lecture 1 - Rheumatic Fever and Heart Disease (2013).
... • Rheumatic fever affect the peri-arteriolar connective tissue • It is believed to be caused by antibody crossreactivity • This cross-reactivity is a Type II hypersensitivity reaction and is termed molecular mimicry ...
... • Rheumatic fever affect the peri-arteriolar connective tissue • It is believed to be caused by antibody crossreactivity • This cross-reactivity is a Type II hypersensitivity reaction and is termed molecular mimicry ...
The Suppression of Immune System Disorders by Passive
... for survival factors, Figure 1. Competition provides a stabilizing mechanism for population size: too many cells and some will not have enough access to the survival factors, too few cells and there will be an abundance of survival factors allowing proliferation of the existing population. The survi ...
... for survival factors, Figure 1. Competition provides a stabilizing mechanism for population size: too many cells and some will not have enough access to the survival factors, too few cells and there will be an abundance of survival factors allowing proliferation of the existing population. The survi ...
LYMPHOID NEOPLASMS
... of disease. Two-thirds of NHLs and virtually all cases of Hodgkin lymphoma present with nontender nodal enlargement (often greater than 2 cm) that can be localized or generalized. The remaining one-third of NHLs arise at extranodal sites (e.g., skin, stomach, or brain). In contrast, the leukemic for ...
... of disease. Two-thirds of NHLs and virtually all cases of Hodgkin lymphoma present with nontender nodal enlargement (often greater than 2 cm) that can be localized or generalized. The remaining one-third of NHLs arise at extranodal sites (e.g., skin, stomach, or brain). In contrast, the leukemic for ...
Slide 1
... • A slight increase in body temperature slows their growth and activity but speeds up your body’s defenses. ...
... • A slight increase in body temperature slows their growth and activity but speeds up your body’s defenses. ...
20 Chapter
... • A slight increase in body temperature slows their growth and activity but speeds up your body’s defenses. ...
... • A slight increase in body temperature slows their growth and activity but speeds up your body’s defenses. ...
Blood - El Camino College
... b. ________________ - have no visible cytoplasmic granules. 1) _________ (30%) - nucleus takes up most of cell; mediate _________ responses in lymphoid tissues. Types include: a) ___ cells - develop into memory cells and plasma cells that secrete _________ against antigens (esp. bacterial) b) ___ ce ...
... b. ________________ - have no visible cytoplasmic granules. 1) _________ (30%) - nucleus takes up most of cell; mediate _________ responses in lymphoid tissues. Types include: a) ___ cells - develop into memory cells and plasma cells that secrete _________ against antigens (esp. bacterial) b) ___ ce ...
Quick Review
... The body responds to a specific antigen It takes a long time for the body to find a B cell that produces the specific antigen Memory cells enable the body to respond to an antigen quicker the second time around ...
... The body responds to a specific antigen It takes a long time for the body to find a B cell that produces the specific antigen Memory cells enable the body to respond to an antigen quicker the second time around ...
The use of immune modulating drugs for the
... production and contact with effector T-cells or antigenpresenting cells is impaired.7,8 Although the precise function of B-cells in MS pathogenesis is unknown, it likely involves antigen presentation, cytokine production, and/or immunoglobulin synthesis.9 Multiple sclerosis is a disease that had no ...
... production and contact with effector T-cells or antigenpresenting cells is impaired.7,8 Although the precise function of B-cells in MS pathogenesis is unknown, it likely involves antigen presentation, cytokine production, and/or immunoglobulin synthesis.9 Multiple sclerosis is a disease that had no ...
Defense against the dark arts
... Produce all lymphocyte types from two groups 1. Group migrates to thymus » Isolated by blood–thymus barrier » Become T cells and reenter bloodstream 2. Group remains in bone to finish development » Become B cells and NK cells ...
... Produce all lymphocyte types from two groups 1. Group migrates to thymus » Isolated by blood–thymus barrier » Become T cells and reenter bloodstream 2. Group remains in bone to finish development » Become B cells and NK cells ...
Molecular Innate Immunity in Teleost Fish: Review and Future Perspectives
... and animals. It is a complex system which, in vertebrates, is composed of cellular and humoral responses. The vertebrate teleost fish, which diverged from the tetrapod lineage about 450 million years ago, has an innate immune component that shows considerable conservation with higher vertebrates par ...
... and animals. It is a complex system which, in vertebrates, is composed of cellular and humoral responses. The vertebrate teleost fish, which diverged from the tetrapod lineage about 450 million years ago, has an innate immune component that shows considerable conservation with higher vertebrates par ...
ILAR 46(2) - Laboratory Animal Boards Study Group
... immunoglobulin-like receptors by the antigen, and the surface cytokine receptors by factors produced by Th lymphocytes. Also a physical interaction between B and Th lymphocytes is required. Innate-Specific interactions: Effector Immune Defenses: The “effector phase” of the immune response is when th ...
... immunoglobulin-like receptors by the antigen, and the surface cytokine receptors by factors produced by Th lymphocytes. Also a physical interaction between B and Th lymphocytes is required. Innate-Specific interactions: Effector Immune Defenses: The “effector phase” of the immune response is when th ...
Lung inflammatory responses
... and characterized by changes to the vascular system. In addition, mobile elements such as neutrophils, eosinophils, macrophages and lymphocytes, serum components and various chemokines and cytokines play a role in both causing and controlling inflammation. Intercellular communication occurs using va ...
