Communicable Disease Policy
... In order to protect the safety and health of MSUB Athletic Training Students, the following Communicable Disease policy has been designed and adopted by the MSUB ATEP. This plan will be utilized by students, ACI/CIs, and the Athletic Training Education Program staff and faculty to assist in the mana ...
... In order to protect the safety and health of MSUB Athletic Training Students, the following Communicable Disease policy has been designed and adopted by the MSUB ATEP. This plan will be utilized by students, ACI/CIs, and the Athletic Training Education Program staff and faculty to assist in the mana ...
postal screening for genital Chlamydia trachomatis and prevalence
... worldwide (1). Among these microorganisms, Chlamydia trachomatis infection (CTI), an obligate intracellular bacterium, with millions of cases reported annually throughout the world is the most common cause of bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STI) with the highest incidence in developing co ...
... worldwide (1). Among these microorganisms, Chlamydia trachomatis infection (CTI), an obligate intracellular bacterium, with millions of cases reported annually throughout the world is the most common cause of bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STI) with the highest incidence in developing co ...
Goals and Objectives of sanitary and epidemic of the conditions of
... and regional departments of various services. SCPs are deployed in the transmission of checkpoints by forces and means of health care. Checkpoints are deployed in towns on main routes, road, railway, water-near their crossing the border quarantine zone, as well as at airports, and if necessary - wi ...
... and regional departments of various services. SCPs are deployed in the transmission of checkpoints by forces and means of health care. Checkpoints are deployed in towns on main routes, road, railway, water-near their crossing the border quarantine zone, as well as at airports, and if necessary - wi ...
Top 10 ways to prevent infection in 2013
... white blood cells and antibodies to prevent infection a second time. However, by getting vaccinated, you “trick” your body into thinking that it has been infected by a particular microbe, hence enhancing its own defenses against subsequent infection. Of course consult your clinician about receiving ...
... white blood cells and antibodies to prevent infection a second time. However, by getting vaccinated, you “trick” your body into thinking that it has been infected by a particular microbe, hence enhancing its own defenses against subsequent infection. Of course consult your clinician about receiving ...
Brucellosis
... An infectious disease that occurs from contact with other animals carrying the Brucella bacteria. Can spread to humans. Bacteria is spread by eating/drinking unpasteurized milk or cheese. People that come in contact with animals or meat are most at risk such as slaughterhouse workers, vets, and ...
... An infectious disease that occurs from contact with other animals carrying the Brucella bacteria. Can spread to humans. Bacteria is spread by eating/drinking unpasteurized milk or cheese. People that come in contact with animals or meat are most at risk such as slaughterhouse workers, vets, and ...
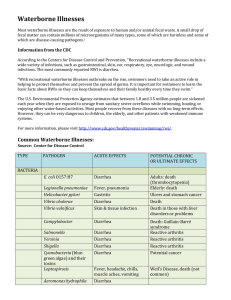
Waterborne Illnesses - Sound Health Explorer
... According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, “Recreational waterborne illnesses include a wide variety of infections, such as gastrointestinal, skin, ear, respiratory, eye, neurologic, and wound infections. The most commonly reported RWI is diarrhea. ...
... According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, “Recreational waterborne illnesses include a wide variety of infections, such as gastrointestinal, skin, ear, respiratory, eye, neurologic, and wound infections. The most commonly reported RWI is diarrhea. ...
outline26497
... b. HIV-infected individuals ultimately succumb less to opportunistic infections than to conditions rarely seen in the first 15 years of the epidemic: kidney disease, liver disease, cardiovascular disease, cancers not specific to HIV. Instead of a ‘death sentence’ that was common in the 80’s, when a ...
... b. HIV-infected individuals ultimately succumb less to opportunistic infections than to conditions rarely seen in the first 15 years of the epidemic: kidney disease, liver disease, cardiovascular disease, cancers not specific to HIV. Instead of a ‘death sentence’ that was common in the 80’s, when a ...
NEW AND EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES
... Initial detection via the astute observer (not via a surveillance system) New disease can involve multiple countries Continued threat from zoonotic agents jumping species boundaries Healthcare workers at high risk with highly communicable diseases Diagnostic methods key to control Epidemics can be c ...
