater the power of which, in W, we can ...
Standard Method of Test for Thermal Conductivity of Rock
... recalibration, constant axial load, controlled side losses, and constant temperature are necessary to achieve this precision. 12.2 Precision of determined thermal conductivity 12.2.1 The standard technique is relative so the intra and interlaboratory precision depends on the precision of the thermal ...
... recalibration, constant axial load, controlled side losses, and constant temperature are necessary to achieve this precision. 12.2 Precision of determined thermal conductivity 12.2.1 The standard technique is relative so the intra and interlaboratory precision depends on the precision of the thermal ...
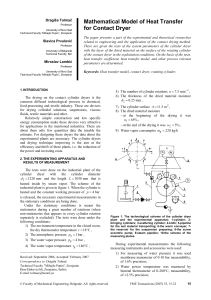
Mathematical Model of Heat Transfer for Contact Dryer
... Taking into account that local values of combined heat transfer coefficient are ( h2m ), the table 4, the variables along the cylinder size, as result they also give changeable technical resistances of heat transfer from the cylinder to air ( 1/ h2m ). So originate also ...
... Taking into account that local values of combined heat transfer coefficient are ( h2m ), the table 4, the variables along the cylinder size, as result they also give changeable technical resistances of heat transfer from the cylinder to air ( 1/ h2m ). So originate also ...
B - National Certification Examination for Energy Managers and
... repeats. The heat pump was developed as a space heating system where low temperature energy from the ambient air, water or earth is raised to heating system temperatures by doing compression work with an electric motor driven compressor 2 Marks ...
... repeats. The heat pump was developed as a space heating system where low temperature energy from the ambient air, water or earth is raised to heating system temperatures by doing compression work with an electric motor driven compressor 2 Marks ...
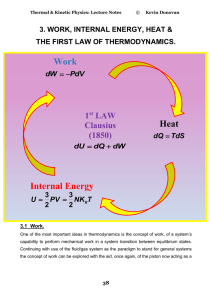
Affinity, Work, and Heat Introduction
... we do P∆V work, where P is the equilibrium pressure PNH3 and ∆V is the volume of a mole of ideal gas at 473.15 K and PNH3 . Because P1V1 = P2V2 for ideal gas, the P∆V work done is identical to what it would be if P was 1 bar, because although the pressure is greater, the volume change is proportiona ...
... we do P∆V work, where P is the equilibrium pressure PNH3 and ∆V is the volume of a mole of ideal gas at 473.15 K and PNH3 . Because P1V1 = P2V2 for ideal gas, the P∆V work done is identical to what it would be if P was 1 bar, because although the pressure is greater, the volume change is proportiona ...
Full-Text PDF
... where Cp, Ø, ρ, nf, n and f respectively represent specific heat capacity, volume fraction, density, nanofluid, nanoparticle and fluid. It has implied that increased thermal conductivity has been translated into decrease in specific heat capacity as shown by Pantzali et al. [24]. However this has no ...
... where Cp, Ø, ρ, nf, n and f respectively represent specific heat capacity, volume fraction, density, nanofluid, nanoparticle and fluid. It has implied that increased thermal conductivity has been translated into decrease in specific heat capacity as shown by Pantzali et al. [24]. However this has no ...
genius 13.1 Introduction. (1) Thermodynamics : It is a branch of
... A lead bullet at 27° C just melts when stopped by an obstacle. Assuming that 25% of heat is absorbed by the obstacle, then the velocity of the bullet at the time of striking (M.P. of lead = 327° C, specific heat of lead = 0.03 cal/gm°C, latent heat of fusion of lead = 6 cal/gm and J = 4.2 J/cal) ...
... A lead bullet at 27° C just melts when stopped by an obstacle. Assuming that 25% of heat is absorbed by the obstacle, then the velocity of the bullet at the time of striking (M.P. of lead = 327° C, specific heat of lead = 0.03 cal/gm°C, latent heat of fusion of lead = 6 cal/gm and J = 4.2 J/cal) ...
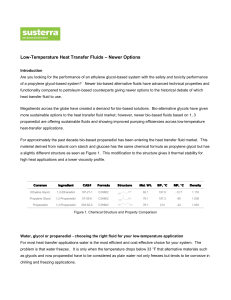
Low-Temperature Heat Transfer Fluids Newer Options
... Heat transfer fluids are widely used in food processing, commercial refrigeration, geothermal, and other lowtemperature heat-transfer applications that typically operate in a temperature range from 0°F to 42°F (-18°C to 6°C). Most heat transfer fluids have lower heat-transfer efficiencies than wate ...
... Heat transfer fluids are widely used in food processing, commercial refrigeration, geothermal, and other lowtemperature heat-transfer applications that typically operate in a temperature range from 0°F to 42°F (-18°C to 6°C). Most heat transfer fluids have lower heat-transfer efficiencies than wate ...
Energy
... Calorimetry: Calculating heat of a change Ex: 1 Heat of fusion of a solid (Hf) How much heat is absorbed per gram, if 10 grams of a solid melts in 300 grams of water, causing the water temperature to decrease by 500C? Step 1: how much heat did the water lose? (heat gained by the solid to melt) For t ...
... Calorimetry: Calculating heat of a change Ex: 1 Heat of fusion of a solid (Hf) How much heat is absorbed per gram, if 10 grams of a solid melts in 300 grams of water, causing the water temperature to decrease by 500C? Step 1: how much heat did the water lose? (heat gained by the solid to melt) For t ...
Heat equation

The heat equation is a parabolic partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or variation in temperature) in a given region over time.