Comparative Study of Rectangular, Trapezoidal and Parabolic
... computational grid is created. Preprocessor consists of input of a flow problem by means of an operator friendly interface and subsequent transformation of this input into form of suitable for the use by the solver. Definition of fluid properties: Specification of appropriate boundary conditions at ...
... computational grid is created. Preprocessor consists of input of a flow problem by means of an operator friendly interface and subsequent transformation of this input into form of suitable for the use by the solver. Definition of fluid properties: Specification of appropriate boundary conditions at ...
- Chemistry Land
... gram of water. Therefore, the calculations will need to adjust for the mass of the rock and the mass of the water. ...
... gram of water. Therefore, the calculations will need to adjust for the mass of the rock and the mass of the water. ...
6.5 Nerves, hormones and homeostasis – summary of mark schemes
... response to bring the system back to normal state / set point / within limits; when the normal state reached, the response is stopped; this prevents over reaction; internal environment fluctuates around norm / small fluctuations; a rise in level would feedback to decrease production; as levels drop ...
... response to bring the system back to normal state / set point / within limits; when the normal state reached, the response is stopped; this prevents over reaction; internal environment fluctuates around norm / small fluctuations; a rise in level would feedback to decrease production; as levels drop ...
Thermochemistry - Harrison High School
... In calculating the total energy required to heat a chunk of ice from a temperature in the area of Part A all the way to a temperature in the area of Part E requires five different steps. The energy from each step (given in kJ) is then added up to give the total energy involved in this (Physical or C ...
... In calculating the total energy required to heat a chunk of ice from a temperature in the area of Part A all the way to a temperature in the area of Part E requires five different steps. The energy from each step (given in kJ) is then added up to give the total energy involved in this (Physical or C ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Similarly, the regulation of body temperature directly affects metabolic rate and exercise capacity and is closely associated with mechanisms controlling blood pressure, gas exchange, and energy balance. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... • Similarly, the regulation of body temperature directly affects metabolic rate and exercise capacity and is closely associated with mechanisms controlling blood pressure, gas exchange, and energy balance. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
International Heat Flow Commission Global Heat Flow Database
... “It is not so much the things I don’t know that cause me problems as the things I know that are not so.” Paraphrased after Mark Twain ...
... “It is not so much the things I don’t know that cause me problems as the things I know that are not so.” Paraphrased after Mark Twain ...
chapter 40 - Biology Junction
... internal temperature, sensing and responding to environmental stimuli, and all other animal activities require fuel in the form of chemical energy. The concept of bioenergetics—how organisms obtain, process, and use energy resources—is a connecting theme in the comparative study of animals. Concep ...
... internal temperature, sensing and responding to environmental stimuli, and all other animal activities require fuel in the form of chemical energy. The concept of bioenergetics—how organisms obtain, process, and use energy resources—is a connecting theme in the comparative study of animals. Concep ...
Nanoscale Heat Transfer using Phonon Boltzmann Transport Equation
... purpose [3-5]. The distribution function is a scalar quantity in the six-dimensional phase space (three space coordinates and three wavevector coordinates). The phonon BTE is also called an equation of phonon radiative transfer (EPRT) when the phonon distribution function is replaced with a phonon i ...
... purpose [3-5]. The distribution function is a scalar quantity in the six-dimensional phase space (three space coordinates and three wavevector coordinates). The phonon BTE is also called an equation of phonon radiative transfer (EPRT) when the phonon distribution function is replaced with a phonon i ...
ME 313 CH 7 Example Solutions
... 30 m/s. The thermophysical properties of module are k = 5.2 W/m.K, cp = 320 J/kg.K, ρ = 2300 kg / m 3 . a) find the required power generation, q ( W / m 3 ) , in a module positioned at a distance 700 mm from the leading edge? b) Find the maximum temperature Tmax in the heat generating module? ...
... 30 m/s. The thermophysical properties of module are k = 5.2 W/m.K, cp = 320 J/kg.K, ρ = 2300 kg / m 3 . a) find the required power generation, q ( W / m 3 ) , in a module positioned at a distance 700 mm from the leading edge? b) Find the maximum temperature Tmax in the heat generating module? ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... 1 watt = 1 J/s,, so a 100 Watt bulb uses 100 J each second We often use the unit of kJ to refer to chemical heat exchanges in a reaction. 1 kJ = 1000 J Energy is also reported in calories: Amount of energy needed to raise 1 gram of water by 1oC 1 cal = 4.184 J; 1 Cal = 4184 J Cal (or kcal) is ...
