Thermodynamics test
... a) Heat is a form of energy and it is contained inside a body b) The temperature of a body does not depend on the internal energy it possesses c) When two bodies of different temperatures are in thermal contact, internal energy are transferred from the body of higher temperature to that of lower tem ...
... a) Heat is a form of energy and it is contained inside a body b) The temperature of a body does not depend on the internal energy it possesses c) When two bodies of different temperatures are in thermal contact, internal energy are transferred from the body of higher temperature to that of lower tem ...
5.1 The Nature of Heat
... • Water can absorb a lot of heat without raising its temperature a lot • It takes a lot more heat energy to increase the temperature of water • Water has a HIGH specific heat which means a LOW temperature compared to other substances ...
... • Water can absorb a lot of heat without raising its temperature a lot • It takes a lot more heat energy to increase the temperature of water • Water has a HIGH specific heat which means a LOW temperature compared to other substances ...
Thermodynamics test
... 8) The temperature of Lightening is 28000 K. Convert this temperature to degrees Fahrenheit. o a) 15644 F b) 15708 oF c) 49940 oF d) 50000 oF (SIG Fig’s) e) 50149 oF 9) An Object starts at 50 C, energy is added until the temperature increases to 60 C for a total ∆T of 10 C. What is the temperature c ...
... 8) The temperature of Lightening is 28000 K. Convert this temperature to degrees Fahrenheit. o a) 15644 F b) 15708 oF c) 49940 oF d) 50000 oF (SIG Fig’s) e) 50149 oF 9) An Object starts at 50 C, energy is added until the temperature increases to 60 C for a total ∆T of 10 C. What is the temperature c ...
Chapter 2 Safe and Smart Physical Activity
... Side stitch- a pain in the lower side of the lower abdomen. (running activities) Microtrauma- Micro-means small Trauma-means injury. Sometimes may not appear on X-ray. Repeated use over time causes injury to eventually appear. Hyperflexion-hyper-too much, flexion-means to bend. Avoid exercises that ...
... Side stitch- a pain in the lower side of the lower abdomen. (running activities) Microtrauma- Micro-means small Trauma-means injury. Sometimes may not appear on X-ray. Repeated use over time causes injury to eventually appear. Hyperflexion-hyper-too much, flexion-means to bend. Avoid exercises that ...
Specific heat
... What type of energy is being transferred from the hot plate to the water? How does this transfer of energy affect the molecules of water? How does this transfer of energy affect the molecules of the liquid inside the thermometer? As particles of water strike the thermometer and transfer their energy ...
... What type of energy is being transferred from the hot plate to the water? How does this transfer of energy affect the molecules of water? How does this transfer of energy affect the molecules of the liquid inside the thermometer? As particles of water strike the thermometer and transfer their energy ...
Practice ws on Ch 5 - mvhs
... lower the sample’s temperature from 56.2 to 19.8 ° C? Answer: 2.53 x 10^4 J 4. A 1.00 M aqueous solution of NaOH, a 0.50 M aqueous solution of H2SO4, and a coffee-cup calorimeter were allowed to stand at a room temperature of 25.4 °C until the temperature of all three reached 25.4 C. A 50.0-mL sampl ...
... lower the sample’s temperature from 56.2 to 19.8 ° C? Answer: 2.53 x 10^4 J 4. A 1.00 M aqueous solution of NaOH, a 0.50 M aqueous solution of H2SO4, and a coffee-cup calorimeter were allowed to stand at a room temperature of 25.4 °C until the temperature of all three reached 25.4 C. A 50.0-mL sampl ...
Workshop National sur l`Hydrogène – Université Kasdi Merbah – Ou
... Radiative transport within the electrode and electrolyte layers, as well as surface-tosurface radiation within the fuel and oxygen flow channels, has the potential to greatly influence temperature fields and overall operating conditions of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC). Radiation from the stack to t ...
... Radiative transport within the electrode and electrolyte layers, as well as surface-tosurface radiation within the fuel and oxygen flow channels, has the potential to greatly influence temperature fields and overall operating conditions of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC). Radiation from the stack to t ...
