Topic 6 CONTROLLING HEAT TRANSFER In this chapter you will
... The same techniques that keep a house warm also keep our __________ warm. On cold days, wear several ___________ - underwear, shirt, sweater, pants, and jacket. Choose inner layers for their __________ weave and thickness. Air trapped in the material serves as insulation. A ___________ outer layer k ...
... The same techniques that keep a house warm also keep our __________ warm. On cold days, wear several ___________ - underwear, shirt, sweater, pants, and jacket. Choose inner layers for their __________ weave and thickness. Air trapped in the material serves as insulation. A ___________ outer layer k ...
physical chemistry lecture 3
... • When the volume is greater than the initial volume, as in expansion, the logarithm in above equation is positive and hence w<0. In this case the system has done work on the surroundings and there is a corresponding reduction in its internal energy. • From the equation also show that more work is d ...
... • When the volume is greater than the initial volume, as in expansion, the logarithm in above equation is positive and hence w<0. In this case the system has done work on the surroundings and there is a corresponding reduction in its internal energy. • From the equation also show that more work is d ...
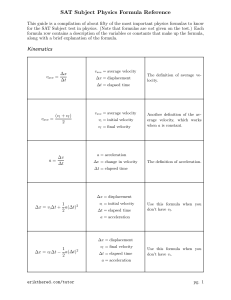
SAT Subject Physics Formula Reference
... For more than one pair of charges, use this formula for each pair, then add all the UE ’s. The potential difference ∆V between two points is defined as the negative of the work done by the electric field per unit charge as charge q moves from one point to the other. Alternately, it is the change in ...
... For more than one pair of charges, use this formula for each pair, then add all the UE ’s. The potential difference ∆V between two points is defined as the negative of the work done by the electric field per unit charge as charge q moves from one point to the other. Alternately, it is the change in ...
Thermodynamics - Faculty
... 1. In the early 1800s, Carnot pointed out the basic working of an ideal (one without internal friction) heat engine. 2. The Carnot cycle (see Figure 12.17 in your textbook) can be described in 4 steps: a) Step 1: The cycle starts with the piston positioned such that V is at a minimum. At this point, ...
... 1. In the early 1800s, Carnot pointed out the basic working of an ideal (one without internal friction) heat engine. 2. The Carnot cycle (see Figure 12.17 in your textbook) can be described in 4 steps: a) Step 1: The cycle starts with the piston positioned such that V is at a minimum. At this point, ...
PHYS-2010: General Physics I Course Lecture Notes Section XIV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser
... 1. In the early 1800s, Carnot pointed out the basic working of an ideal (one without internal friction) heat engine. 2. The Carnot cycle (see Figure 12.17 in your textbook) can be described in 4 steps: a) Step 1: The cycle starts with the piston positioned such that V is at a minimum. At this point, ...
... 1. In the early 1800s, Carnot pointed out the basic working of an ideal (one without internal friction) heat engine. 2. The Carnot cycle (see Figure 12.17 in your textbook) can be described in 4 steps: a) Step 1: The cycle starts with the piston positioned such that V is at a minimum. At this point, ...
Measuring and Using Energy Changes
... - Whenever there is a temperature difference between two objects, kinetic energy is transferred as heat from the hotter object to the colder object. - You measure the heat being transferred in a reaction or other process by monitoring temperature change. - Therefore, you must minimize any heat trans ...
... - Whenever there is a temperature difference between two objects, kinetic energy is transferred as heat from the hotter object to the colder object. - You measure the heat being transferred in a reaction or other process by monitoring temperature change. - Therefore, you must minimize any heat trans ...
Heat Capacity. Enthalpy. Magnetic Systems.
... heat. The answer is, of course: “it depends”. Naturally you expect a positive (negative) Q will contribute to an increase (decrease) in temperature. But we can be considerably more precise about it. The idea of heat capacity is that it characterizes the change in temperature ∆T for a given amount of ...