... Initial detection via the astute observer (not via a surveillance system) New disease can involve multiple countries Continued threat from zoonotic agents jumping species boundaries Healthcare workers at high risk with highly communicable diseases Diagnostic methods key to control Epidemics can be c ...
The Microbial World and You
... Bacteria, when capitalized, refers to the domain. When not capitalized, it usually describes any prokaryotic cell.) Bacterial cells generally have one of three shapes: bacillus (rodlike), coccus (spherical or ovoid), and spiral (curved or corkscrew). Individual bacteria may form pairs, chains, or ot ...
... Bacteria, when capitalized, refers to the domain. When not capitalized, it usually describes any prokaryotic cell.) Bacterial cells generally have one of three shapes: bacillus (rodlike), coccus (spherical or ovoid), and spiral (curved or corkscrew). Individual bacteria may form pairs, chains, or ot ...
Proctitis
... before a diagnosis is made. Molecular tests for bacterial pathogens are becoming more widespread and have improved sensitivity over culture, although antimicrobial susceptibility testing still requires a positive culture.27 ...
... before a diagnosis is made. Molecular tests for bacterial pathogens are becoming more widespread and have improved sensitivity over culture, although antimicrobial susceptibility testing still requires a positive culture.27 ...
Infections in the Elderly
... In the area of patient safety, recent attention has focused on diagnostic error. The reduction of diagnostic error is an important goal because of its associated morbidity and potential preventability. A critical subset of diagnostic errors arises through cognitive errors, especially those associate ...
... In the area of patient safety, recent attention has focused on diagnostic error. The reduction of diagnostic error is an important goal because of its associated morbidity and potential preventability. A critical subset of diagnostic errors arises through cognitive errors, especially those associate ...
Brief C.V. - Emory Biology
... I have been modeling the dynamics of immune responses and host-pathogen interactions since my postdoctoral fellowship at Imperial College in 1991. I approach problems in immunology and epidemiology from an ecological and evolutionary viewpoint. At the within-host level, I view the immune system as a ...
... I have been modeling the dynamics of immune responses and host-pathogen interactions since my postdoctoral fellowship at Imperial College in 1991. I approach problems in immunology and epidemiology from an ecological and evolutionary viewpoint. At the within-host level, I view the immune system as a ...
Optometry: Open Access
... laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) and surface ablation (SA) techniques (PRK, LASEK and epi-LASIK). The real prevalence of infectious keratitis after refractive surgery is difficult to determine, due to its rarity. In 2010 we reported a prevalence of 72 cases in 204,586 LASIK procedures, a 0.035% ...
... laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) and surface ablation (SA) techniques (PRK, LASEK and epi-LASIK). The real prevalence of infectious keratitis after refractive surgery is difficult to determine, due to its rarity. In 2010 we reported a prevalence of 72 cases in 204,586 LASIK procedures, a 0.035% ...
Plague
... is inversely proportional to the time elapsed post-infection before therapy is started. A number of killed whole-cell vaccines have been approved for the prophylaxis of plague in those who may be exposed to the bacterium through travel to endemic areas, or as an occupational hazard. Although thought ...
... is inversely proportional to the time elapsed post-infection before therapy is started. A number of killed whole-cell vaccines have been approved for the prophylaxis of plague in those who may be exposed to the bacterium through travel to endemic areas, or as an occupational hazard. Although thought ...
Lecture 12
... Once pathogen has entered host, it is successful at evading defense mechanisms by not being immunogenic In most cases, spirochetes persist in host for extended periods, late presentation of disease appears to be due to the presence of viable organisms ...
... Once pathogen has entered host, it is successful at evading defense mechanisms by not being immunogenic In most cases, spirochetes persist in host for extended periods, late presentation of disease appears to be due to the presence of viable organisms ...
