The Balance of Nature and Human Impact. Klaus
... services. The challenge for humans will be to understand how much impact and change the planet’s natural environment supports before the occurrence of ‘‘tipping points’’ that will jeopardize the planet’s capacity to deliver the ecosystem services that support seven billion people (probably nine bill ...
... services. The challenge for humans will be to understand how much impact and change the planet’s natural environment supports before the occurrence of ‘‘tipping points’’ that will jeopardize the planet’s capacity to deliver the ecosystem services that support seven billion people (probably nine bill ...
Causes of extinction
... – Habitat loss – Introduced species – Disruption of ecosystem interactions – Pollution – Loss of genetic variation – Catastrophic disturbances ...
... – Habitat loss – Introduced species – Disruption of ecosystem interactions – Pollution – Loss of genetic variation – Catastrophic disturbances ...
ecosystem stability
... reflect the responses of the species and populations in the community. • Species respond to environmental change in ways that enable them to maintain homeostasis. • Populations respond in ways that reflect the success or failure of members of the population to survive and reproduce. ...
... reflect the responses of the species and populations in the community. • Species respond to environmental change in ways that enable them to maintain homeostasis. • Populations respond in ways that reflect the success or failure of members of the population to survive and reproduce. ...
density factors - Dr. Richard Thomas: Introduction and Contact
... 2. Irruptive: populations explode to high levels then return to a stable level or crash. 3. Chaotic: irregular fluctuations that are not predictable 4. Cyclic: population’s size varies on a fairly regular basis. Draw examples of each below: ...
... 2. Irruptive: populations explode to high levels then return to a stable level or crash. 3. Chaotic: irregular fluctuations that are not predictable 4. Cyclic: population’s size varies on a fairly regular basis. Draw examples of each below: ...
Ecology - AaronFreeman
... Orchids can grow on the moss The trees are not harmed or helped but the moss and the orchids have a place to live. ...
... Orchids can grow on the moss The trees are not harmed or helped but the moss and the orchids have a place to live. ...
Biodiversity Threats
... A conflict of interest for conservationists? • Biodiversity degrades with monetary-based approaches ...
... A conflict of interest for conservationists? • Biodiversity degrades with monetary-based approaches ...
Full PDF - Phyllomedusa - Journal of Herpetology
... changes may disappear from the reserve. As civilization approaches, stream pollution and air pollution may occur, causing changes in density or even the demise of some species. Sorting these kinds of changes from natural fluctuations will be a challenge. One example has already occurred. In a long-t ...
... changes may disappear from the reserve. As civilization approaches, stream pollution and air pollution may occur, causing changes in density or even the demise of some species. Sorting these kinds of changes from natural fluctuations will be a challenge. One example has already occurred. In a long-t ...
Populations PPT ecology_-_part_4_-_populations
... species: a species that immigrates into an ecosystem and is able to outcompete other species. Exhibits exponential growth because it is unusually successful in its new niche. ...
... species: a species that immigrates into an ecosystem and is able to outcompete other species. Exhibits exponential growth because it is unusually successful in its new niche. ...
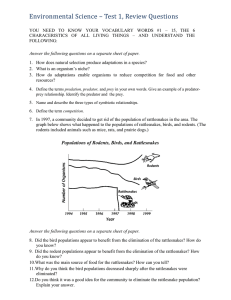
Populations of Rodents, Birds, and Rattlesnakes
... Interpreting Graphs In what year did a sudden change occur in the sizes of all three populations? What happened to the size of each population? Inferring What can you infer from the data about the types of interactions between mallard ducks, raccoons, and snapping turtles? Explain your answer. Essay ...
... Interpreting Graphs In what year did a sudden change occur in the sizes of all three populations? What happened to the size of each population? Inferring What can you infer from the data about the types of interactions between mallard ducks, raccoons, and snapping turtles? Explain your answer. Essay ...
BCB322: Landscape Ecology
... • Permanent ponds experience extinction through population stochastic effects (random dry periods, over predation by migrant species, low seasonal birth success) • However, extinction in permanent ponds is low (<=8.5%), indicating migration between ponds and consequent reduction in local extinctions ...