Table S1: Properties of Antigorite as a Model
... et al., 1976; Evans, 2004; O’Hanley, 1996; Deer, Howie and Zussman, 2009), its dehydration curve is well characterized to high pressures and it has a simple serpentine breakdown reaction involving no other starting phases. Among the common rock-forming serpentine minerals, antigorite is also stable ...
... et al., 1976; Evans, 2004; O’Hanley, 1996; Deer, Howie and Zussman, 2009), its dehydration curve is well characterized to high pressures and it has a simple serpentine breakdown reaction involving no other starting phases. Among the common rock-forming serpentine minerals, antigorite is also stable ...
The Facts about Nutec Thermal Properties 11 5 12.pub
... thermal transmission properties by means of the heat flow meter apparatus. This is the same test method required and is noted as indispensable for the application of SANS 204 ...
... thermal transmission properties by means of the heat flow meter apparatus. This is the same test method required and is noted as indispensable for the application of SANS 204 ...
Physical Science
... 58. Materials such as air, wood, and rubber that do not allow heat to pass through them easily are called ____________________________. 59. The transfer of heat energy by movement of matter is called _________________________. 60. A device that absorbs radiant energy from the Sun is a(n) ___________ ...
... 58. Materials such as air, wood, and rubber that do not allow heat to pass through them easily are called ____________________________. 59. The transfer of heat energy by movement of matter is called _________________________. 60. A device that absorbs radiant energy from the Sun is a(n) ___________ ...
Chapter 7: Energy and Chemical Change
... • The amount of heat absorbed or released by a chemical reaction is called the heat of reaction • A calorimeter can be used to measure the heat of reaction • Calorimeters are usually designed to measure heats of reaction under conditions of constant volume or constant pressure • Pressure is the amo ...
... • The amount of heat absorbed or released by a chemical reaction is called the heat of reaction • A calorimeter can be used to measure the heat of reaction • Calorimeters are usually designed to measure heats of reaction under conditions of constant volume or constant pressure • Pressure is the amo ...
Chapter 11 Notes - Mr-Durands
... Heat: Energy that is transferred from one substance to another. • Represented by a “q” or “H” in an equation. Heat is measured in Joules (J) or calories (cal.), the same units as energy. Heat flows from hot objects to cold objects. Only changes in heat can be detected. ...
... Heat: Energy that is transferred from one substance to another. • Represented by a “q” or “H” in an equation. Heat is measured in Joules (J) or calories (cal.), the same units as energy. Heat flows from hot objects to cold objects. Only changes in heat can be detected. ...
CCC HOH FUK TONG COLLEGE
... Mary of weight W stands inside a lift. The life is moving upwards at a constant acceleration. Let the normal force exerted on Mary by the floor be R, which of the following statements is/are correct? (1) R is greater than W in magnitude. (2) R and W are in opposite directions. (3) R and W form an ac ...
... Mary of weight W stands inside a lift. The life is moving upwards at a constant acceleration. Let the normal force exerted on Mary by the floor be R, which of the following statements is/are correct? (1) R is greater than W in magnitude. (2) R and W are in opposite directions. (3) R and W form an ac ...
Comparison of Heat Loss by Sample Building Component
... Comparison of Heat Loss by Sample Building Component Windows vs. Walls Formula: Heat Loss (BTU/hr) = UA Where U = Thermal transmittance Where A = Area Where = Delta T (temperature difference) Use the formula for calculating heat loss to discuss window replacement as an energy savings measure. Use th ...
... Comparison of Heat Loss by Sample Building Component Windows vs. Walls Formula: Heat Loss (BTU/hr) = UA Where U = Thermal transmittance Where A = Area Where = Delta T (temperature difference) Use the formula for calculating heat loss to discuss window replacement as an energy savings measure. Use th ...
chapter 4 : heat
... Energy is transferred from *( A , B ) to *( A , B ) at a faster rate. Energy is transferred from *( A , B ) to *( A , B ) at a slower rate. Temperature A will *( increase , decrease ). Temperature B will *( increase , decrease ). The net heat will flow from *( A , B ) to *( A , B ) until they are at ...
... Energy is transferred from *( A , B ) to *( A , B ) at a faster rate. Energy is transferred from *( A , B ) to *( A , B ) at a slower rate. Temperature A will *( increase , decrease ). Temperature B will *( increase , decrease ). The net heat will flow from *( A , B ) to *( A , B ) until they are at ...