... heat. The answer is, of course: “it depends”. Naturally you expect a positive (negative) Q will contribute to an increase (decrease) in temperature. But we can be considerably more precise about it. The idea of heat capacity is that it characterizes the change in temperature ∆T for a given amount of ...
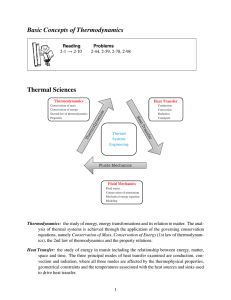
Chapter 3: THERMODYNAMICS
... -Thermodynamics is the study of the relationship between the energy transformation in the system and other physical quantities such as temperature, pressure and volume (P, V, T). -A thermodynamic equation of state is a mathematical relationship of the thermodynamic or state variables, such as pressu ...
... -Thermodynamics is the study of the relationship between the energy transformation in the system and other physical quantities such as temperature, pressure and volume (P, V, T). -A thermodynamic equation of state is a mathematical relationship of the thermodynamic or state variables, such as pressu ...
Document
... from a house is through the windows. Calculate the rate of heat flow through a glass window 2.0 m x 1.5 m in area and 3.2 mm thick, if the temperatures at the inner and outer surfaces are 15.0°C and 14.0°C, respectively. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... from a house is through the windows. Calculate the rate of heat flow through a glass window 2.0 m x 1.5 m in area and 3.2 mm thick, if the temperatures at the inner and outer surfaces are 15.0°C and 14.0°C, respectively. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Baskin School of Engineering, University of California Santa Cruz
... there’s 10°C temperature difference between an aggressor and a victim. Furthermore, high temperature operation reduces the lifetime of an IC. Both electromigration and oxide breakdown are exponential functions of temperature. Compounding the problem is the fact that the cost of an IC’s thermal packa ...
... there’s 10°C temperature difference between an aggressor and a victim. Furthermore, high temperature operation reduces the lifetime of an IC. Both electromigration and oxide breakdown are exponential functions of temperature. Compounding the problem is the fact that the cost of an IC’s thermal packa ...
Thermal conductivity of individual silicon nanowires
... 130 K, respectively. This is in sharp contrast to the peak of bulk Si that occurs at about 25 K. The shift of the peak suggests that, as the wire diameter is reduced, the phonon boundary scattering dominates over phonon–phonon umklapp scattering, which decreases the thermal conductivity with an incr ...
... 130 K, respectively. This is in sharp contrast to the peak of bulk Si that occurs at about 25 K. The shift of the peak suggests that, as the wire diameter is reduced, the phonon boundary scattering dominates over phonon–phonon umklapp scattering, which decreases the thermal conductivity with an incr ...
The state of a simple compressible system is completely specified by
... any of these must be considered, then one additional property must be known for each added effect. Example: for motion (kinetic) effects, velocity must be known. “Compressible” = volume not fixed. “Independent” = one property of a pair can be changed without affecting the other. Example: a. temperat ...
... any of these must be considered, then one additional property must be known for each added effect. Example: for motion (kinetic) effects, velocity must be known. “Compressible” = volume not fixed. “Independent” = one property of a pair can be changed without affecting the other. Example: a. temperat ...
Review of fundamental principles ? Thermodynamics : Part I
... Everything external to the system is the surroundings. The system is separated from the surroundings by the system boundaries. Thermodynamic systems can be further classified into closed systems, open systems and isolated systems. A control volume, which may be considered as an open system, is defin ...
... Everything external to the system is the surroundings. The system is separated from the surroundings by the system boundaries. Thermodynamic systems can be further classified into closed systems, open systems and isolated systems. A control volume, which may be considered as an open system, is defin ...
