CHAPTER 40
... Physical laws also constrain the maximum size of animals. As body dimensions increase, a thicker skeleton is required to maintain adequate support. In addition, as bodies increase in size, the muscles required for locomotion represent an increasing fraction of the total body mass. At a certain size, ...
... Physical laws also constrain the maximum size of animals. As body dimensions increase, a thicker skeleton is required to maintain adequate support. In addition, as bodies increase in size, the muscles required for locomotion represent an increasing fraction of the total body mass. At a certain size, ...
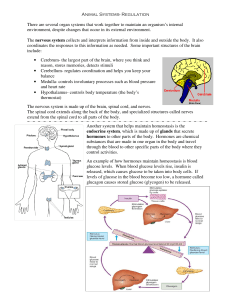
Animal Systems- Regulation There are several organ systems that
... Animal Systems- Regulation There are several organ systems that work together to maintain an organism’s internal environment, despite changes that occur in its external environment. The nervous system collects and interprets information from inside and outside the body. It also coordinates the respo ...
... Animal Systems- Regulation There are several organ systems that work together to maintain an organism’s internal environment, despite changes that occur in its external environment. The nervous system collects and interprets information from inside and outside the body. It also coordinates the respo ...
Body System Structures Function
... broken down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and distributed to cells. The blood stream transports molecules to the cells. The main organ systems that interact in nutrient absorption are the digestive and circulatory systems. Regulation is the process of body systems working together to m ...
... broken down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and distributed to cells. The blood stream transports molecules to the cells. The main organ systems that interact in nutrient absorption are the digestive and circulatory systems. Regulation is the process of body systems working together to m ...
Measuring Time in Meters
... It’s pretty clear that vertical distance is the same sort of thing as horizontal distance, and that we measure them in different units for reasons of convention and convenience, not because there’s some fundamental difference between the two sorts of things. Let me provide an example in which that w ...
... It’s pretty clear that vertical distance is the same sort of thing as horizontal distance, and that we measure them in different units for reasons of convention and convenience, not because there’s some fundamental difference between the two sorts of things. Let me provide an example in which that w ...
Thermos Flask
... good quality thermos flask with silvered lining filled with hot water Action The students examine the flask and explain how the three processes of heat transfer are affected by the flask. They should note that while the liquid inside is hot, and hence the inner wall is also hot, the outer wall is at ...
... good quality thermos flask with silvered lining filled with hot water Action The students examine the flask and explain how the three processes of heat transfer are affected by the flask. They should note that while the liquid inside is hot, and hence the inner wall is also hot, the outer wall is at ...
File
... environment. • Most reptiles, fishes, and amphibians are ectothermsthey pick up heat from their environment and lose heat to their environment. • Most bask in the sun for heat, and burrow unground to cool down. • Ectotherms have low metabolisms when resting, thus generating little heat. • When activ ...
... environment. • Most reptiles, fishes, and amphibians are ectothermsthey pick up heat from their environment and lose heat to their environment. • Most bask in the sun for heat, and burrow unground to cool down. • Ectotherms have low metabolisms when resting, thus generating little heat. • When activ ...
Page 73 - ClassZone
... Earth’s Heat Events that gave rise to the formation of Earth generated heat. Some of the heat that caused Earth’s layers to form came from meteorite impacts, and some arose as the weight of overlying materials caused compression in Earth’s interior. Heat was also generated by the decay of radioactiv ...
... Earth’s Heat Events that gave rise to the formation of Earth generated heat. Some of the heat that caused Earth’s layers to form came from meteorite impacts, and some arose as the weight of overlying materials caused compression in Earth’s interior. Heat was also generated by the decay of radioactiv ...
6 Physical Properties and Principles I. Review of Fundamental
... ICE ----------HEAT----- WATER-------HEAT -------WATER VAPOR (<32 degrees) ...
... ICE ----------HEAT----- WATER-------HEAT -------WATER VAPOR (<32 degrees) ...
File
... Physical laws also constrain the maximum size of animals. As body dimensions increase, a thicker skeleton is required to maintain adequate support. In addition, as bodies increase in size, the muscles required for locomotion represent an increasing fraction of the total body mass. At a certain size, ...
... Physical laws also constrain the maximum size of animals. As body dimensions increase, a thicker skeleton is required to maintain adequate support. In addition, as bodies increase in size, the muscles required for locomotion represent an increasing fraction of the total body mass. At a certain size, ...
system
... •Given two out of three of any of the following quantities, be able to calculate the third: change in heat for the system, change in work for the system, overall change in energy for the system •Given initial heat and final heat, be able to calculate the change in enthalpy for a system •Be able to d ...
