AP Chap 43 The IMMUNE SYSTEM right one
... almost all nucleated cells of the body • Class II MHC molecules are found on immune cells such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells. They digest antigens and display pieces of the antigen with their MHC complex and are called antigen-presenting cells ...
... almost all nucleated cells of the body • Class II MHC molecules are found on immune cells such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells. They digest antigens and display pieces of the antigen with their MHC complex and are called antigen-presenting cells ...
lec1-host parasite r..
... Lysozyme: Basic protein found in microphage (PMN) as well as most tissue fluids except CSF, sweet and urine. It destroys the cell wall of bacteria. Interferons(IFN): C-reactive protein (CRP): Measure of inflammation produced in liver in response to inflammatory chemicals. ...
... Lysozyme: Basic protein found in microphage (PMN) as well as most tissue fluids except CSF, sweet and urine. It destroys the cell wall of bacteria. Interferons(IFN): C-reactive protein (CRP): Measure of inflammation produced in liver in response to inflammatory chemicals. ...
Transplant Immunology Principles
... • Involvement of broader cellular and humoral responses including nonspecific immunity ...
... • Involvement of broader cellular and humoral responses including nonspecific immunity ...
Exam Key 3 2008
... __T___2. Both eosinophils and mast cells are important mediators of allergic responses. __F___3. Most pollen allergens contain a single allergenic component. __T___4. Transfusion reactions are a manifestation of type II hypersensitivity. ___T__5. The initial step in the process of mast-cell degranul ...
... __T___2. Both eosinophils and mast cells are important mediators of allergic responses. __F___3. Most pollen allergens contain a single allergenic component. __T___4. Transfusion reactions are a manifestation of type II hypersensitivity. ___T__5. The initial step in the process of mast-cell degranul ...
CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY (T * CELL)
... • Assist other white blood cells in immunologic processes, including: - maturation of B-cell into plasma cell - activation of cytotoxic T cells and microphage, among other functions. • These cells are also known as CD4+ T cells because they express the CD4+ glycoprotein on their surface. ...
... • Assist other white blood cells in immunologic processes, including: - maturation of B-cell into plasma cell - activation of cytotoxic T cells and microphage, among other functions. • These cells are also known as CD4+ T cells because they express the CD4+ glycoprotein on their surface. ...
Accessary cells: in adaptive immunity are cells aid in the response
... can induce antibody production (not bind to the antibody) Antigen:antibody complexes (immune complexes): non-covalently associated group Antigenic determinant (epitope): the portion of an antigenic molecule bound by a given antibody Antigenic drift (shift): point mutations of viral genes cause small ...
... can induce antibody production (not bind to the antibody) Antigen:antibody complexes (immune complexes): non-covalently associated group Antigenic determinant (epitope): the portion of an antigenic molecule bound by a given antibody Antigenic drift (shift): point mutations of viral genes cause small ...
Projects
... Viruses are intracellular parasites, which need cellular components to replicate. While many individual interactions between an infecting virus and cellular host factors have been identified, their all-over complex interplay in terms of dynamics and outcomes are not well understood. The aim of this ...
... Viruses are intracellular parasites, which need cellular components to replicate. While many individual interactions between an infecting virus and cellular host factors have been identified, their all-over complex interplay in terms of dynamics and outcomes are not well understood. The aim of this ...
Immune system and its importance for homeostasis. Component
... Barrier functions of the human body and defense mechanisms. Non-specific cellular and humoral immune mechanisms. Specific cellular and humoral immune mechanisms. Phagocytosis and its importance for immunity. Neutrophils, their ontogenesis and function. Natural killer cells. Interferons. Characterist ...
... Barrier functions of the human body and defense mechanisms. Non-specific cellular and humoral immune mechanisms. Specific cellular and humoral immune mechanisms. Phagocytosis and its importance for immunity. Neutrophils, their ontogenesis and function. Natural killer cells. Interferons. Characterist ...
Teacher`s Guide Vocabulary
... Fanconi’s Anemia: A disease passed down through families that mainly affects the bone marrow and results in decreased production of all types of blood cells. Hepatitis B: A virus that infects the liver. It is spread through contact with the blood and body fluids of an infected person. Hepatitis C: A ...
... Fanconi’s Anemia: A disease passed down through families that mainly affects the bone marrow and results in decreased production of all types of blood cells. Hepatitis B: A virus that infects the liver. It is spread through contact with the blood and body fluids of an infected person. Hepatitis C: A ...
Autoimmune diseases
... prone to develop lupus-like autoimmunity. Various mechanisms have been invoked, including failure to clear immune complexes and loss of B-cell self-tolerance. It has also been proposed that deficiency of C1q results in defective phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells. Many cells normally undergo ap ...
... prone to develop lupus-like autoimmunity. Various mechanisms have been invoked, including failure to clear immune complexes and loss of B-cell self-tolerance. It has also been proposed that deficiency of C1q results in defective phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells. Many cells normally undergo ap ...
