Total Temperature Measurements of Laminar Gas Flow at Micro
... temperature in thermal boundary conditions of ...
... temperature in thermal boundary conditions of ...
A Novel Computational Approach to Combine the Optical and Thermal
... receiver. CFD is regularly used in this regard and 2-D domains can be considered if the aim is only to have an estimate of the thermal losses of an LFC cavity, i.e. if the actual heat transferred to the HTF of a specific mirror field is not the aim of the simulation (Moghimi et al., 2014, 2015). To ...
... receiver. CFD is regularly used in this regard and 2-D domains can be considered if the aim is only to have an estimate of the thermal losses of an LFC cavity, i.e. if the actual heat transferred to the HTF of a specific mirror field is not the aim of the simulation (Moghimi et al., 2014, 2015). To ...
Name - shssci
... close to 2.00 g as possible of sodium hydroxide pellets to the beaker. Measure and record the combined mass of the beaker and sodium hydroxide to the nearest 0.01 g. (Do this operation as quickly as possible to avoid error due to absorption of water by the NaOH.) 3. Measure and record the temperatur ...
... close to 2.00 g as possible of sodium hydroxide pellets to the beaker. Measure and record the combined mass of the beaker and sodium hydroxide to the nearest 0.01 g. (Do this operation as quickly as possible to avoid error due to absorption of water by the NaOH.) 3. Measure and record the temperatur ...
Pressure-Temperature-Time Paths of Regional - Cin
... There is abundant evidence of the emplacement of granitic, and to a lesser extent mafic and ultramafic, bodies during regional metamorphism. In addition, stable isotope studies point to the widespread cooling of intrusives by hydrothermal systems. These observations are sometimes taken to imply that ...
... There is abundant evidence of the emplacement of granitic, and to a lesser extent mafic and ultramafic, bodies during regional metamorphism. In addition, stable isotope studies point to the widespread cooling of intrusives by hydrothermal systems. These observations are sometimes taken to imply that ...
2. Energy Balance of Buildings
... the room, but quite contrary they help to heat up the room in accordance with the principle of conservation of energy. Thus, the internal heat gain corresponds once again to the wattage of the appliances. For cold climates the internal heat gain is welcomed as it contributes to the heating of the ho ...
... the room, but quite contrary they help to heat up the room in accordance with the principle of conservation of energy. Thus, the internal heat gain corresponds once again to the wattage of the appliances. For cold climates the internal heat gain is welcomed as it contributes to the heating of the ho ...
Full Text
... second alternative would be to carry out the combustion using the powder form itself. This is justifiable since heat combustion is dependent only on the chemical composition of the substance and not its physical form. However, the pellet form is preferred as it slows down the reaction since less sur ...
... second alternative would be to carry out the combustion using the powder form itself. This is justifiable since heat combustion is dependent only on the chemical composition of the substance and not its physical form. However, the pellet form is preferred as it slows down the reaction since less sur ...
Deep-Seated Oceanic Heat Flow, Heat Deficits, and Hydrothermal
... rock environments where advective heat loss is greatest. Seafloor drilling provides opportunities to measure subsurface temperature fields and thermal blankets (Johnson and Hutnak, 1996) make possible the computation of heat flow in bare rock environments, but the cost of both of these techniques pr ...
... rock environments where advective heat loss is greatest. Seafloor drilling provides opportunities to measure subsurface temperature fields and thermal blankets (Johnson and Hutnak, 1996) make possible the computation of heat flow in bare rock environments, but the cost of both of these techniques pr ...
Institutionen för systemteknik Department of Electrical Engineering Camera Chip
... vehicle it is possible to increase sight range and make it easier to detect pedestrians and wildlife in low light condition. ...
... vehicle it is possible to increase sight range and make it easier to detect pedestrians and wildlife in low light condition. ...