... •Given two out of three of any of the following quantities, be able to calculate the third: change in heat for the system, change in work for the system, overall change in energy for the system •Given initial heat and final heat, be able to calculate the change in enthalpy for a system •Be able to d ...
If your child receives a soft tissue injury, commonly known as a
... In order to avoid the sudden cold shock feeling when applying an ice pack, place a towel over the region before applying the ice. Follow the 20min ON/20min OFF rule. Ice massage involves applying ice directly to skin over the injured area. The cooling effect will occur in four stages, referred to as ...
... In order to avoid the sudden cold shock feeling when applying an ice pack, place a towel over the region before applying the ice. Follow the 20min ON/20min OFF rule. Ice massage involves applying ice directly to skin over the injured area. The cooling effect will occur in four stages, referred to as ...
Chapter 6
... • Some energy can be lost as heat (ex: frictional heating), represented by q • Heat vs. Temperature: TEMPERATURE reflects movement of particles. HEAT deals with transfer of energy between two objects due to a temperature difference. • Energy can also be transferred through work (force activing over ...
... • Some energy can be lost as heat (ex: frictional heating), represented by q • Heat vs. Temperature: TEMPERATURE reflects movement of particles. HEAT deals with transfer of energy between two objects due to a temperature difference. • Energy can also be transferred through work (force activing over ...
1.1 Units of Measurement
... cold an object is. The SI unit for reporting temperature is Kelvin (K). See the comparison of the three scales: ...
... cold an object is. The SI unit for reporting temperature is Kelvin (K). See the comparison of the three scales: ...
Heat exchanger design for hot air ericsson
... As power unit of micro-cogeneration devices are most used gas combustion engines, as fuel is used natural gas. Into the engine is transferred fuel, through combustion we are gaining mechanical work on the output shaft and the heat energy is transferred through cooling system to the cooling heat exch ...
... As power unit of micro-cogeneration devices are most used gas combustion engines, as fuel is used natural gas. Into the engine is transferred fuel, through combustion we are gaining mechanical work on the output shaft and the heat energy is transferred through cooling system to the cooling heat exch ...
AP Physics – Thermodynamics Wrapup
... 1. You should understand the "mechanical equivalent of heat" so you can calculate how much a substance will be heated by the performance of a specified quantity of mechanical work. This just means that you should be able to convert from calories to Joules and Joules to calories. It also involves the ...
... 1. You should understand the "mechanical equivalent of heat" so you can calculate how much a substance will be heated by the performance of a specified quantity of mechanical work. This just means that you should be able to convert from calories to Joules and Joules to calories. It also involves the ...
Energy, Work and Heat
... • A property of a substance, like pressure, temperature, and volume, • Cannot be measured directly • Normally given with respect to some reference value. • Usually used in connection with an "open" system problem in thermodynamics • Specific enthalpy (h) h = u + Pv where u is the specific internal e ...
... • A property of a substance, like pressure, temperature, and volume, • Cannot be measured directly • Normally given with respect to some reference value. • Usually used in connection with an "open" system problem in thermodynamics • Specific enthalpy (h) h = u + Pv where u is the specific internal e ...
WS F: Phase Change Problems Worksheet
... 19. Calculate the amount of energy released by cooling 59 grams of liquid water from +25°C to ice at -25°C. (Be aware of units: kJ or J?) How many steps does this take? 25 ( l ) 0 ( l ) : Q mcT (59 g )( 4.18 g JC )( 25C ) 6166 J 6.2kJ 0 ( l ) 0 ( s ) : Q H fus m (0.333 g JC ...
... 19. Calculate the amount of energy released by cooling 59 grams of liquid water from +25°C to ice at -25°C. (Be aware of units: kJ or J?) How many steps does this take? 25 ( l ) 0 ( l ) : Q mcT (59 g )( 4.18 g JC )( 25C ) 6166 J 6.2kJ 0 ( l ) 0 ( s ) : Q H fus m (0.333 g JC ...
U3 S1 L3 calorimetry
... 2. A calorimeter designed to have negligible heat loss is used to determine the specific heat capacity of metals. A piece of thallium having a mass of 111.2 g is warmed to 95.0ºC and placed into the calorimeter containing 125.00 g of water at 12.5ºC. The water temperature goes up to 14.9ºC. Use this ...
... 2. A calorimeter designed to have negligible heat loss is used to determine the specific heat capacity of metals. A piece of thallium having a mass of 111.2 g is warmed to 95.0ºC and placed into the calorimeter containing 125.00 g of water at 12.5ºC. The water temperature goes up to 14.9ºC. Use this ...