... • Permanent ponds experience extinction through population stochastic effects (random dry periods, over predation by migrant species, low seasonal birth success) • However, extinction in permanent ponds is low (<=8.5%), indicating migration between ponds and consequent reduction in local extinctions ...
ch5_sec3
... • Competition has several possible outcomes. • Sometimes, one species wins, and the other loses. The loser is eliminated from the habitat. ...
... • Competition has several possible outcomes. • Sometimes, one species wins, and the other loses. The loser is eliminated from the habitat. ...
Allowing extinction: should we let species go?
... concept of triage in conservation biology. They argue for the use of triage when allocating resources to competing conservation demands. Contrary to simply being an efficient approach, however, we feel that application of triage has the potential to mimic carnage of the 19th century battlefields fro ...
... concept of triage in conservation biology. They argue for the use of triage when allocating resources to competing conservation demands. Contrary to simply being an efficient approach, however, we feel that application of triage has the potential to mimic carnage of the 19th century battlefields fro ...
Populations - Liberty Union High School District
... the effect of density- dependent factors increases and limits population growth S-shaped growth curve (logistic growth) ...
... the effect of density- dependent factors increases and limits population growth S-shaped growth curve (logistic growth) ...
2.3 Effect of Bioaccumulation on Ecosystems
... Amphibians are valuable indicators of environmental health because they’re sensitive to chemical changes. Since the 80s the world amphibian population has declined & birth deformities have increased. This may be due to: drought, increased UV rays, pollution, habitat loss, parasites & diseases. ...
... Amphibians are valuable indicators of environmental health because they’re sensitive to chemical changes. Since the 80s the world amphibian population has declined & birth deformities have increased. This may be due to: drought, increased UV rays, pollution, habitat loss, parasites & diseases. ...
density-dependent limiting factors
... Usually Abiotic Factors Non-Living things Natural disasters ...
... Usually Abiotic Factors Non-Living things Natural disasters ...
Lecture 09 - Extinction vulnerability
... Its ecosystems are highly degraded, its human population rapidly expanded from 2.5 million in 1900 to 12 million in 1990 Conservationists are closely watching Madagascar because there are so many endemic species to be lost but many efforts are on-going to ...
... Its ecosystems are highly degraded, its human population rapidly expanded from 2.5 million in 1900 to 12 million in 1990 Conservationists are closely watching Madagascar because there are so many endemic species to be lost but many efforts are on-going to ...
Populations and Communities Section 3 Carving a Niche
... • Competition has several possible outcomes. • Sometimes, one species wins, and the other loses. The loser is eliminated from the habitat. ...
... • Competition has several possible outcomes. • Sometimes, one species wins, and the other loses. The loser is eliminated from the habitat. ...
Ch 5_section 3 NOTES - Le Mars Community Schools
... • Competition has several possible outcomes. • Sometimes, one species wins, and the other loses. The loser is eliminated from the habitat. ...
... • Competition has several possible outcomes. • Sometimes, one species wins, and the other loses. The loser is eliminated from the habitat. ...
of the Rio Bosque
... “lost” their legs millions of years ago). Generally, amphibians produce naked, unprotected eggs that must be laid in water to avoid desiccation. Reptile eggs are surrounded by protective membranes and usually an outer shell, so they can be deposited on land with less risk of drying out. ...
... “lost” their legs millions of years ago). Generally, amphibians produce naked, unprotected eggs that must be laid in water to avoid desiccation. Reptile eggs are surrounded by protective membranes and usually an outer shell, so they can be deposited on land with less risk of drying out. ...
Decline in amphibian populations

Since the 1980s, declines in amphibian populations, including population crashes and mass localized extinctions, have been noted from locations all over the world. These declines are perceived as one of the most critical threats to global biodiversity, and several causes are believed to be involved, including disease, habitat destruction and modification, exploitation, pollution, pesticide use, introduced species, and ultraviolet-B radiation (UV-B). However, many of the causes of amphibian declines are still poorly understood, and the topic is currently a subject of much ongoing research. Calculations based on extinction rates suggest that the current extinction rate of amphibians could be 211 times greater than the background extinction rate and the estimate goes up to 25,000–45,000 times if endangered species are also included in the computation.