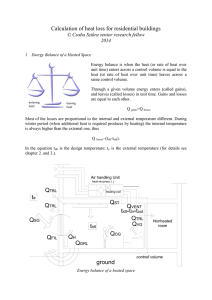
Calculation of heat loss for buildings
... In country by country there are slightly difference between the recognize design temperatures for domestic and other rooms. Design temperatures is mainly depends on the activity in the room, but it should be chosen to ensure satisfactory comfort conditions. If there are significant differences betwe ...
... In country by country there are slightly difference between the recognize design temperatures for domestic and other rooms. Design temperatures is mainly depends on the activity in the room, but it should be chosen to ensure satisfactory comfort conditions. If there are significant differences betwe ...
Pot. Temp handout - Mechanical Engineering | University of Utah
... Potential temperature is the temperature that a parcel of air at pressure P and temperature T would have if it were adiabaticaly brought to a reference pressure Po. The potential temperature helps determine the buoyancy of a dry displaced fluid parcel relative to its surroundings. For a static fluid ...
... Potential temperature is the temperature that a parcel of air at pressure P and temperature T would have if it were adiabaticaly brought to a reference pressure Po. The potential temperature helps determine the buoyancy of a dry displaced fluid parcel relative to its surroundings. For a static fluid ...
Engineering Building Room 2303 Mail Code Phone: 818-677
... Extensive thermodynamic variables, such as volume, V, internal energy, U, enthalpy, H, entropy, S, Helmholtz function, A = U – TS, and Gibbs function, G = H – TS, depend on the size of the system (i.e., the amount of mass, m, in the system.) Intensive variables such as the temperature, T, and the pr ...
... Extensive thermodynamic variables, such as volume, V, internal energy, U, enthalpy, H, entropy, S, Helmholtz function, A = U – TS, and Gibbs function, G = H – TS, depend on the size of the system (i.e., the amount of mass, m, in the system.) Intensive variables such as the temperature, T, and the pr ...
PY2P10 Finn Problems Chap 4
... AS > 0. (Hint: (a - b)t ) 0 for a and b real.) 5.10 Considertwo identicalbodiesof heat capacityC" and with negligiblethermal expansioncoefficients.Show that when they are placed in thermal contact in an adiabatic enclosuretheir hnal temperature is ( Tt * Tr)12 where TL and T2 are their initial tempe ...
... AS > 0. (Hint: (a - b)t ) 0 for a and b real.) 5.10 Considertwo identicalbodiesof heat capacityC" and with negligiblethermal expansioncoefficients.Show that when they are placed in thermal contact in an adiabatic enclosuretheir hnal temperature is ( Tt * Tr)12 where TL and T2 are their initial tempe ...
Combustion Chemistry
... • Internal energy is the total energy of molecules in the working fluid – a sum of kinetic and potential energies. ...
... • Internal energy is the total energy of molecules in the working fluid – a sum of kinetic and potential energies. ...
Temperature, Thermal Energy, and Heat
... matter are in constant motion. Kinetic energy is the energy of a particle or an object due to its motion. When particles collide, kinetic energy is transferred between them. The particles of a substance move at different speeds depending on the state of the substance. The particles of a gas have mor ...
... matter are in constant motion. Kinetic energy is the energy of a particle or an object due to its motion. When particles collide, kinetic energy is transferred between them. The particles of a substance move at different speeds depending on the state of the substance. The particles of a gas have mor ...
2521/103 ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND DRAWING Oct/Nov.2010
... (b) A hallow steel shaft has external and internal diameter of 100mm and 62.5 mm respectively. When transmitting power it is observed to twist through an angle of 1.80 over a length of 3m. The modulus of rigidity of the steel is 85kN/mm2. Determine the: i. Maximum shear stress induced in the materia ...
... (b) A hallow steel shaft has external and internal diameter of 100mm and 62.5 mm respectively. When transmitting power it is observed to twist through an angle of 1.80 over a length of 3m. The modulus of rigidity of the steel is 85kN/mm2. Determine the: i. Maximum shear stress induced in the materia ...