Volcanic Acid-Base Reaction
... The volcano “erupted” when the acidic vinegar came into contact with the alkaline (or basic) baking soda, which neutralized it. The volcano then emitted carbon dioxide, which created the bubbles and popping noises. Strong acids and strong bases form corrosion on surfaces. When acids react with bases ...
... The volcano “erupted” when the acidic vinegar came into contact with the alkaline (or basic) baking soda, which neutralized it. The volcano then emitted carbon dioxide, which created the bubbles and popping noises. Strong acids and strong bases form corrosion on surfaces. When acids react with bases ...
File
... high, level areas called lava plateaus. First, lava flows out of several long cracks in an area. The thin, runny lava travels far before cooling and solidifying. Again and again, floods of lava flow on top of earlier floods. After millions of years, these layers of lava can form high plateaus. One e ...
... high, level areas called lava plateaus. First, lava flows out of several long cracks in an area. The thin, runny lava travels far before cooling and solidifying. Again and again, floods of lava flow on top of earlier floods. After millions of years, these layers of lava can form high plateaus. One e ...
Teacher`s Guide - Discovery Education
... What important function do volcanoes perform for the Earth? (Volcanoes act like cooling vents by releasing heat from Earth's core.) ...
... What important function do volcanoes perform for the Earth? (Volcanoes act like cooling vents by releasing heat from Earth's core.) ...
Study Guide: Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... 1. Different types of dangers associated with earthquakes and how the earthquake causes those dangers ...
... 1. Different types of dangers associated with earthquakes and how the earthquake causes those dangers ...
Volcanoes - geographylyndon
... • These are usually found at destructive boundaries. • Cone volcanoes are tall and steep-sided. • Cone volcanoes are formed by eruptions of thick, viscous (sticky) lava. • The thick lava moves relatively slowly and hardens quickly to form new rock - this explains the formation of a cone shape. • Eru ...
... • These are usually found at destructive boundaries. • Cone volcanoes are tall and steep-sided. • Cone volcanoes are formed by eruptions of thick, viscous (sticky) lava. • The thick lava moves relatively slowly and hardens quickly to form new rock - this explains the formation of a cone shape. • Eru ...
Tick, Tick, Boom Danger Zone
... Danger Zone Volcanoes are a huge hazard around the world, they exist almost everywhere, but they “commonly form along convergent plate boundaries”(Holt, ...
... Danger Zone Volcanoes are a huge hazard around the world, they exist almost everywhere, but they “commonly form along convergent plate boundaries”(Holt, ...
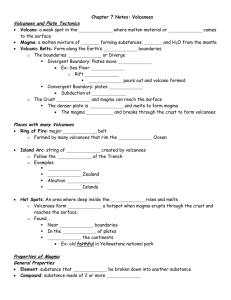
Chapter 7 Notes: Volcanoes Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcano Magma
... Volcanic Belts: Form along the Earth’s _______________ boundaries o The boundaries _______________ or Diverge Divergent Boundary: Plates move _______________ Ex: Sea Floor _______________ o Rift _______________ _______________ pours out and volcano formed Convergent Boundary: plates ________ ...
... Volcanic Belts: Form along the Earth’s _______________ boundaries o The boundaries _______________ or Diverge Divergent Boundary: Plates move _______________ Ex: Sea Floor _______________ o Rift _______________ _______________ pours out and volcano formed Convergent Boundary: plates ________ ...
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY
... Cinder cones are the smallest and have steep sides that are formed largely by the piling up of ash, cinders, and rocks. All of these materials are called pyroclastic ("fire-broken") and have been explosively erupted from the vent of the volcano. As the material falls back to the ground, it generally ...
... Cinder cones are the smallest and have steep sides that are formed largely by the piling up of ash, cinders, and rocks. All of these materials are called pyroclastic ("fire-broken") and have been explosively erupted from the vent of the volcano. As the material falls back to the ground, it generally ...
