Ch.40 - Jamestown School District
... B cells provide immunity against antigens & pathogens in the body fluids - Humoral immunity T cells defend against abnormal cells & pathogens inside living cells - Cellmediated immunity ...
... B cells provide immunity against antigens & pathogens in the body fluids - Humoral immunity T cells defend against abnormal cells & pathogens inside living cells - Cellmediated immunity ...
A1984TB51600001
... cited is the fact that it was published at a time when the concept of Fc receptors was in its infancy and great interest was being shown in phenotypic differences between B cells and I cells. Subsequently, numerous groups have confirmed the 1 original observa2 tions’ although both we and others have ...
... cited is the fact that it was published at a time when the concept of Fc receptors was in its infancy and great interest was being shown in phenotypic differences between B cells and I cells. Subsequently, numerous groups have confirmed the 1 original observa2 tions’ although both we and others have ...
prevent - Model High School
... for proteins crucial for the immune system are defective. Children born with SCID have no immune system. • Gene therapy has been used to inject a good copy of the defective gene into blood cells or bone marrow cells. In several cases this has been effective, though it is still experimental. ...
... for proteins crucial for the immune system are defective. Children born with SCID have no immune system. • Gene therapy has been used to inject a good copy of the defective gene into blood cells or bone marrow cells. In several cases this has been effective, though it is still experimental. ...
system defence system defence - Pro
... to defend against disease-causing microorganisms. As your body constantly fights off the threat of unwanted guests like bacteria and germs, the immune system can become depleted. Signs such as tiredness, lethargy, recurrent colds, sore throats or chest infections and the inability to recover from th ...
... to defend against disease-causing microorganisms. As your body constantly fights off the threat of unwanted guests like bacteria and germs, the immune system can become depleted. Signs such as tiredness, lethargy, recurrent colds, sore throats or chest infections and the inability to recover from th ...
Diapositive 1
... molecule (SLAM and CD150) family expressed in cells of the immune system ; plays a role in the terminal differentiation of TFH cells and induces bidirectional stimulation of T (TFH) and B (GC) cells ...
... molecule (SLAM and CD150) family expressed in cells of the immune system ; plays a role in the terminal differentiation of TFH cells and induces bidirectional stimulation of T (TFH) and B (GC) cells ...
VL 08lecture2008
... Recognizes antigens (molecular signatures) specific for each pathogen Effective against both intra- and extracellular pathogens Two main components: Humoral immunity - Relies on Antibodies produced by B-lymphocytes - Fights pathogens outside of cells ...
... Recognizes antigens (molecular signatures) specific for each pathogen Effective against both intra- and extracellular pathogens Two main components: Humoral immunity - Relies on Antibodies produced by B-lymphocytes - Fights pathogens outside of cells ...
The Era of Immunotherapeutics: Overcoming the challenges to fulfill
... downregulates neuregulin-1 (NRG-1), increasing the chance of developing serious heart problems.(9) It turns out that the same pathways involved with progression of these cancers are also critical for normal cardiac function. Thus, it is important to balance the therapeutic benefit of an agent agains ...
... downregulates neuregulin-1 (NRG-1), increasing the chance of developing serious heart problems.(9) It turns out that the same pathways involved with progression of these cancers are also critical for normal cardiac function. Thus, it is important to balance the therapeutic benefit of an agent agains ...
CHAPTER 19 Natural Defenses Against Disease
... • plasma cells produce – IgM first – may switch to other classes of antibodies • same antigen specificity • different function – accomplished by switching constant regions ...
... • plasma cells produce – IgM first – may switch to other classes of antibodies • same antigen specificity • different function – accomplished by switching constant regions ...
Chapt07 Lecture 13ed Pt 3
... • Each B cell has a unique receptor called a BCR that binds a specific antigen. ...
... • Each B cell has a unique receptor called a BCR that binds a specific antigen. ...
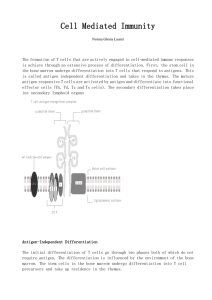
Cell Mediated Immunity
... The formation of T cells that are actively engaged in cell-mediated immune responses is achieve through an extensive process of differentiation. First, the stem cell in the bone marrow undergo differentiation into T cells that respond to antigens. This is called antigen independent differentiation a ...
... The formation of T cells that are actively engaged in cell-mediated immune responses is achieve through an extensive process of differentiation. First, the stem cell in the bone marrow undergo differentiation into T cells that respond to antigens. This is called antigen independent differentiation a ...
- Dr. Robert Fox
... (recently approved for multiple sclerosis) • It can sequester lymphocytes in lymph nodes, preventing them from moving to the central nervous system for autoimmune responses in multiple sclerosis, and was originally proposed as a anti-rejection medication indicated posttransplantation. • It has been ...
... (recently approved for multiple sclerosis) • It can sequester lymphocytes in lymph nodes, preventing them from moving to the central nervous system for autoimmune responses in multiple sclerosis, and was originally proposed as a anti-rejection medication indicated posttransplantation. • It has been ...
