Herpetology 483/583
... What are the main energy consuming activities in the body that contribute to BMR? What is specific dynamic action (SDA)? Compare and contrast calorimetry and respirometry. What is the respiratory quotient (RQ) and how can it help us understand the source of metabolic energy (often meaning the recent ...
... What are the main energy consuming activities in the body that contribute to BMR? What is specific dynamic action (SDA)? Compare and contrast calorimetry and respirometry. What is the respiratory quotient (RQ) and how can it help us understand the source of metabolic energy (often meaning the recent ...
Heat
... 1. Where does heat come from and how does it travel? Nearly all heat in Earth’s atmosphere comes from the Sun. 2. What kinds of energy do we receive from the Sun? Most of the energy from the Sun travels to Earth as visible light and infrared radiation (which we feel as heat). We receive a small amou ...
... 1. Where does heat come from and how does it travel? Nearly all heat in Earth’s atmosphere comes from the Sun. 2. What kinds of energy do we receive from the Sun? Most of the energy from the Sun travels to Earth as visible light and infrared radiation (which we feel as heat). We receive a small amou ...
Thermochemistry
... • Is a form of potential energy because it is based on the position of atoms in a substance • Different types of atoms and different arrangement of atoms results in the storage of different amounts of chemical energy • During a chemical reaction, chemical energy may be 1) stored 2) released as heat ...
... • Is a form of potential energy because it is based on the position of atoms in a substance • Different types of atoms and different arrangement of atoms results in the storage of different amounts of chemical energy • During a chemical reaction, chemical energy may be 1) stored 2) released as heat ...
Transfer of Thermal Energy worksheet - dubai
... If you have stood in front of a fireplace or near a campfire, you have felt the heat transfer known as radiation. The side of you nearest the fire warms, while your other side remains unaffected by the heat. Although you are surrounded by air, the air has nothing to do with this transfer of heat. He ...
... If you have stood in front of a fireplace or near a campfire, you have felt the heat transfer known as radiation. The side of you nearest the fire warms, while your other side remains unaffected by the heat. Although you are surrounded by air, the air has nothing to do with this transfer of heat. He ...
Science 7ACC Midterm Review
... Thermal expansion is the increase in volume of a matter due to an increase in temperature. Thermal energy is the total amount of kinetic energy and depends on temperature, mass, and the type of substance. A substance at a lower temperature can have more thermal energy than a substance at a hig ...
... Thermal expansion is the increase in volume of a matter due to an increase in temperature. Thermal energy is the total amount of kinetic energy and depends on temperature, mass, and the type of substance. A substance at a lower temperature can have more thermal energy than a substance at a hig ...
The Second Law: Definition of Entropy
... powered by steam, but it turned out to be quite difficult to build one that was efficient enough to get anything done! In an engine engine, there is a cycle in which fuel is burned to heat gas inside the piston. The expansion of the piston leads to cooling and work. Compression readies the piston fo ...
... powered by steam, but it turned out to be quite difficult to build one that was efficient enough to get anything done! In an engine engine, there is a cycle in which fuel is burned to heat gas inside the piston. The expansion of the piston leads to cooling and work. Compression readies the piston fo ...
The increasing number of heat pumps is not growing the peak
... Even during the coldest periods, heat pumps will reduce the power demand in the existing single-family houses in the future. On the other hand, new houses built by 2030 will increase the overall peak power demand in the studied house stock by 1 – 8 % during the coldest hours, if power loads will not ...
... Even during the coldest periods, heat pumps will reduce the power demand in the existing single-family houses in the future. On the other hand, new houses built by 2030 will increase the overall peak power demand in the studied house stock by 1 – 8 % during the coldest hours, if power loads will not ...
13 Calories of nuts
... Here, q is the amount heat transferred to or from the system being studied. The value of q will be negative if the system is losing heat during the process (exothermic) or positive if heat is gained (endothermic). The symbol m represents the mass of the system in grams and c is the specific heat cap ...
... Here, q is the amount heat transferred to or from the system being studied. The value of q will be negative if the system is losing heat during the process (exothermic) or positive if heat is gained (endothermic). The symbol m represents the mass of the system in grams and c is the specific heat cap ...
energy test - mrcarlsonschemistryclass
... transferred into kinetic energy as it falls? 3) If a room is at 25°C, what is the temperature in Kelvin? 4) A car uses potential energy which is stored in a fossil fuel and turns it into kinetic energy when the car moves. What type of kinetic energy is being used that has the car moving? 5) When a r ...
