Stars, Constellations, and the Celestial Sphere
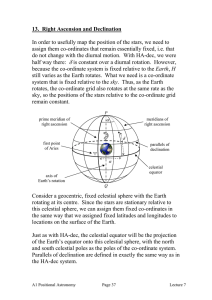
... The horizon for an observer at O is the intersection of a plane tangent to Earth at O with the celestial sphere. Everything that the observer can see is above the tangent plane (represented by the green line in the figure). The angle between the celestial equator (yellow line) and the horizon (gree ...
... The horizon for an observer at O is the intersection of a plane tangent to Earth at O with the celestial sphere. Everything that the observer can see is above the tangent plane (represented by the green line in the figure). The angle between the celestial equator (yellow line) and the horizon (gree ...
4. in-flight calibration plan
... always in the plane of the spacecraft and it is necessary to yaw up 9˚ and roll up to 35˚ in order that CIPS can observe the terminator at the correct latitude and longitude. The baffle systems are required to reduce any signal from direct solar illumination or from sun light scattered spacecraft su ...
... always in the plane of the spacecraft and it is necessary to yaw up 9˚ and roll up to 35˚ in order that CIPS can observe the terminator at the correct latitude and longitude. The baffle systems are required to reduce any signal from direct solar illumination or from sun light scattered spacecraft su ...
Triangulation
... Method of determining distance based on the principles of geometry. A distant object is sighted from two well-separated locations. The distance between the two locations and the angle between the line joining them and the line to the distant object are all that are necessary to ascertain the object' ...
... Method of determining distance based on the principles of geometry. A distant object is sighted from two well-separated locations. The distance between the two locations and the angle between the line joining them and the line to the distant object are all that are necessary to ascertain the object' ...
PROBLEM SET #9 SOLUTIONS AST142 1. Quasar luminosity
... Figure 1. Angle and lengths for a relativistically moving gas blob. The blob moves at speed v with respect to the galaxy and at an angle θ with respect to the line of sight to a distant observer that is distance d from the galaxy. 3. Apparent Velocity for a Relativistic Object (Superluminal Motion) ...
... Figure 1. Angle and lengths for a relativistically moving gas blob. The blob moves at speed v with respect to the galaxy and at an angle θ with respect to the line of sight to a distant observer that is distance d from the galaxy. 3. Apparent Velocity for a Relativistic Object (Superluminal Motion) ...
Celestial Navigation
... (distance). The DR and observed positions rarely coincide. There is a discrepancy, due to such factors as leeway or tidal streams. The DR position is fundamental ...
... (distance). The DR and observed positions rarely coincide. There is a discrepancy, due to such factors as leeway or tidal streams. The DR position is fundamental ...
Microlensing Studies in Crowded Fields
... spread functions so take much longer to survey a given number of targets. • Adaptive optics can give excellent resolution but only over a tiny field of view (a few arcseconds in the visible). • The only method that can routinely give Hubble resolution from the ground is Lucky Imaging. ...
... spread functions so take much longer to survey a given number of targets. • Adaptive optics can give excellent resolution but only over a tiny field of view (a few arcseconds in the visible). • The only method that can routinely give Hubble resolution from the ground is Lucky Imaging. ...
Powerpoint - UIUC HEP Group
... The first sufficiently accurate (to 5 seconds during a transatlantic voyage) marine chronometer was tested by John Harrison in 1761. Of course, the positions of the stars on the sky must be accurately measured. This was one of the important tasks of the Greenwich Observatory (and others). ...
... The first sufficiently accurate (to 5 seconds during a transatlantic voyage) marine chronometer was tested by John Harrison in 1761. Of course, the positions of the stars on the sky must be accurately measured. This was one of the important tasks of the Greenwich Observatory (and others). ...