Transplant Physiology of Sep 16 2009 by Dr. A. Gangji
... • Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) system is synonymous with the human Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) • In humans, it’s called HLA due to expression of gene products on surface of WBC • These terms describe a group of genes on chromosome 6 that encode a variety of cell surface markers, antigen ...
... • Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) system is synonymous with the human Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) • In humans, it’s called HLA due to expression of gene products on surface of WBC • These terms describe a group of genes on chromosome 6 that encode a variety of cell surface markers, antigen ...
Bcl-6 and NF-κB cistromes mediate opposing regulation of the
... expressed by a variety of cell types, particularly in the immune system, but also by epithelial and endothelial cells Following interaction with their ligands they induce the transcription of a wide set of genes involved in inflammation ( pro-inflammatory cytokines, cytokine receptors, adhesion mole ...
... expressed by a variety of cell types, particularly in the immune system, but also by epithelial and endothelial cells Following interaction with their ligands they induce the transcription of a wide set of genes involved in inflammation ( pro-inflammatory cytokines, cytokine receptors, adhesion mole ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology
... Most lymphocyte activation involves glycoproteins of cell surfaces called MHC molecules Class I molecules display antigens on surface of nucleated cells, resulting in destruction of cells Class II molecules display antigens on surface of antigen-presenting cells, resulting in activation of immune ...
... Most lymphocyte activation involves glycoproteins of cell surfaces called MHC molecules Class I molecules display antigens on surface of nucleated cells, resulting in destruction of cells Class II molecules display antigens on surface of antigen-presenting cells, resulting in activation of immune ...
8.2 Structure of DNA
... histamine from damaged body cells • Pathogens are engulfed when pseudopodia surround the pathogen and then fuse, sequestering it in an internal vesicle • The vesicle may then fuse with the lysosome to digest the pathogen • Some of the pathogens antigenic fragments may be presented on the surface of ...
... histamine from damaged body cells • Pathogens are engulfed when pseudopodia surround the pathogen and then fuse, sequestering it in an internal vesicle • The vesicle may then fuse with the lysosome to digest the pathogen • Some of the pathogens antigenic fragments may be presented on the surface of ...
Innate Immune Responses in Cattle
... are five main subgroups of murine DC (Shortman and Liu 2002), which are classified by the presence or absence of CD4, CD8α, CD11b, and the interdigitating DC marker CD205: cDCs (CD8a+), CD11b type, pDCs, Langerhans cells in the skin, and Mo-DCs. DCs located in the epidermis (Langerhans cells) can al ...
... are five main subgroups of murine DC (Shortman and Liu 2002), which are classified by the presence or absence of CD4, CD8α, CD11b, and the interdigitating DC marker CD205: cDCs (CD8a+), CD11b type, pDCs, Langerhans cells in the skin, and Mo-DCs. DCs located in the epidermis (Langerhans cells) can al ...
powerpoint is here
... arise from macrophages outside CNS switch from resting to active state ...
... arise from macrophages outside CNS switch from resting to active state ...
PRIMARY IDs
... CR3, and CD18/CD11c (CR4 or p150,95) • These molecules are expressed on different classes of leukocytes and mediate their adhesion to endothelium ...
... CR3, and CD18/CD11c (CR4 or p150,95) • These molecules are expressed on different classes of leukocytes and mediate their adhesion to endothelium ...
Nutrition and Immune System in Livestock`s: Mini Review
... problematic than humoral assessment as assays are plagued by difficulties in standardization, biological variability, imprecision and technical complexity [20]. ...
... problematic than humoral assessment as assays are plagued by difficulties in standardization, biological variability, imprecision and technical complexity [20]. ...
Static
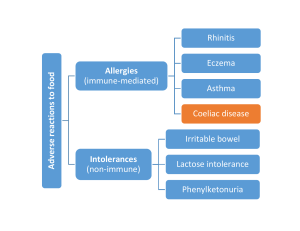
... Immune-mediated reaction to gluten in intestine Most people have no problem with gluten Thus disease attributable mainly to host factors ...
... Immune-mediated reaction to gluten in intestine Most people have no problem with gluten Thus disease attributable mainly to host factors ...
Blood - World of Teaching
... molecules of O2 associates and dissociates with O2 contains iron ...
... molecules of O2 associates and dissociates with O2 contains iron ...
Lymphatic System
... – Tears contain an enzyme that breaks down the cell wall of many bacteria – Saliva is antibacterial – Nasal passages and lungs are coated in mucus, so many germs not killed immediately are trapped in the mucus and swallowed. ...
... – Tears contain an enzyme that breaks down the cell wall of many bacteria – Saliva is antibacterial – Nasal passages and lungs are coated in mucus, so many germs not killed immediately are trapped in the mucus and swallowed. ...
Immunology Hypersensitivity Autoimmune Disease Infectious
... from vacca (= cow), term coined by Pasteur in honor of Jenner’s cowpox/chicken pox studies Herd immunity: When a critical mass is immune to an infection, this infection is less likely to spread to individuals who are not immune ...
... from vacca (= cow), term coined by Pasteur in honor of Jenner’s cowpox/chicken pox studies Herd immunity: When a critical mass is immune to an infection, this infection is less likely to spread to individuals who are not immune ...