Historical Perspective of Microbiology 1. Ancient History: (pre
... using toilets and sewers dating back as far as 2800 BC. ! The first cities to use Water Pipes made of clay were in the Indus Valley of India around 2700 BC and in the palace of Knossos on Crete around 2000 BC. Metal pipes were used in Egypt as far back as 2450 BC. ! The Romans in 315 AD had public l ...
... using toilets and sewers dating back as far as 2800 BC. ! The first cities to use Water Pipes made of clay were in the Indus Valley of India around 2700 BC and in the palace of Knossos on Crete around 2000 BC. Metal pipes were used in Egypt as far back as 2450 BC. ! The Romans in 315 AD had public l ...
Multiple Contributory Factors to the Age
... to prior immunity alone should be avoided. The difficulty in resolving the separate effects of prior protection and exposure compounds the already complex problem of interpreting serological data directly as an indicator of protection. In the case of H3N2v, 3 studies have shown similar qualitative tr ...
... to prior immunity alone should be avoided. The difficulty in resolving the separate effects of prior protection and exposure compounds the already complex problem of interpreting serological data directly as an indicator of protection. In the case of H3N2v, 3 studies have shown similar qualitative tr ...
bloodborne pathogens 2016-2017 - Western Dubuque Community
... False-Anyone can be a potential carrier of HIV and the Hepatitis viruses. True- Chronic Hepatitis B is a serious disease that can result in long-term health problems, including liver damage, liver failure leading to cirrhosis, liver cancer, or even death. True- Hepatitis B virus can survive outside ...
... False-Anyone can be a potential carrier of HIV and the Hepatitis viruses. True- Chronic Hepatitis B is a serious disease that can result in long-term health problems, including liver damage, liver failure leading to cirrhosis, liver cancer, or even death. True- Hepatitis B virus can survive outside ...
snc4m quiz review
... Article: Bacteria: More Than Pathogens - Provide examples of harmful and helpful bacteria. - Differences between viruses and bacteria Handout: Pathogens - Definition of Pathogen - Scenarios: What type of pathogen caused them? - Terms: Microorganism, Parasite, Disease, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Vec ...
... Article: Bacteria: More Than Pathogens - Provide examples of harmful and helpful bacteria. - Differences between viruses and bacteria Handout: Pathogens - Definition of Pathogen - Scenarios: What type of pathogen caused them? - Terms: Microorganism, Parasite, Disease, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Vec ...
cdc facts about infectious diseases
... Adults need tetanus and diphtheria boosters repeated every 10 years. Shots are often needed for protection from infectious diseases when traveling to other countries. ...
... Adults need tetanus and diphtheria boosters repeated every 10 years. Shots are often needed for protection from infectious diseases when traveling to other countries. ...
Etiologic agents of cervicovaginitis in Turkish women
... statistically significant (p<0.001). The difference between the C. trachomatis infection rate in infertile patients and in non-infertile patients was found as not statistically significant (p>0.05). These results are similar to those of other studies.21,23 Neisseria gonorrheae is a sexually transm ...
... statistically significant (p<0.001). The difference between the C. trachomatis infection rate in infertile patients and in non-infertile patients was found as not statistically significant (p>0.05). These results are similar to those of other studies.21,23 Neisseria gonorrheae is a sexually transm ...
Hospital-acquired infection

Hospital-acquired infection (HAI) — also known as nosocomial infection — is an infection whose development is favored by a hospital environment, such as one acquired by a patient during a hospital visit or one developing among hospital staff. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated roughly 1.7 million hospital-associated infections, from all types of microorganisms, including bacteria, combined, cause or contribute to 99,000 deaths each year. In Europe, where hospital surveys have been conducted, the category of gram-negative infections are estimated to account for two-thirds of the 25,000 deaths each year. Nosocomial infections can cause severe pneumonia and infections of the urinary tract, bloodstream and other parts of the body. Many types are difficult to attack with antibiotics, and antibiotic resistance is spreading to gram-negative bacteria that can infect people outside the hospital.Hospital-acquired infections are an important category of hospital-acquired conditions. HAI is sometimes expanded as healthcare-associated infection to emphasize that infections can be correlated with health care in various settings (not just hospitals), which is also true of hospital-acquired conditions generally.