![Electrical Circuits II [Opens in New Window]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007521861_1-4da59151bb70a291acd72b2f18430da6-300x300.png)
Upgrading the Rotor Ground Fault Protection on Electric Generators
... generators without warning, causing severe damage to rotors and forcing extended outages that can be extremely costly. Often power plant operators assume they have operating protective relays that will either shut down the generator (and possibly the plant) or initiate alarms at the onset of field g ...
... generators without warning, causing severe damage to rotors and forcing extended outages that can be extremely costly. Often power plant operators assume they have operating protective relays that will either shut down the generator (and possibly the plant) or initiate alarms at the onset of field g ...
Topic 2 – Controlling and using electric currents
... transferring (heat) energy to them This transfer of heat energy can be beneficial – e.g in electric fires and kettles However, this heating effect of an electric current can cause problems…e.g: o Some electrical appliances can produce so much waste heat energy that they could cause burns if touched ...
... transferring (heat) energy to them This transfer of heat energy can be beneficial – e.g in electric fires and kettles However, this heating effect of an electric current can cause problems…e.g: o Some electrical appliances can produce so much waste heat energy that they could cause burns if touched ...
Background for Alert
... increase, simultaneously damaging many transformers across the bulk power system. At each vulnerable transformer, the level of saturation of its core and reactive power consumption is amplified with increasing GIC levels. Because geomagnetically induced current flows occur simultaneously in many tra ...
... increase, simultaneously damaging many transformers across the bulk power system. At each vulnerable transformer, the level of saturation of its core and reactive power consumption is amplified with increasing GIC levels. Because geomagnetically induced current flows occur simultaneously in many tra ...
(GFCI) with Self Test and Lockout
... are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC) or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. SCILLC owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent ...
... are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC) or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. SCILLC owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent ...
notes
... We will see how to REFER the secondary impedance to the primary side in the next set of notes. [1] K. Su, “Fundamentals of Circuits, Electronics, and Signal Analysis,” Houghton ...
... We will see how to REFER the secondary impedance to the primary side in the next set of notes. [1] K. Su, “Fundamentals of Circuits, Electronics, and Signal Analysis,” Houghton ...
Specification texts
... with connecting cable 2.0 m long with Sub-D 9-pin connection. For use on fire and smoke dampers, with electric or pneumatic trigger devices working by the zero-current closed / depressurised closed functional principle, and with magnetic clamp and lifting magnet. Two sensors self-monitoring permanen ...
... with connecting cable 2.0 m long with Sub-D 9-pin connection. For use on fire and smoke dampers, with electric or pneumatic trigger devices working by the zero-current closed / depressurised closed functional principle, and with magnetic clamp and lifting magnet. Two sensors self-monitoring permanen ...
Electric Reliability Troubleshooting Guide
... cables, bus work, or a transformer physically very close (in the wall or next room) Electronic lighting ...
... cables, bus work, or a transformer physically very close (in the wall or next room) Electronic lighting ...
K0CQ-CSVHF2010
... Low Z TL I have to admit only about half the professional references mention the restriction on the simple formula and no ARRL resources mention that. The close spaced formula comes from work of Harold Wheeler about 1939 where he found that the charges on close spaced wires concentrated where the ...
... Low Z TL I have to admit only about half the professional references mention the restriction on the simple formula and no ARRL resources mention that. The close spaced formula comes from work of Harold Wheeler about 1939 where he found that the charges on close spaced wires concentrated where the ...
92KB - NZQA
... Industry Training Organisations must be granted consent to assess against standards by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Providers and Industry Training Organisations, which have been granted consent and which are assessing against unit standards must enga ...
... Industry Training Organisations must be granted consent to assess against standards by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Providers and Industry Training Organisations, which have been granted consent and which are assessing against unit standards must enga ...
Building a CTI Power Supply
... temperature. Stop when the regulator begins to feel unreasonably warm to the touch, and then back off one module or so. Also keep an eye on your train transformer to make sure you’re not exceeding its rated output as well. When you reach the rated limits of the power supply circuit, you can simply b ...
... temperature. Stop when the regulator begins to feel unreasonably warm to the touch, and then back off one module or so. Also keep an eye on your train transformer to make sure you’re not exceeding its rated output as well. When you reach the rated limits of the power supply circuit, you can simply b ...
Transformers - Electrical Devices, Instrumentation And
... the first cycle, or at 60 Hertz, in about 4/1000 sec. This may reduce the severity of damage and is recommended with certain transformer installations even if fire and dielectric breakdown potentials are low. See the requirements for askarel, LFLI and large oil units in Table 1. A lesser level of pr ...
... the first cycle, or at 60 Hertz, in about 4/1000 sec. This may reduce the severity of damage and is recommended with certain transformer installations even if fire and dielectric breakdown potentials are low. See the requirements for askarel, LFLI and large oil units in Table 1. A lesser level of pr ...
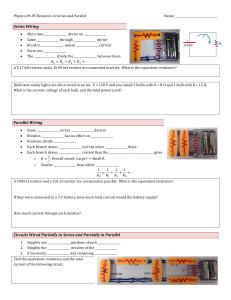
Physics 09-05 Resistors in Series and Parallel
... 10. An 1800-W toaster, a 1400-W electric frying pan, and a 75-W lamp are plugged into the same outlet in a 15-A, 120-V circuit. (The three devices are in parallel when plugged into the same socket.). (a) What current is drawn by each device? (b) Will this combination blow the 15-A fuse? (OpenStax 21 ...
... 10. An 1800-W toaster, a 1400-W electric frying pan, and a 75-W lamp are plugged into the same outlet in a 15-A, 120-V circuit. (The three devices are in parallel when plugged into the same socket.). (a) What current is drawn by each device? (b) Will this combination blow the 15-A fuse? (OpenStax 21 ...
Power LED`s - simplest light with constant
... use or surrounding environmental conditions you subject the LED's to. Or to put in another way: "this is better than using a resistor". It's more consistent, more efficient, and more flexible. It's ideal for High-power LED's especially, and can be used for any number and configuration of normal or h ...
... use or surrounding environmental conditions you subject the LED's to. Or to put in another way: "this is better than using a resistor". It's more consistent, more efficient, and more flexible. It's ideal for High-power LED's especially, and can be used for any number and configuration of normal or h ...
PowaTRIM Theory of Operation.
... This negative current is achieved in the winding direction of the choke coils and reactors. Let us assume we are looking at phase B. When phase C and phase A are magnetically induced in phase B, they are subjected to a 180-degrees phase shift as they pass through the choke coils. The wave form in ph ...
... This negative current is achieved in the winding direction of the choke coils and reactors. Let us assume we are looking at phase B. When phase C and phase A are magnetically induced in phase B, they are subjected to a 180-degrees phase shift as they pass through the choke coils. The wave form in ph ...
End Semester Examination-2004
... 8. Paralleling of CTs can be a source of error in 3-phase fault protection of feeder. 9. Two CTs rated100:5 C20 are connected in series, the new effective CT can be described by 100:5 C40. 10. A ring bus-bar configuration is superior to the double bus double breaker configuration. 11. A ground relay ...
... 8. Paralleling of CTs can be a source of error in 3-phase fault protection of feeder. 9. Two CTs rated100:5 C20 are connected in series, the new effective CT can be described by 100:5 C40. 10. A ring bus-bar configuration is superior to the double bus double breaker configuration. 11. A ground relay ...