Appendix A – Heat transfer coefficients
... gas phase since, in both cases, the heat exchange conditions are the same: natural convection on a vertical plate. For the heat exchange between the rabble arms and the gas phase, the Nusselt number is calculated with the same equation A.14 on the hearths 1 to 6. In the hearths 7 and 8, the Nusselt ...
... gas phase since, in both cases, the heat exchange conditions are the same: natural convection on a vertical plate. For the heat exchange between the rabble arms and the gas phase, the Nusselt number is calculated with the same equation A.14 on the hearths 1 to 6. In the hearths 7 and 8, the Nusselt ...
Post Reading Test
... 6. Suppose you wanted to increase the amount of carbon dioxide that could be dissolved in a sample of water. Which change should you make to the water? A. Increase its temperature. B. Increase its pressure. C. Increase its salinity. D. none of the above Correct Answer: B Feedback: The answer is B be ...
... 6. Suppose you wanted to increase the amount of carbon dioxide that could be dissolved in a sample of water. Which change should you make to the water? A. Increase its temperature. B. Increase its pressure. C. Increase its salinity. D. none of the above Correct Answer: B Feedback: The answer is B be ...
Worksheet
... air temperature has risen 0.6 oC in the past 100 years. These cannot be replenished and release other pollutants into the atmosphere during complete or partial combustion. The CO2 produced is a greenhouse gas (causes a rise in air and sea temperatures). Renewable energy sources are increasingly in d ...
... air temperature has risen 0.6 oC in the past 100 years. These cannot be replenished and release other pollutants into the atmosphere during complete or partial combustion. The CO2 produced is a greenhouse gas (causes a rise in air and sea temperatures). Renewable energy sources are increasingly in d ...
CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS energy = anything that has the
... air temperature has risen 0.6 oC in the past 100 years. These cannot be replenished and release other pollutants into the atmosphere during complete or partial combustion. The CO2 produced is a greenhouse gas (causes a rise in air and sea temperatures). Renewable energy sources are increasingly in d ...
... air temperature has risen 0.6 oC in the past 100 years. These cannot be replenished and release other pollutants into the atmosphere during complete or partial combustion. The CO2 produced is a greenhouse gas (causes a rise in air and sea temperatures). Renewable energy sources are increasingly in d ...
MME 4713 Polymers D4-DSC
... If we keep heating our polymer past its Tc, eventually we'll reach another thermal transition, one called melting. When we reach the polymer's melting temperature, or Tm, those polymer crystals begin to fall apart, that is they melt. The chains come out of their ordered arrangements, and begin to mo ...
... If we keep heating our polymer past its Tc, eventually we'll reach another thermal transition, one called melting. When we reach the polymer's melting temperature, or Tm, those polymer crystals begin to fall apart, that is they melt. The chains come out of their ordered arrangements, and begin to mo ...
Class Notes
... Physical laws also constrain the maximum size of animals. As body dimensions increase, a thicker skeleton is required to maintain adequate strength. In addition, as bodies increase in size, the muscles required for locomotion represent an increasing fraction of the total body mass. At a certain size ...
... Physical laws also constrain the maximum size of animals. As body dimensions increase, a thicker skeleton is required to maintain adequate strength. In addition, as bodies increase in size, the muscles required for locomotion represent an increasing fraction of the total body mass. At a certain size ...
Ch. 40
... Physical laws also constrain the maximum size of animals. As body dimensions increase, a thicker skeleton is required to maintain adequate strength. In addition, as bodies increase in size, the muscles required for locomotion represent an increasing fraction of the total body mass. At a certain size ...
... Physical laws also constrain the maximum size of animals. As body dimensions increase, a thicker skeleton is required to maintain adequate strength. In addition, as bodies increase in size, the muscles required for locomotion represent an increasing fraction of the total body mass. At a certain size ...
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia is elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation that occurs when a body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. Extreme temperature elevation then becomes a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent disability or death.The most common causes include heat stroke and adverse reactions to drugs. The former is an acute temperature elevation caused by exposure to excessive heat, or combination of heat and humidity, that overwhelms the heat-regulating mechanisms. The latter is a relatively rare side effect of many drugs, particularly those that affect the central nervous system. Malignant hyperthermia is a rare complication of some types of general anesthesia.Hyperthermia differs from fever in that the body's temperature set point remains unchanged. The opposite is hypothermia, which occurs when the temperature drops below that required to maintain normal metabolism.