New Assay: Respiratory Virus Panel by PCR
... 3. Brandt, C. D., H. W. Kim, et al. (1969). "Infections in 18,000 infants and children in a controlled study of respiratory tract disease. I. Adenovirus pathogenicity in relation to serologic type and illness syndrome." Am J Epidemiol ...
... 3. Brandt, C. D., H. W. Kim, et al. (1969). "Infections in 18,000 infants and children in a controlled study of respiratory tract disease. I. Adenovirus pathogenicity in relation to serologic type and illness syndrome." Am J Epidemiol ...
APEC EINet - Asia-Pacific Advanced Network
... Email communication with Ministry of Health and other agencies in Southeast and East Asia. Videoconference with Hawaii’s Tripler Army Medical Center regarding possible CivilMilitary collaborations. Teleconference with “Uplift International”-NGO with longstanding ties to Indonesian medical community ...
... Email communication with Ministry of Health and other agencies in Southeast and East Asia. Videoconference with Hawaii’s Tripler Army Medical Center regarding possible CivilMilitary collaborations. Teleconference with “Uplift International”-NGO with longstanding ties to Indonesian medical community ...
Swine-origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus: An Update
... The emergence of influenza A (H1N1) 91 years ago led to a disastrous global pandemic. In the present scenario, the swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus (S-OIV) infection, a reassorted influenza virus was first reported from Mexico in March 18, 2009.1 The spread rapidly occurred to neighboring Unite ...
... The emergence of influenza A (H1N1) 91 years ago led to a disastrous global pandemic. In the present scenario, the swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus (S-OIV) infection, a reassorted influenza virus was first reported from Mexico in March 18, 2009.1 The spread rapidly occurred to neighboring Unite ...
Kineta`s Novel Broad Spectrum Antivirals Trigger Effective Natural
... reported their first deaths from a MERS outbreak this week. The results were presented and discussed in a talk by Kristin Bedard, PhD, Director and Head of Virology, at the Novel Antiviral Therapies for Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses: Bench to Beside Conference in Austin. “Kineta’s molecule ...
... reported their first deaths from a MERS outbreak this week. The results were presented and discussed in a talk by Kristin Bedard, PhD, Director and Head of Virology, at the Novel Antiviral Therapies for Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses: Bench to Beside Conference in Austin. “Kineta’s molecule ...
A Confirmed Imported Case of Human Infection
... A(H7N9) virus were recorded in Hong Kong since December 2013. Cumulatively, a total of 757 confirmed human H7N9 cases have been reported globally since March 2013, including at least 300 deaths (as of March 18, 2016). These included 735 cases in Mainland China and 22 cases exported from Mainland Chi ...
... A(H7N9) virus were recorded in Hong Kong since December 2013. Cumulatively, a total of 757 confirmed human H7N9 cases have been reported globally since March 2013, including at least 300 deaths (as of March 18, 2016). These included 735 cases in Mainland China and 22 cases exported from Mainland Chi ...
ID Webquest Instructions for Teachers
... In 1918, as World War I was coming to an end, a flu pandemic was beginning in the United States. The pandemic was caused by a shift in the H1N1 strain of the flu virus. [6] By the end of the epidemic, over 675,000 Americans and more than 50 million people worldwide were killed by the pandemic. Altho ...
... In 1918, as World War I was coming to an end, a flu pandemic was beginning in the United States. The pandemic was caused by a shift in the H1N1 strain of the flu virus. [6] By the end of the epidemic, over 675,000 Americans and more than 50 million people worldwide were killed by the pandemic. Altho ...
Reprint
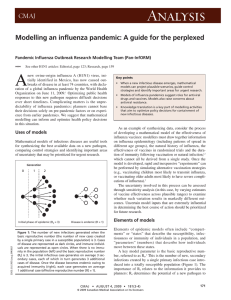
... used to estimate the final size of the epidemic with and without control measures (Figure 2). Models provide a systematic way to estimate R0, which reflects the product of duration of infectiousness, contact numbers per unit time and infectiousness per contact. As each of these quantities increases, ...
... used to estimate the final size of the epidemic with and without control measures (Figure 2). Models provide a systematic way to estimate R0, which reflects the product of duration of infectiousness, contact numbers per unit time and infectiousness per contact. As each of these quantities increases, ...
Virus - WordPress.com
... A virus is a small infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of other organisms. Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms Viruses are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Viruses are parasites. They can't multiply on their own, s ...
... A virus is a small infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of other organisms. Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms Viruses are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Viruses are parasites. They can't multiply on their own, s ...
