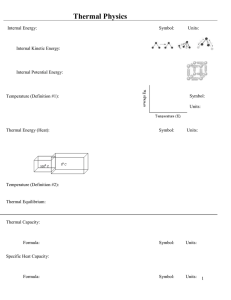
Heat and Temperature - University of Utah
... A calorie is defined as the amount of heat that needs to be added to 1 gram of water in order to raise its temperature by 1 degree Kelvin. Water has a relatively high heat capacity, which is important in biology and engineering: Prevents your body (= mostly water) from heating up too quickly during ...
... A calorie is defined as the amount of heat that needs to be added to 1 gram of water in order to raise its temperature by 1 degree Kelvin. Water has a relatively high heat capacity, which is important in biology and engineering: Prevents your body (= mostly water) from heating up too quickly during ...
Unit B: Understanding Energy Conversion Technologies
... C. The coolant evaporates as it gets ________________. It is pumped to the _________________. D. When it reaches the ___________________, pressure is applied to change it back into a ________________. E. The _____________________ is pumped to these coils. Thermal energy is __________________ i ...
... C. The coolant evaporates as it gets ________________. It is pumped to the _________________. D. When it reaches the ___________________, pressure is applied to change it back into a ________________. E. The _____________________ is pumped to these coils. Thermal energy is __________________ i ...
08 Johnson, Dwight L, and Dahiya, Jai N. doc - M-STEM
... experiments using warm water are the hardest ones because it is difficult deciding on what temperature to keep the hot plates at. The hot plates that were used had 5 different temperature settings ranging from low to 5, with 5 being the highest. The best setting for the warm beaker is between 2 and ...
... experiments using warm water are the hardest ones because it is difficult deciding on what temperature to keep the hot plates at. The hot plates that were used had 5 different temperature settings ranging from low to 5, with 5 being the highest. The best setting for the warm beaker is between 2 and ...
Fluids and Viscosity Chapter 7 Particle Theory of Matter (PTM)
... Hot Air Balloons – the inside of the balloon is heated. As the particles gain energy from the heat, the air particles inside the balloon begin to move around and spread further apart from one another. As the density of the air in the balloon decreases, it becomes less dense than the air around the b ...
... Hot Air Balloons – the inside of the balloon is heated. As the particles gain energy from the heat, the air particles inside the balloon begin to move around and spread further apart from one another. As the density of the air in the balloon decreases, it becomes less dense than the air around the b ...
Chapter 5, Problem 1
... Assumptions 1 Heat transfer is steady since there is no indication of any change with time. 2 Heat transfer is one-dimensional since the plate is large relative to its thickness, and there is thermal symmetry about the center plane 3 Thermal conductivity is constant. 4 Heat generation is uniform. Pr ...
... Assumptions 1 Heat transfer is steady since there is no indication of any change with time. 2 Heat transfer is one-dimensional since the plate is large relative to its thickness, and there is thermal symmetry about the center plane 3 Thermal conductivity is constant. 4 Heat generation is uniform. Pr ...
WS Specific Heat 2
... WS Specific Heat 2 1. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 19.68 g of calcium from 18.00 °C to 82.40 °C? The specific heat of calcium is 0.647 J/g°C. 2. 400.0 J of heat are applied to a sample of beryllium. Its temperature increases from 22.00 °C to 50.00 °C. What is the sample’s ma ...
... WS Specific Heat 2 1. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 19.68 g of calcium from 18.00 °C to 82.40 °C? The specific heat of calcium is 0.647 J/g°C. 2. 400.0 J of heat are applied to a sample of beryllium. Its temperature increases from 22.00 °C to 50.00 °C. What is the sample’s ma ...
Electronic properties of CeNi Si compound M. F
... Temperature dependence of the specific heat for CeNi4Si was analyzed. These studies were supported by magnetic susceptibility, electrical resistivity and X-ray photoemission spectroscopy measurements. CeNi4Si is paramagnetic and follows the Curie–Weiss law with μeff = 0.52 μB/f.u. and θP = –2 K. Thi ...
... Temperature dependence of the specific heat for CeNi4Si was analyzed. These studies were supported by magnetic susceptibility, electrical resistivity and X-ray photoemission spectroscopy measurements. CeNi4Si is paramagnetic and follows the Curie–Weiss law with μeff = 0.52 μB/f.u. and θP = –2 K. Thi ...
Chapter 7 - Chemical Reactions
... Given the balanced equation above for the reaction of calcium carbide and water, how many grams of calcium carbide, CaC2 will react with 3 moles of water? ...
... Given the balanced equation above for the reaction of calcium carbide and water, how many grams of calcium carbide, CaC2 will react with 3 moles of water? ...
From control-mass systems to control
... whereas W accounts for the work through the whole frontier. Similarly, q is the heat input through the wall by unit of mass flow rate. The entropy balance is used to compute the entropy generated inside, although a detailed integration of the entropy flow would be required if the process is not adia ...
... whereas W accounts for the work through the whole frontier. Similarly, q is the heat input through the wall by unit of mass flow rate. The entropy balance is used to compute the entropy generated inside, although a detailed integration of the entropy flow would be required if the process is not adia ...
Thermal Analysis of Heat Transfer Enhancement
... Figure 3(a). Highest heat transfer coefficient is at Re 150 for 0.5% vol % with 7.3% higher as compared to base fluid. The heat transfer coefficient increases as both the volume concentration and Re number are increased for all Al2O3 nanofluids. The addition of nano particles have enhanced the therm ...
... Figure 3(a). Highest heat transfer coefficient is at Re 150 for 0.5% vol % with 7.3% higher as compared to base fluid. The heat transfer coefficient increases as both the volume concentration and Re number are increased for all Al2O3 nanofluids. The addition of nano particles have enhanced the therm ...