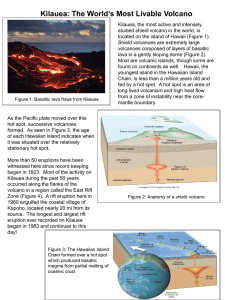
Kilauea: The World`s Most Livable Volcano
... Shield volcanoes are extremely large volcanoes composed of layers of basaltic lava in a gently sloping dome (Figure 2). Most are volcanic islands, though some are found on continents as well. Hawaii, the youngest island in the Hawaiian Island Chain, is less than a million years old and fed by a hot ...
... Shield volcanoes are extremely large volcanoes composed of layers of basaltic lava in a gently sloping dome (Figure 2). Most are volcanic islands, though some are found on continents as well. Hawaii, the youngest island in the Hawaiian Island Chain, is less than a million years old and fed by a hot ...
Volcanoes
... • Nuée ardentes are mobile dense clouds of incandescent ash that can move downhill at speeds up to 100 , km/hr. Mt Pelee destroyed St. Pierre on the island of Martinique, West Indies in 1902 ...
... • Nuée ardentes are mobile dense clouds of incandescent ash that can move downhill at speeds up to 100 , km/hr. Mt Pelee destroyed St. Pierre on the island of Martinique, West Indies in 1902 ...
volcanoes - an-0001
... pushes to go to the earth’s crust. • Earth’s crust is separated into different pieces known as tectonic plates. • These plates fit right together like a giant jigsaw puzzle. ...
... pushes to go to the earth’s crust. • Earth’s crust is separated into different pieces known as tectonic plates. • These plates fit right together like a giant jigsaw puzzle. ...
Volcano
... cornfield that had been there for as long as he could remember was giving off smoke. Throughout the night, hot glowing cinders were thrown high into the air. In just a few days, a cinder cone several hundred meters high covered his cornfield. ...
... cornfield that had been there for as long as he could remember was giving off smoke. Throughout the night, hot glowing cinders were thrown high into the air. In just a few days, a cinder cone several hundred meters high covered his cornfield. ...
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park - Cook/Lowery15
... flows, they continue to destroy whatever is remaining in the path of the lava. Many plants may become extinct because there are not as many as there used to be and the animals continue to eat whatever is remaining for food. Once the plants stop growing or become extinct, animals that eat the plants ...
... flows, they continue to destroy whatever is remaining in the path of the lava. Many plants may become extinct because there are not as many as there used to be and the animals continue to eat whatever is remaining for food. Once the plants stop growing or become extinct, animals that eat the plants ...
Build a Volcano
... The Nature of Volcanoes Volcanoes are built by the accumulation of their own eruptive products—lava, bombs (crusted over ash flows), and tephra (airborne ash and dust). A volcano is most commonly a conical hill or mountain built around a vent that connects with reservoirs of molten rock below the su ...
... The Nature of Volcanoes Volcanoes are built by the accumulation of their own eruptive products—lava, bombs (crusted over ash flows), and tephra (airborne ash and dust). A volcano is most commonly a conical hill or mountain built around a vent that connects with reservoirs of molten rock below the su ...
Volcanoes
... together. All this pushing and pulling creates breaks in the Earth's surface, just like a cut on your arm breaks the skin. Like a cut on your arm, sometimes something escapes from breaks in the Earth's surface. ...
... together. All this pushing and pulling creates breaks in the Earth's surface, just like a cut on your arm breaks the skin. Like a cut on your arm, sometimes something escapes from breaks in the Earth's surface. ...
Faizan - WordPress.com
... A bowl or sheild shaped Volcano in the middle with long-gentle slopes made by basaltic lava flows,called flood basalt. ...
... A bowl or sheild shaped Volcano in the middle with long-gentle slopes made by basaltic lava flows,called flood basalt. ...
Chapter 9 Section 1 Notes
... 1. _________________________eruptions are the most common type of eruption. 2. These eruptions produce relatively calm flows of ______________. Explosive Eruptions 1. ________________________ eruptions are much rarer than nonexplosive eruptions. 2. During an explosive eruption, clouds of hot debris, ...