... transferred into kinetic energy as it falls? 3) If a room is at 25°C, what is the temperature in Kelvin? 4) A car uses potential energy which is stored in a fossil fuel and turns it into kinetic energy when the car moves. What type of kinetic energy is being used that has the car moving? 5) When a r ...
Experiment SHC metal and water
... 1. Measure and record the mass m of the metal sample using the electronic balance. 2. Tie the metal sample with a piece of thread and suspend it in a beaker of water. Suspend a thermometer alongside the metal sample but make sure they do not touch. Ensure that both the sample and the thermometer are ...
... 1. Measure and record the mass m of the metal sample using the electronic balance. 2. Tie the metal sample with a piece of thread and suspend it in a beaker of water. Suspend a thermometer alongside the metal sample but make sure they do not touch. Ensure that both the sample and the thermometer are ...
Mechanical Engineering 2007 Papers
... (C) Xe (D)X ME 11 /24 Q.54 The piston rod of diameter 20 mrn and length 700 mrn in a hydraulic cylinder is subjected to a compressive force of 10 kN due to the internal pressure. The end conditions for the rod may be assumed as guided at the piston end and hinged at the other end. The Young's modulu ...
... (C) Xe (D)X ME 11 /24 Q.54 The piston rod of diameter 20 mrn and length 700 mrn in a hydraulic cylinder is subjected to a compressive force of 10 kN due to the internal pressure. The end conditions for the rod may be assumed as guided at the piston end and hinged at the other end. The Young's modulu ...
Heat & Energy
... • Specific Heat: Each material needs a certain amount of heat to raise its temp one degree; usually less than one calorie. • One calorie is equivalent to 4.19 joules, enough energy to raise one gram of matter 428 metres higher. ...
... • Specific Heat: Each material needs a certain amount of heat to raise its temp one degree; usually less than one calorie. • One calorie is equivalent to 4.19 joules, enough energy to raise one gram of matter 428 metres higher. ...
Document
... • Food is measured in Calories, or 1000 calories (kilocalorie). • A joule is the SI unit of heat and energy, equivalent to 0.2390 calories. • 1 calorie = 4.184 J or 1 J = 0.2390 calories ...
... • Food is measured in Calories, or 1000 calories (kilocalorie). • A joule is the SI unit of heat and energy, equivalent to 0.2390 calories. • 1 calorie = 4.184 J or 1 J = 0.2390 calories ...
PPT
... Joule’s Law states: “if a gas expands without doing any work, and under adiabatic conditions, the temperature of the gas remains constant.” Corollary: Molecules of an ideal gas do not exert any attractive or repulsive forces ...
... Joule’s Law states: “if a gas expands without doing any work, and under adiabatic conditions, the temperature of the gas remains constant.” Corollary: Molecules of an ideal gas do not exert any attractive or repulsive forces ...
Chapter 14 – Temperature and Heat
... are three types of temperature scale – Celsius, Fahrenheit and Kelvin with unit of 0C, 0F and K respectively. Fortunately, many physical properties of materials change sufficiently with temperature to be used as the bases for thermometers. The ice point and the steam point of water are two convenien ...
... are three types of temperature scale – Celsius, Fahrenheit and Kelvin with unit of 0C, 0F and K respectively. Fortunately, many physical properties of materials change sufficiently with temperature to be used as the bases for thermometers. The ice point and the steam point of water are two convenien ...
Numerical investigation on thermal non
... Condensation in the presence of non condensable gas (NCG), involving phase change and simultaneous heat and mass transfer progress, is common in many industries applications including nuclear, refrigeration, petrochemical, desalination and power industries. As there exists complex hydrodynamic inter ...
... Condensation in the presence of non condensable gas (NCG), involving phase change and simultaneous heat and mass transfer progress, is common in many industries applications including nuclear, refrigeration, petrochemical, desalination and power industries. As there exists complex hydrodynamic inter ...
Study Questions for Test # 2
... How is it possible for a person in a coma to regulate his/her body temperature without being conscious. Describe the sequence of events involved in heat stroke. This is an example of positive feedback. What does it mean to say something is a positive feedback system? What should be done immediately ...
... How is it possible for a person in a coma to regulate his/her body temperature without being conscious. Describe the sequence of events involved in heat stroke. This is an example of positive feedback. What does it mean to say something is a positive feedback system? What should be done immediately ...