(Revised) Text for Sections 5.7 to 5.9 5.7 WHERE AND HOW MUCH
... The concepts of heat flow and the related thermal properties of materials discussed in earlier sections apply to steady-state heat transfer. A steady state is defined as the state in which the temperatures at all points within an assembly remain constant over time. The opposite of a steady state is ...
... The concepts of heat flow and the related thermal properties of materials discussed in earlier sections apply to steady-state heat transfer. A steady state is defined as the state in which the temperatures at all points within an assembly remain constant over time. The opposite of a steady state is ...
Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning in Smart Energy
... In that way air can be supplied at low temperatures without causing draught or unpleasant temperature differences. Pollutions are diluted down to acceptable concentrations. In displacement ventilation air is supplied to the room with low velocity in the occupied space or close to this. The temperatu ...
... In that way air can be supplied at low temperatures without causing draught or unpleasant temperature differences. Pollutions are diluted down to acceptable concentrations. In displacement ventilation air is supplied to the room with low velocity in the occupied space or close to this. The temperatu ...
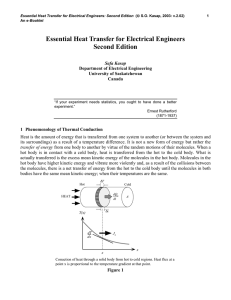
EssentialHeatTransfer - University Courses in Electronic Materials
... where ∆V is the voltage difference across a conductor of resistance R2 and I is the current flow. The rate of heat flow, Q ′, and the temperature difference, ∆T, correspond to the current, Ι, and potential difference, ∆V, respectively. Thermal resistance is the thermal analog of electrical resistanc ...
... where ∆V is the voltage difference across a conductor of resistance R2 and I is the current flow. The rate of heat flow, Q ′, and the temperature difference, ∆T, correspond to the current, Ι, and potential difference, ∆V, respectively. Thermal resistance is the thermal analog of electrical resistanc ...
\bf {The First Law of Thermodynamics for Closed Systems}\\
... The convective heat transfer coefficient is an experimentally determined parameter that depends upon the surface geometry, the nature of the fluid motion, the properties of the fluid, and the bulk fluid velocity. Ranges of the convective heat transfer coefficient are ...
... The convective heat transfer coefficient is an experimentally determined parameter that depends upon the surface geometry, the nature of the fluid motion, the properties of the fluid, and the bulk fluid velocity. Ranges of the convective heat transfer coefficient are ...
Thermoelectric Cooling A Closer Look.indd
... components is an inadvisable way to avoid over heating. Exposing equipment to ambient dirt and debris can cause damage over time. It is also can increase the risk of shock to those working around the area. For these reasons, it is best to have a cooling component in place as part of your system. Bef ...
... components is an inadvisable way to avoid over heating. Exposing equipment to ambient dirt and debris can cause damage over time. It is also can increase the risk of shock to those working around the area. For these reasons, it is best to have a cooling component in place as part of your system. Bef ...
as PDF
... flows in triangular shaped enclosures have received less attention than those in rectangular geometries, even though the topic has been of interest for more than two decades Heat transfer through an attic space into or out of buildings is an important issue for attic shaped houses in both hot and col ...
... flows in triangular shaped enclosures have received less attention than those in rectangular geometries, even though the topic has been of interest for more than two decades Heat transfer through an attic space into or out of buildings is an important issue for attic shaped houses in both hot and col ...
Heat wave

A heat wave is a prolonged period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity, especially in oceanic climate countries. While definitions vary, a heat wave is measured relative to the usual weather in the area and relative to normal temperatures for the season. Temperatures that people from a hotter climate consider normal can be termed a heat wave in a cooler area if they are outside the normal climate pattern for that area.The term is applied both to routine weather variations and to extraordinary spells of heat which may occur only once a century. Severe heat waves have caused catastrophic crop failures, thousands of deaths from hyperthermia, and widespread power outages due to increased use of air conditioning. A heat wave is considered extreme weather, and a danger because heat and sunlight may overheat the human body.