Dynamic Inertia Weight Particle Swarm Optimization for Solving
... left blank (white) and which will be colored (black), based on the numbers at the side of the grid. The resulting pattern of colored or left blank squares makes up a hidden picture, which is the solution to the puzzle. The resulting picture must obey all the following three conditions: ...
... left blank (white) and which will be colored (black), based on the numbers at the side of the grid. The resulting pattern of colored or left blank squares makes up a hidden picture, which is the solution to the puzzle. The resulting picture must obey all the following three conditions: ...
Homework 1
... (that is, if x12 = 8, x13 = 3, x22 = 6 and so on), then x11 = 9. Proof: Suppose x11 = 9. Then since square(1, 1) = square(2, 1) = square(2, 2) = square(2, 3), rule 4 tells us that none of x21 , x22 , nor x23 can be 9. Similarly, since x37 = 9, none of x27 , x28 , nor x29 can be 9. Thus by rule 2 (wi ...
... (that is, if x12 = 8, x13 = 3, x22 = 6 and so on), then x11 = 9. Proof: Suppose x11 = 9. Then since square(1, 1) = square(2, 1) = square(2, 2) = square(2, 3), rule 4 tells us that none of x21 , x22 , nor x23 can be 9. Similarly, since x37 = 9, none of x27 , x28 , nor x29 can be 9. Thus by rule 2 (wi ...
N-1 - bYTEBoss
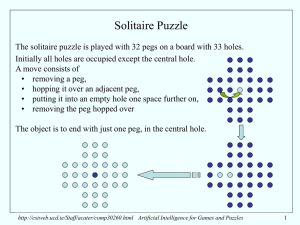
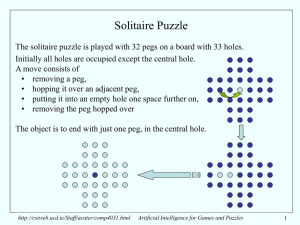
... solved by a brute-force method such as outlined earlier. 4+ Gb of storage and a few hours (?) of CPU should either do it, or prove it cannot be done. For “solving Solitaire” to be really interesting from an AI point of view, it should be that there are heuristics which can be used to effectively pru ...
... solved by a brute-force method such as outlined earlier. 4+ Gb of storage and a few hours (?) of CPU should either do it, or prove it cannot be done. For “solving Solitaire” to be really interesting from an AI point of view, it should be that there are heuristics which can be used to effectively pru ...
Document
... solved by a brute-force method such as outlined earlier. 4+ Gb of storage and a few hours (?) of CPU should either do it, or prove it cannot be done. For “solving Solitaire” to be really interesting from an AI point of view, it should be that there are heuristics which can be used to effectively pru ...
... solved by a brute-force method such as outlined earlier. 4+ Gb of storage and a few hours (?) of CPU should either do it, or prove it cannot be done. For “solving Solitaire” to be really interesting from an AI point of view, it should be that there are heuristics which can be used to effectively pru ...
project
... – Take user input as an assertion of fact, modify the rules to make the inference engine run again with the new fact and after checking the correctness, retract the ...
... – Take user input as an assertion of fact, modify the rules to make the inference engine run again with the new fact and after checking the correctness, retract the ...
Ferda - Knowledge Engineering Group
... with the aid of logic (EverMiner) Support for ontology Broadening of current procedures to ...
... with the aid of logic (EverMiner) Support for ontology Broadening of current procedures to ...
Picture Puzzle, Rocket Student Lesson
... Mat the Puzzle pieces with tag board for durability. 3. Adhere the negative part of the 9" x 12" Puzzle to a piece of cardstock and create the puzzle frame. Adhere the frame to tag board for durability. 4. Insert the colored Puzzle Pieces to assemble the Rocket Picture Puzzle ...
... Mat the Puzzle pieces with tag board for durability. 3. Adhere the negative part of the 9" x 12" Puzzle to a piece of cardstock and create the puzzle frame. Adhere the frame to tag board for durability. 4. Insert the colored Puzzle Pieces to assemble the Rocket Picture Puzzle ...
Nonogram

Nonograms, also known as Hanjie, Picross or Griddlers, are picture logic puzzles in which cells in a grid must be colored or left blank according to numbers at the side of the grid to reveal a hidden picture. In this puzzle type, the numbers are a form of discrete tomography that measures how many unbroken lines of filled-in squares there are in any given row or column. For example, a clue of ""4 8 3"" would mean there are sets of four, eight, and three filled squares, in that order, with at least one blank square between successive groups.These puzzles are often black and white, describing a binary image, but they can also be colored. If colored, the number clues are also colored to indicate the color of the squares. Two differently colored numbers may have a space in between them. For example, a black four followed by a red two could mean four black boxes, some empty spaces, and two red boxes, or it could simply mean four black boxes followed immediately by two red ones.Nonograms have no theoretical limits on size, and are not restricted to square layouts.