... 1 watt = 1 J/s,, so a 100 Watt bulb uses 100 J each second We often use the unit of kJ to refer to chemical heat exchanges in a reaction. 1 kJ = 1000 J Energy is also reported in calories: Amount of energy needed to raise 1 gram of water by 1oC 1 cal = 4.184 J; 1 Cal = 4184 J Cal (or kcal) is ...
notes for meteorofe - pams
... Condensation – Water vapor (gas) turns back to a liquid. (energy required / cold) -cloud formation. Precipitation – Water that is so heavy it falls as liquid / solid. Sublimation – Solid state turns directly to a gas state skipping liquid phase. Evapotranspiration/ transpiration – Water released by ...
... Condensation – Water vapor (gas) turns back to a liquid. (energy required / cold) -cloud formation. Precipitation – Water that is so heavy it falls as liquid / solid. Sublimation – Solid state turns directly to a gas state skipping liquid phase. Evapotranspiration/ transpiration – Water released by ...
The Skin
... Body systems that work with the integumentary system; Send sensory information to the nervous system, the respiratory and circulatory system provide oxygen, the digestive system provides nutrients and energy, skin is part of the excretory system ...
... Body systems that work with the integumentary system; Send sensory information to the nervous system, the respiratory and circulatory system provide oxygen, the digestive system provides nutrients and energy, skin is part of the excretory system ...
ME 2322 – Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 14 Complete
... 20. (10 pt) Both the energy and mass balance must be satisfied for all thermodynamic systems. 21. (10 pt) When an initially empty rigid tank is filled from a constant fluid property source, the final specific internal energy of the fluid in the tank must equal the specific enthalpy of the source. 22 ...
... 20. (10 pt) Both the energy and mass balance must be satisfied for all thermodynamic systems. 21. (10 pt) When an initially empty rigid tank is filled from a constant fluid property source, the final specific internal energy of the fluid in the tank must equal the specific enthalpy of the source. 22 ...
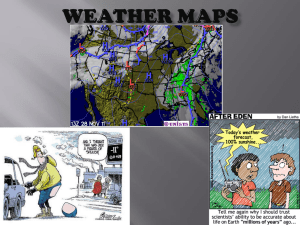
Weather maps
... High pressure areas are produced by cooler, heavier, sinking air. This air contains less moisture and is more stable. In the summer, high pressure usually means sustained sunshine, few clouds, low winds, high temperatures, and dry weather. In winter, the lack of cloud cover can cause the temperature ...
... High pressure areas are produced by cooler, heavier, sinking air. This air contains less moisture and is more stable. In the summer, high pressure usually means sustained sunshine, few clouds, low winds, high temperatures, and dry weather. In winter, the lack of cloud cover can cause the temperature ...
Heat Transfer: A Practical Approach
... A 3-m diameter spherical tank filled with liquid nitrogen at 1 atm and -196°C is exposed to convection and radiation with the surrounding air and surfaces. The rate of evaporation of liquid nitrogen in the tank as a result of the heat gain from the surroundings for the cases of no insulation, 5-cm t ...
... A 3-m diameter spherical tank filled with liquid nitrogen at 1 atm and -196°C is exposed to convection and radiation with the surrounding air and surfaces. The rate of evaporation of liquid nitrogen in the tank as a result of the heat gain from the surroundings for the cases of no insulation, 5-cm t ...
Cold Stress
... Table of Contents Cold Stress: What is it?...................................................... 2 Types of Heat Loss! ............................................................ 2 What is Happening in your Body?..................................... 3 Cold Weather Challenges for Workers............ ...
... Table of Contents Cold Stress: What is it?...................................................... 2 Types of Heat Loss! ............................................................ 2 What is Happening in your Body?..................................... 3 Cold Weather Challenges for Workers............ ...
Product Code: HTC
... silicone rectifiers and semi-conductors, thermostats, power resistors and radiators, to name but a few. When the contact surfaces are placed together, a firm metal-to-metal contact will only be achieved on 40 – 60% of the interface, depending on the smoothness of the surfaces. This means that air, w ...
... silicone rectifiers and semi-conductors, thermostats, power resistors and radiators, to name but a few. When the contact surfaces are placed together, a firm metal-to-metal contact will only be achieved on 40 – 60% of the interface, depending on the smoothness of the surfaces. This means that air, w ...