Chicken embros
... virus, ducks studies indicated that this recombinant virus could work as a bivalent vaccine against the challenge of both lethal DEV and H5N1 virus in ducks (Liu J et al, 2011, Journal of Virology).So far, we have finished the both laboratory and field tests of this vaccine. In addition, on the basi ...
... virus, ducks studies indicated that this recombinant virus could work as a bivalent vaccine against the challenge of both lethal DEV and H5N1 virus in ducks (Liu J et al, 2011, Journal of Virology).So far, we have finished the both laboratory and field tests of this vaccine. In addition, on the basi ...
Infectious Diseases in Industry
... • Reduces the risk of infection and symptoms • Reduces the risk of spreading the flu • Reduces the risk of dangerous complications of influenza • Influenza vaccination of healthy working adults saves $47 per person annually in health care costs and sick days ...
... • Reduces the risk of infection and symptoms • Reduces the risk of spreading the flu • Reduces the risk of dangerous complications of influenza • Influenza vaccination of healthy working adults saves $47 per person annually in health care costs and sick days ...
Influenza Complications
... Influenza is a serious infectious disease that can cause severe illness in people of all ages even if they are in good health. An individual’s response to influenza is difficult to predict. Some people will experience mild symptoms, while the virus may cause serious infection or death in others. Inf ...
... Influenza is a serious infectious disease that can cause severe illness in people of all ages even if they are in good health. An individual’s response to influenza is difficult to predict. Some people will experience mild symptoms, while the virus may cause serious infection or death in others. Inf ...
Influenza
... Specimens for clinical diagnosis of Influenza are tested by the duplex real-time PCR assay for INF A & INF B Any Influenza A-positive samples are then screened further with a second H5N1-specific assay targeting the haemagglutinin gene. All positive specimens are forwarded to the QH Public Health Vi ...
... Specimens for clinical diagnosis of Influenza are tested by the duplex real-time PCR assay for INF A & INF B Any Influenza A-positive samples are then screened further with a second H5N1-specific assay targeting the haemagglutinin gene. All positive specimens are forwarded to the QH Public Health Vi ...
A List of Notifiable Scheduled Infectious Diseases (as
... Acute poliomyelitis Amoebic dysentery Anthrax Bacillary dysentery Botulism Chickenpox Chikungunya fever Cholera Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease Dengue fever Diphtheria Enterovirus 71 infection Food poisoning Haemophilus influenzae ...
... Acute poliomyelitis Amoebic dysentery Anthrax Bacillary dysentery Botulism Chickenpox Chikungunya fever Cholera Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease Dengue fever Diphtheria Enterovirus 71 infection Food poisoning Haemophilus influenzae ...
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS
... Respiratory syncytial virus is probably the most common cause of viral respiratory disease in infants RSV is an RNA virus, member of Paramyxoviridae family, genus Pneumovirus RSV replication occur initially in epithelial cells of the nasopharynx spread into the lower repiratory tract and cause bro ...
... Respiratory syncytial virus is probably the most common cause of viral respiratory disease in infants RSV is an RNA virus, member of Paramyxoviridae family, genus Pneumovirus RSV replication occur initially in epithelial cells of the nasopharynx spread into the lower repiratory tract and cause bro ...
Notes: Spread, Treatment, and Prevention of Disease
... An influenza pandemic occurs when a new subtype of virus arises. This means humans have little or no immunity to it; therefore, everyone is at risk. The virus spreads easily from person to person, such as through sneezing or coughing. As it spreads, the virus can begin to cause serious illness world ...
... An influenza pandemic occurs when a new subtype of virus arises. This means humans have little or no immunity to it; therefore, everyone is at risk. The virus spreads easily from person to person, such as through sneezing or coughing. As it spreads, the virus can begin to cause serious illness world ...
Pulmonary Lecture Preview
... Acute Bronchitis is generally viewed as a self limiting condition, due to upper airway infection ...
... Acute Bronchitis is generally viewed as a self limiting condition, due to upper airway infection ...
H1N1 Influenza – Part 1, Understanding Flu and the Current P
... Part I--Understanding Influenza and the Current Influenza Pandemic Part II--Understanding the Terminology Part III—Understanding H1N1 Influenza A Part IV—Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for EMS Part V--Decontamination of Ambulances Part VI—Influenza and EMTALA ...
... Part I--Understanding Influenza and the Current Influenza Pandemic Part II--Understanding the Terminology Part III—Understanding H1N1 Influenza A Part IV—Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for EMS Part V--Decontamination of Ambulances Part VI—Influenza and EMTALA ...