... and characterized by changes to the vascular system. In addition, mobile elements such as neutrophils, eosinophils, macrophages and lymphocytes, serum components and various chemokines and cytokines play a role in both causing and controlling inflammation. Intercellular communication occurs using va ...
Detecting Cytokine Release from Single T-cells
... immunospot (ELISpot) assay.6,7 FC-based analysis relies on detection of cytokines accumulated inside fixed and permeabilized cells and therefore has limited options for time-course experiments or postdetection processing of cells. ELISpot, on the other hand, can be used for detecting cytokines relea ...
... immunospot (ELISpot) assay.6,7 FC-based analysis relies on detection of cytokines accumulated inside fixed and permeabilized cells and therefore has limited options for time-course experiments or postdetection processing of cells. ELISpot, on the other hand, can be used for detecting cytokines relea ...
microbiology ch 42 [9-4
... EBV protects itself by expression antiapoptotic functions, induction of immunomodulatory pathways, and inhibition of antigen presentation by MHC molecules Clinical Syndromes Acute mononucleosis syndrome – low-grade fever, fatigue, pharyngitis, cervical lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and peripher ...
... EBV protects itself by expression antiapoptotic functions, induction of immunomodulatory pathways, and inhibition of antigen presentation by MHC molecules Clinical Syndromes Acute mononucleosis syndrome – low-grade fever, fatigue, pharyngitis, cervical lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and peripher ...
1 Bacterial Meningitis
... glyco-conjugates which mimic neuronal adhesion molecules and thus do not trigger an appropriate protective antibody response. This is particularly true for the type B capsule, which fails to elicit a protective antibody response. Host factors which predispose toward meningococcal disease include fac ...
... glyco-conjugates which mimic neuronal adhesion molecules and thus do not trigger an appropriate protective antibody response. This is particularly true for the type B capsule, which fails to elicit a protective antibody response. Host factors which predispose toward meningococcal disease include fac ...
3: Cellular Level Experiments
... membrane binding as well as permeability to calcium is altered and the subsequent transport of calcium across the membrane transfers the information signal to the interior of the cell. Because of this function, calcium is said to be a “second messenger”. Calcium acts in a multitude of ways in its ca ...
... membrane binding as well as permeability to calcium is altered and the subsequent transport of calcium across the membrane transfers the information signal to the interior of the cell. Because of this function, calcium is said to be a “second messenger”. Calcium acts in a multitude of ways in its ca ...
Potassium channel modulators for the treatment of autoimmune
... During normal immune responses white blood cells protect the body from antigens such as bacteria, viruses, toxins, cancer cells • The cellular immune system attacks infected cells with CD4 (helper) and CD8 (cytotoxic) T cells • The humoral system responds to bacteria and viruses by instigating att ...
... During normal immune responses white blood cells protect the body from antigens such as bacteria, viruses, toxins, cancer cells • The cellular immune system attacks infected cells with CD4 (helper) and CD8 (cytotoxic) T cells • The humoral system responds to bacteria and viruses by instigating att ...
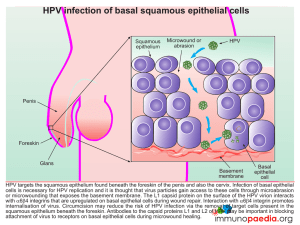
HPV infection of basal squamous epithelial cells
... HPV genetic material is replicated in the nucleus of infected cells in the form of a closed circular episome that is amplified to high copy numbers following differentiation of basal epithelial cells into keratinocytes. Importantly, the HPV E2 gene encodes a transcription factor E2 that suppresses t ...
... HPV genetic material is replicated in the nucleus of infected cells in the form of a closed circular episome that is amplified to high copy numbers following differentiation of basal epithelial cells into keratinocytes. Importantly, the HPV E2 gene encodes a transcription factor E2 that suppresses t ...
the HLA complex
... peptides from cytoplasm cannot reach class II MHC proteins, whereas peptides from endosomal compartments cannot reach class I MHC proteins foreign peptides encountered in association with class I proteins signal the cell has succumbed to a pathogen -> call for destruction foreign peptides encountere ...
... peptides from cytoplasm cannot reach class II MHC proteins, whereas peptides from endosomal compartments cannot reach class I MHC proteins foreign peptides encountered in association with class I proteins signal the cell has succumbed to a pathogen -> call for destruction foreign peptides encountere ...
Innate immune system

The innate immune system, also known as the nonspecific immune system, is an important subsystem of the overall immune system that comprises the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms. The cells of the innate system recognize and respond to pathogens in a generic way, but, unlike the adaptive immune system (which is found only in vertebrates), it does not confer long-lasting or protective immunity to the host. Innate immune systems provide immediate defense against infection, and are found in all classes of plant and animal life. They include both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.The innate immune system is an evolutionarily older defense strategy, and is the dominant immune system found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms.The major functions of the vertebrate innate immune system include: Recruiting immune cells to sites of infection, through the production of chemical factors, including specialized chemical mediators, called cytokines Activation of the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells The identification and removal of foreign substances present in organs, tissues, the blood and lymph, by specialised white blood cells Activation of the adaptive immune system through a process known as antigen presentation Acting as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents.↑ ↑ ↑