Chapter 10 Test Form A Chapter 10 Test Form B
... particles and an object at low temperature has lower-energy particles. Energy is transferred as heat from the higher-energy particles to the lower-energy particles through collisions of the higher with the lower energy particles. 17. The ice begins to melt and change into water. 18. Thermal conducti ...
... particles and an object at low temperature has lower-energy particles. Energy is transferred as heat from the higher-energy particles to the lower-energy particles through collisions of the higher with the lower energy particles. 17. The ice begins to melt and change into water. 18. Thermal conducti ...
Chapter 6 - Saint Leo University Faculty
... 1) Hess’s Law states that the overall enthalpy change for a reaction is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps in the reaction. H is NOT dependent upon the pathway taken, since H is a state function. 2) Characteristics of H changes A) If a reaction is reversed, the sign ...
... 1) Hess’s Law states that the overall enthalpy change for a reaction is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps in the reaction. H is NOT dependent upon the pathway taken, since H is a state function. 2) Characteristics of H changes A) If a reaction is reversed, the sign ...
HEAT
... chemical bonds of a substance • the kinds of atoms and their arrangement in the substance determine the amount of energy stored in the substance. ...
... chemical bonds of a substance • the kinds of atoms and their arrangement in the substance determine the amount of energy stored in the substance. ...
Exam 4 - Nicholls State University
... should you do to remove the screws? (The coefficient of linear expansion for steel is 11 ×10-6 °C-1. The coefficient for brass is 19×10-6 °C-1.) a. heat the parts c. Not enough information given b. cool the parts 3. Which of these is the Kelvin temperature scale not based upon? a. freezing point of ...
... should you do to remove the screws? (The coefficient of linear expansion for steel is 11 ×10-6 °C-1. The coefficient for brass is 19×10-6 °C-1.) a. heat the parts c. Not enough information given b. cool the parts 3. Which of these is the Kelvin temperature scale not based upon? a. freezing point of ...
Warehouse Conversions
... The size and position of windows should be carefully planned according to the direction they face. Protect east, north and west facing windows from summer overheating by using external shading devices such as overhangs, adjustable awnings, shutters, deciduous trees and vines. Unprotected single glaz ...
... The size and position of windows should be carefully planned according to the direction they face. Protect east, north and west facing windows from summer overheating by using external shading devices such as overhangs, adjustable awnings, shutters, deciduous trees and vines. Unprotected single glaz ...
unit 9: thermal physics
... macroscopically as an increase in temperature. At the melting point, a temperature is reached at which the kinetic energy of the molecules is so great that they begin to break the permanent bonds that hold them fixed in place and begin to move about relative to each other. As the solid continues to ...
... macroscopically as an increase in temperature. At the melting point, a temperature is reached at which the kinetic energy of the molecules is so great that they begin to break the permanent bonds that hold them fixed in place and begin to move about relative to each other. As the solid continues to ...
T h - Website Staff UI
... Stirling’s approximation: ln N! N ln N + 0(N) for large N S mix k N A N B ln N A N B N A ln N A N B ln N B k N A N B ln N A N B X A ln N A X B ln N B k N A N B X A ln X A X B ln X B 0 ...
... Stirling’s approximation: ln N! N ln N + 0(N) for large N S mix k N A N B ln N A N B N A ln N A N B ln N B k N A N B ln N A N B X A ln N A X B ln N B k N A N B X A ln X A X B ln X B 0 ...
Page|1 - askIITians
... In isobaric process the pressure on the system remains constant during any operation. ...
... In isobaric process the pressure on the system remains constant during any operation. ...
Flame Temperature and Chemical Equilibrium
... successively brackeEng the soluEon within this range. • The temperature is then calculated by employing a Newton iteraEon on ...
... successively brackeEng the soluEon within this range. • The temperature is then calculated by employing a Newton iteraEon on ...
Thermal Physics - Physics Lectures
... Boyle’s law: The volume of a sample of a gas varies inversely as the pressure, if the temperature remains constant : PV = const. How to measure pressure: barometers and monometers III) Temperature: Heat, thermal equilibrium The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics allows us to use a system C (thermome ...
... Boyle’s law: The volume of a sample of a gas varies inversely as the pressure, if the temperature remains constant : PV = const. How to measure pressure: barometers and monometers III) Temperature: Heat, thermal equilibrium The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics allows us to use a system C (thermome ...
Heat - Indian Institute of Technology Madras
... transfer occurs when there is relative motion between a fluid and an object. As the relative velocity increases, the rate of convective heat transfer also increases. Radiative heat exchange occurs through space. Even when two objects at different temperatures are not in physical contact, photons emi ...
... transfer occurs when there is relative motion between a fluid and an object. As the relative velocity increases, the rate of convective heat transfer also increases. Radiative heat exchange occurs through space. Even when two objects at different temperatures are not in physical contact, photons emi ...
Sustainable Design of Wind-catcher of an Earth-to-Air
... showed that the temperature of the air inside is much lower than the air temperature of the traditional wind tower space and wind tower with a wet column was more effective during high wind while the tower equipped with wet surfaces was more effective during low wind. Either Safari & Hosseinnia (200 ...
... showed that the temperature of the air inside is much lower than the air temperature of the traditional wind tower space and wind tower with a wet column was more effective during high wind while the tower equipped with wet surfaces was more effective during low wind. Either Safari & Hosseinnia (200 ...
Physical Science Grade 7
... • Potential Energy- stored energy • Thermal Energy- Heat Energy • Thermal Pollution- waste heat given off into the environment ...
... • Potential Energy- stored energy • Thermal Energy- Heat Energy • Thermal Pollution- waste heat given off into the environment ...