Immune Responses
... (a) promote adherence 2) phagocyte mobilization 3) tissue repair G) Fever 1) caused by pyrogens a) any chemical that causes an increase in body temperature b) most often released from WBC, as well as some bacteria 2) promote sequestration of iron & zinc 3) may aid interferon, inhibit microbe growth, ...
... (a) promote adherence 2) phagocyte mobilization 3) tissue repair G) Fever 1) caused by pyrogens a) any chemical that causes an increase in body temperature b) most often released from WBC, as well as some bacteria 2) promote sequestration of iron & zinc 3) may aid interferon, inhibit microbe growth, ...
Immune System
... C) After reading the subsection on inflammatory response (Page 959), explain what phagocytosis is, name two examples of cells capable of this process, and how histamines aid in this process. D) Be able to describe the general make up of the human body’s immune system. Include the structures and orga ...
... C) After reading the subsection on inflammatory response (Page 959), explain what phagocytosis is, name two examples of cells capable of this process, and how histamines aid in this process. D) Be able to describe the general make up of the human body’s immune system. Include the structures and orga ...
Circulation and gas exchange
... Lymphocytes that migrate from the bone marrow to the thymus, a gland in the upper region of the chest, develop into T cells (T for thymus). Lymphocytes that remain in the bone marrow and continue their maturation there become B cells. Mature B cells and T cells are most concentrated in lymph nodes, ...
... Lymphocytes that migrate from the bone marrow to the thymus, a gland in the upper region of the chest, develop into T cells (T for thymus). Lymphocytes that remain in the bone marrow and continue their maturation there become B cells. Mature B cells and T cells are most concentrated in lymph nodes, ...
Differences Between Acute and Chronic Inflammation
... 1. Increased blood flow 1. Infiltration of Mononuclear Phagocyting Cells a. Transient vasocontriction upon endothelial a. Macrophages injury i. Circulate as monocytes and reach site of b. Followed by released of cytokines that injury within 24 – 48 hrs and transform promotes vasodilation leads to wa ...
... 1. Increased blood flow 1. Infiltration of Mononuclear Phagocyting Cells a. Transient vasocontriction upon endothelial a. Macrophages injury i. Circulate as monocytes and reach site of b. Followed by released of cytokines that injury within 24 – 48 hrs and transform promotes vasodilation leads to wa ...
LACZIK_Pharmacology - 4 practice
... Vaccination is a good example, when not antibodies but inactivated or attenuated pathogens or purified antigens from pathogens are administered sc. Immune response depends on the immune state o the recipient, immune protection needs time to develop, but long term protection is provided (memory cells ...
... Vaccination is a good example, when not antibodies but inactivated or attenuated pathogens or purified antigens from pathogens are administered sc. Immune response depends on the immune state o the recipient, immune protection needs time to develop, but long term protection is provided (memory cells ...
The First and Second Lines of Defense Against Disease
... This sensation is temporary and only lasts until the healing is finished. ...
... This sensation is temporary and only lasts until the healing is finished. ...
CyTOF ICS
... Production of cytokines plays an important role in the immune response. Cytokines are involved in many different pathways including the induction of many anti-viral proteins by IFN gamma, the induction of T cell proliferation by IL-2 and the inhibition of viral gene expression and replication by TNF ...
... Production of cytokines plays an important role in the immune response. Cytokines are involved in many different pathways including the induction of many anti-viral proteins by IFN gamma, the induction of T cell proliferation by IL-2 and the inhibition of viral gene expression and replication by TNF ...
2016 department of medicine research day
... Adaptive immune resistance is a mechanism by which tumor cells limit host immune response via upregulation of the programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and ligation to the programmed death-1 (PD1) receptor on antigen-specific CD8 T cells. Recent studies of the PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor in nonsmall cell ...
... Adaptive immune resistance is a mechanism by which tumor cells limit host immune response via upregulation of the programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and ligation to the programmed death-1 (PD1) receptor on antigen-specific CD8 T cells. Recent studies of the PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor in nonsmall cell ...
PHA 321 - Biosciences II
... B) show induration because of an influx of sensitized T cells and macrophages C) peak at 4 to six hours after exposure to antigen D) depend on the activities of the Fc portion of antibodies E) are characterized by a wheal and flare reaction ...
... B) show induration because of an influx of sensitized T cells and macrophages C) peak at 4 to six hours after exposure to antigen D) depend on the activities of the Fc portion of antibodies E) are characterized by a wheal and flare reaction ...
Psychoneuroimmunology

Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI), also referred to as psychoendoneuroimmunology (PENI), is the study of the interaction between psychological processes and the nervous and immune systems of the human body. PNI takes an interdisciplinary approach, incorporating psychology, neuroscience, immunology, physiology, genetics, pharmacology, molecular biology, psychiatry, behavioral medicine, infectious diseases, endocrinology, and rheumatology.The main interests of PNI are the interactions between the nervous and immune systems and the relationships between mental processes and health. PNI studies, among other things, the physiological functioning of the neuroimmune system in health and disease; disorders of the neuroimmune system (autoimmune diseases; hypersensitivities; immune deficiency); and the physical, chemical and physiological characteristics of the components of the neuroimmune system in vitro, in situ, and in vivo.