HTC Heat Transfer Compound
... silicone rectifiers and semi-conductors, thermostats, power resistors and radiators, to name but a few. When the contact surfaces are placed together, a firm metal-to-metal contact will only be achieved on 40 – 60% of the interface, depending on the smoothness of the surfaces. This means that air, w ...
... silicone rectifiers and semi-conductors, thermostats, power resistors and radiators, to name but a few. When the contact surfaces are placed together, a firm metal-to-metal contact will only be achieved on 40 – 60% of the interface, depending on the smoothness of the surfaces. This means that air, w ...
The HUMAN BODY
... b. Food (nutrients needed to supply energy and raw materials for building new living matter) c. Oxygen (used in releasing energy from nutrients) d. Heat (a byproduct of metabolism; its presence governs the rate at which reactions occur) e. Pressure (force required to facilitate movement of air or fl ...
... b. Food (nutrients needed to supply energy and raw materials for building new living matter) c. Oxygen (used in releasing energy from nutrients) d. Heat (a byproduct of metabolism; its presence governs the rate at which reactions occur) e. Pressure (force required to facilitate movement of air or fl ...
KS4 What is Energy Used For
... Reacting to the external temperature In order to understand what happens, think about what your body does when it is hot or cold outside. How do you react? ...
... Reacting to the external temperature In order to understand what happens, think about what your body does when it is hot or cold outside. How do you react? ...
Chemistry 2 Final Exam Review_MC
... Calculate the value of Hrxn for the rxn: 2F2 + 2H2O 4HF + O2 17. What law did you use to solve this problem? 18. A 22.2 g sample of silver absorbs 65.5 J of heat energy when its temperature is raised from 31.0C to 43.5C . Find the specific heat of silver. 19. How much heat is required to raise ...
... Calculate the value of Hrxn for the rxn: 2F2 + 2H2O 4HF + O2 17. What law did you use to solve this problem? 18. A 22.2 g sample of silver absorbs 65.5 J of heat energy when its temperature is raised from 31.0C to 43.5C . Find the specific heat of silver. 19. How much heat is required to raise ...
Experiment 2 Lab sheet
... Measurements of the distance through which the masses fell and the temperature change of the water allowed Joule to determine the work performed and the heat produced. With many such experiments, Joule demonstrated that the ratio between work performed and heat produced was constant. In modern units ...
... Measurements of the distance through which the masses fell and the temperature change of the water allowed Joule to determine the work performed and the heat produced. With many such experiments, Joule demonstrated that the ratio between work performed and heat produced was constant. In modern units ...
Organ Systems - Cloudfront.net
... - used to release energy from nutrients • Heat - form of energy - partly controls rate of metabolic reactions • Pressure - application of force on an object - atmospheric pressure – important for breathing - hydrostatic pressure – keeps blood flowing ...
... - used to release energy from nutrients • Heat - form of energy - partly controls rate of metabolic reactions • Pressure - application of force on an object - atmospheric pressure – important for breathing - hydrostatic pressure – keeps blood flowing ...
6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis
... homeostasis involves maintaining a constant internal environment; involves the concept of negative feedback; a deviation from the norm is the stimulus to trigger the mechanisms to restore the norm / OWTTE; body temperature in mammals must be maintained at a constant level for enzymes; controlled by ...
... homeostasis involves maintaining a constant internal environment; involves the concept of negative feedback; a deviation from the norm is the stimulus to trigger the mechanisms to restore the norm / OWTTE; body temperature in mammals must be maintained at a constant level for enzymes; controlled by ...
Air Temperature
... On the valley floor, cold and dense air cannot rise. Smoke and other pollutants are trapped. Thus, valley bottom is colder and more frequently polluted than nearby hillsides. ...
... On the valley floor, cold and dense air cannot rise. Smoke and other pollutants are trapped. Thus, valley bottom is colder and more frequently polluted than nearby hillsides. ...
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia is elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation that occurs when a body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. Extreme temperature elevation then becomes a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent disability or death.The most common causes include heat stroke and adverse reactions to drugs. The former is an acute temperature elevation caused by exposure to excessive heat, or combination of heat and humidity, that overwhelms the heat-regulating mechanisms. The latter is a relatively rare side effect of many drugs, particularly those that affect the central nervous system. Malignant hyperthermia is a rare complication of some types of general anesthesia.Hyperthermia differs from fever in that the body's temperature set point remains unchanged. The opposite is hypothermia, which occurs when the temperature drops below that required to maintain normal metabolism.