Endotherms
... some of the time, while allowing it to be controlled by the environment other timesHeterotherms e.g., animals that hibernate - bats, marmots, hummingbirds, But Not Bears ...
... some of the time, while allowing it to be controlled by the environment other timesHeterotherms e.g., animals that hibernate - bats, marmots, hummingbirds, But Not Bears ...
Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology: Overview of Fundamental
... • Radiation: involves emission of EM energy from the surface of hot body into the transparent cooler surroundings. Not important in cool rocks, but increasingly important at T’s >1200°C • Advection: involves flow of a liquid through openings in a rock whose T is different from the fluid (mass flux). ...
... • Radiation: involves emission of EM energy from the surface of hot body into the transparent cooler surroundings. Not important in cool rocks, but increasingly important at T’s >1200°C • Advection: involves flow of a liquid through openings in a rock whose T is different from the fluid (mass flux). ...
Word
... b. Water boils above 100 0C at higher pressures c. Water boils below 100 0C at lower pressures C. Condensation 1. The conversion of a gas to a liquid by the removal of energy IV. Freezing and Melting A. Freezing Point 1. The temperature at which the solid and liquid are in equilibrium at 1 atm 2. Fo ...
... b. Water boils above 100 0C at higher pressures c. Water boils below 100 0C at lower pressures C. Condensation 1. The conversion of a gas to a liquid by the removal of energy IV. Freezing and Melting A. Freezing Point 1. The temperature at which the solid and liquid are in equilibrium at 1 atm 2. Fo ...
Hurt Building: Atlanta, GA - High Performing Buildings
... 5 4 Y E A R S L AT E R T H E H U R T ’ S S Y S T E M S S T I L L D E L I V E R Much of the Hurt Building’s air-handling system stands just as it was in 1956. Motors have been replaced, chilled water coils have been changed out, but other parts, such as the steam coils, are original. And, the system ...
... 5 4 Y E A R S L AT E R T H E H U R T ’ S S Y S T E M S S T I L L D E L I V E R Much of the Hurt Building’s air-handling system stands just as it was in 1956. Motors have been replaced, chilled water coils have been changed out, but other parts, such as the steam coils, are original. And, the system ...
Chapter 7 Thermal and Energy Systems
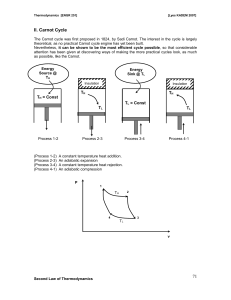
... • The sources of energy, or heat reservoirs, are large enough so that their temperatures do not change as heat is removed or added. ...
... • The sources of energy, or heat reservoirs, are large enough so that their temperatures do not change as heat is removed or added. ...
Science Unit 5 Powerpoint 2 Energy
... Electric current flows through a path called a circuit. A circuit is like a big loop. In order for the current to flow through the loop, the path must have no breaks; in other words, it must be closed. A closed circuit has no breaks in it. An open circuit has a break. ...
... Electric current flows through a path called a circuit. A circuit is like a big loop. In order for the current to flow through the loop, the path must have no breaks; in other words, it must be closed. A closed circuit has no breaks in it. An open circuit has a break. ...
Validation of Molecular Dynamics simulations of evaporation and
... Since the invention of the integrated circuit, the power consumption increases with a factor of 10 every 6 years [1]. It is widely believed that this trend will continue [2]. If no energy is removed, the processor will heat up; this causes malfunction or even breakdown. Processors can be cooled by f ...
... Since the invention of the integrated circuit, the power consumption increases with a factor of 10 every 6 years [1]. It is widely believed that this trend will continue [2]. If no energy is removed, the processor will heat up; this causes malfunction or even breakdown. Processors can be cooled by f ...
First law of thermodynamics - Richard Barrans’s web site
... • Both the system and surroundings can be reset to the initial state • Requires no non-conservative processes – no friction – no contact between different temperatures ...
... • Both the system and surroundings can be reset to the initial state • Requires no non-conservative processes – no friction – no contact between different temperatures ...