28-4 Homeostasis PowerPoint
... Large ectotherms run into trouble if temperatures get very cold at night or stay cold for long periods. A large animal takes a long time to warm up in the sun after a cold night. Endotherms survive more easily during cool nights or in cold weather They generate and conserve body heat. But the high m ...
... Large ectotherms run into trouble if temperatures get very cold at night or stay cold for long periods. A large animal takes a long time to warm up in the sun after a cold night. Endotherms survive more easily during cool nights or in cold weather They generate and conserve body heat. But the high m ...
living with the lab
... conservation of energy Energy can change form, but it can’t be created or destroyed. Within an isolated system, energy is constant. ...
... conservation of energy Energy can change form, but it can’t be created or destroyed. Within an isolated system, energy is constant. ...
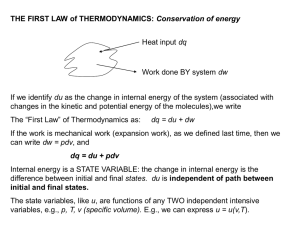
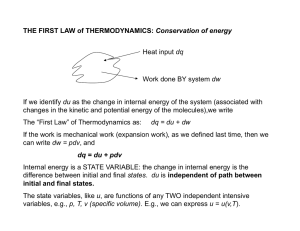
THE FIRST LAW of THERMODYNAMICS: Conservation of energy
... Joule’s Law states: “if a gas expands without doing any work, and under adiabatic conditions, the temperature of the gas remains constant.” Corollary: Molecules of an ideal gas do not exert any attractive or repulsive forces ...
... Joule’s Law states: “if a gas expands without doing any work, and under adiabatic conditions, the temperature of the gas remains constant.” Corollary: Molecules of an ideal gas do not exert any attractive or repulsive forces ...
Calorimetry Lab
... B. Do you think all the ice melted? Explain. ___________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ C. Look at the GRAPH. The graph shows two separate stages: the heating of the ice and then the melting of the ice. How much did the water’s temperature ...
... B. Do you think all the ice melted? Explain. ___________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ C. Look at the GRAPH. The graph shows two separate stages: the heating of the ice and then the melting of the ice. How much did the water’s temperature ...
File - Ashvin Patel
... • It can be doped by Boron, Arsenic, Copper, Cadmium etc. • It can be divided in very thin slices called wafers required for constructing the solar cells. • It can withstand high temperature, has high boiling point. • Its resistance decreases with increase in temperature. ...
... • It can be doped by Boron, Arsenic, Copper, Cadmium etc. • It can be divided in very thin slices called wafers required for constructing the solar cells. • It can withstand high temperature, has high boiling point. • Its resistance decreases with increase in temperature. ...
Specific Heat of Metals - TI Education
... energy, Q in joules, needed to change the temperature of an object is: Q = mC@T (a mnemonic to help remember this formula is “mcat”) where m is the mass of the object, C is its specific heat, and @T is its change in temperature in Celsius. There are two ways for the students to find the sample's spe ...
... energy, Q in joules, needed to change the temperature of an object is: Q = mC@T (a mnemonic to help remember this formula is “mcat”) where m is the mass of the object, C is its specific heat, and @T is its change in temperature in Celsius. There are two ways for the students to find the sample's spe ...
Binnie Thermochemistry Practice
... 9. When a 94.3 g piece of gold (specific heat 0.13 J/g·°C) and a 94.3g piece of iron (specific heat 0.46 J/g·°C) each at 10OC absorb an equal amount of heat (A) the gold will end up with the higher final temperature. (B) the iron will end up with the higher final temperature. (C) they will end up a ...
... 9. When a 94.3 g piece of gold (specific heat 0.13 J/g·°C) and a 94.3g piece of iron (specific heat 0.46 J/g·°C) each at 10OC absorb an equal amount of heat (A) the gold will end up with the higher final temperature. (B) the iron will end up with the higher final temperature. (C) they will end up a ...
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia is elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation that occurs when a body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. Extreme temperature elevation then becomes a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent disability or death.The most common causes include heat stroke and adverse reactions to drugs. The former is an acute temperature elevation caused by exposure to excessive heat, or combination of heat and humidity, that overwhelms the heat-regulating mechanisms. The latter is a relatively rare side effect of many drugs, particularly those that affect the central nervous system. Malignant hyperthermia is a rare complication of some types of general anesthesia.Hyperthermia differs from fever in that the body's temperature set point remains unchanged. The opposite is hypothermia, which occurs when the temperature drops below that required to maintain normal metabolism.