... 1. _________________________eruptions are the most common type of eruption. 2. These eruptions produce relatively calm flows of ______________. Explosive Eruptions 1. ________________________ eruptions are much rarer than nonexplosive eruptions. 2. During an explosive eruption, clouds of hot debris, ...
Volcanoes are classified as active or inactive
... Volcanoes are classified as active or inactive. Inactive volcanoes are older and have usually erupted many times. A volcano is described as active if it is currently erupting or expected to erupt eventually. Eruption Stage A volcanic eruption occurs when lava, gasses, and other subterranean matter c ...
... Volcanoes are classified as active or inactive. Inactive volcanoes are older and have usually erupted many times. A volcano is described as active if it is currently erupting or expected to erupt eventually. Eruption Stage A volcanic eruption occurs when lava, gasses, and other subterranean matter c ...
No Slide Title
... How would the volcanic ash interfere with plane engines, our lungs, and car engines? ...
... How would the volcanic ash interfere with plane engines, our lungs, and car engines? ...
chapter 4 volcanoes
... Volcanoes are classified as active or inactive. Inactive volcanoes are older and have usually erupted many times. A volcano is described as active if it is currently erupting or expected to erupt eventually. Eruption Stage A volcanic eruption occurs when lava, gasses, and other subterranean matter c ...
... Volcanoes are classified as active or inactive. Inactive volcanoes are older and have usually erupted many times. A volcano is described as active if it is currently erupting or expected to erupt eventually. Eruption Stage A volcanic eruption occurs when lava, gasses, and other subterranean matter c ...
What IS A VOLCANO?
... where lava reaches the surface. - The Vents - is the main conduit through which magma moves towards to get to the surface. The Crater - sits at the top of a volcano and is the location where much of the lava, gas, rock fragments and ash are ejected from. ...
... where lava reaches the surface. - The Vents - is the main conduit through which magma moves towards to get to the surface. The Crater - sits at the top of a volcano and is the location where much of the lava, gas, rock fragments and ash are ejected from. ...
msword - rgs.org
... In the last lesson pupils understood that volcanoes are primarily (but not exclusively) located on the boundary between two tectonic plates. In its simplest terms a volcano is formed when magma penetrates the Earth’s crust. This magma then cools and hardens to form solid rock, creating a mountain. V ...
... In the last lesson pupils understood that volcanoes are primarily (but not exclusively) located on the boundary between two tectonic plates. In its simplest terms a volcano is formed when magma penetrates the Earth’s crust. This magma then cools and hardens to form solid rock, creating a mountain. V ...
Olympus Mons

Olympus Mons /ɵˌlɪmpəs ˈmɒnz/ (Latin for Mount Olympus) is a very large shield volcano on the planet Mars. By one measure, it has a height of nearly 25 km (16 mi). Olympus Monsstands almost three times as tall as Mount Everest's height above sea level. It is the youngest of the large volcanoes on Mars, having formed during Mars's Amazonian Period. It is currently the largest volcano discovered in the Solar System and had been known to astronomers since the late 19th century as the albedo feature Nix Olympica (Latin for ""Olympic Snow""). Its mountainous nature was suspected well before space probes confirmed its identity as a mountain.The volcano is located in Mars's western hemisphere at approximately 18.65°N 226.2°E / 18.65; 226.2, just off the northwestern edge of the Tharsis bulge. The western portion of the volcano lies in the Amazonis quadrangle (MC-8) and the central and eastern portions in the adjoining Tharsis quadrangle (MC-9). Two impact craters on Olympus Mons have been assigned provisional names by the International Astronomical Union. They are the 15.6 km (9.7 mi)-diameter Karzok crater (18°25′N 131°55′W) and the 10.4 km (6.5 mi)-diameter Pangboche crater (17°10′N 133°35′W). The craters are notable for being two of several suspected source areas for shergottites, the most abundant class of Martian meteorites.