S-OIV Overview for EMS Personnel
... Part I--Understanding Influenza and the Current Influenza Pandemic Part II--Understanding the Terminology Part III—Understanding H1N1 Influenza A Part IV—Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for EMS Part V--Decontamination of Ambulances Part VI—Influenza and EMTALA ...
... Part I--Understanding Influenza and the Current Influenza Pandemic Part II--Understanding the Terminology Part III—Understanding H1N1 Influenza A Part IV—Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for EMS Part V--Decontamination of Ambulances Part VI—Influenza and EMTALA ...
Tdap for Healthcare Workers
... 40,000 deaths & 500,000 cases every year in the US One dose of PPV vaccine given at age 65 or older, OR in presence of chronic health condition ...
... 40,000 deaths & 500,000 cases every year in the US One dose of PPV vaccine given at age 65 or older, OR in presence of chronic health condition ...
Influenza
... Influenza A and B • Symptoms: – High fever, cough, myalgias, fatigue, headache, sore throat and nasal congestion ...
... Influenza A and B • Symptoms: – High fever, cough, myalgias, fatigue, headache, sore throat and nasal congestion ...
Creating the Future for CDC in the 21st Century
... Reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction Rapid diagnostic testing ...
... Reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction Rapid diagnostic testing ...
Goals
... Describe infectious diseases with pandemic potential and those of global concern Understand the potential for epidemic spread of respiratory viruses and arthropod-borne viruses ...
... Describe infectious diseases with pandemic potential and those of global concern Understand the potential for epidemic spread of respiratory viruses and arthropod-borne viruses ...
Document
... Infectious period: unknown– one day before to 7 days following illness onset – Children, especially younger children, maybe infectious up to 10 days. ...
... Infectious period: unknown– one day before to 7 days following illness onset – Children, especially younger children, maybe infectious up to 10 days. ...
modEs of tRansmIssIon REadIng
... flu continues to be a threat. Since the most recently described avian influenza is relatively novel to humans and can cause serious disease due to lack of human immunity, it has the potential to cause a pandemic if the virus becomes easily transmissible. The most recent avian influenza outbreaks hav ...
... flu continues to be a threat. Since the most recently described avian influenza is relatively novel to humans and can cause serious disease due to lack of human immunity, it has the potential to cause a pandemic if the virus becomes easily transmissible. The most recent avian influenza outbreaks hav ...
File - Ms. Pati at Green Oaks
... determined that this Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus is contagious. • At this time, it is not known how easily the virus spreads between people. ...
... determined that this Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus is contagious. • At this time, it is not known how easily the virus spreads between people. ...
Influenza

Influenza, commonly known as ""the flu"", is an infectious disease caused by the influenza virus. Symptoms can be mild to severe. The most common symptoms include: a high fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pains, headache, coughing, and feeling tired. These symptoms typically begin two days after exposure to the virus and most last less than a week. The cough, however, may last for more than two weeks. In children there may be nausea and vomiting but these are not common in adults. Nausea and vomiting occur more commonly in the unrelated infection gastroenteritis, which is sometimes inaccurately referred to as ""stomach flu"" or ""24-hour flu"". Complications of influenza may include viral pneumonia, secondary bacterial pneumonia, sinus infections, and worsening of previous health problems such as asthma or heart failure.Three types of influenza affect people. Usually, the virus is spread through the air from coughs or sneezes. This is believed to occur mostly over relatively short distances. It can also be spread by touching surfaces contaminated by the virus and then touching the mouth or eyes. A person may be infectious to others both before and during the time they are sick. The infection may be confirmed by testing the throat, sputum, or nose for the virus. A number of rapid tests are available; however, people may still have the infection if the results are negative. A type of polymerase chain reaction that detects the virus's RNA is more accurate.Frequent hand washing reduces the risk of infection because the virus is inactivated by soap. Wearing a surgical mask is also useful. Yearly vaccinations against influenza are recommended by the World Health Organization for those at high risk. The vaccine is usually effective against three or four types of influenza. It is usually well tolerated. A vaccine made for one year may not be useful in the following year, since the virus evolves rapidly. Antiviral drugs such as the neuraminidase inhibitors oseltamivir among others have been used to treat influenza. Their benefits in those who are otherwise healthy do not appear to be greater than their risks. No benefit has been found in those with other health problems.Influenza spreads around the world in a yearly outbreak, resulting in about three to five million cases of severe illness and about 250,000 to 500,000 deaths. In the Northern and Southern parts of the world outbreaks occur mainly in winter while in areas around the equator outbreaks may occur at any time of the year. Death occurs mostly in the young, the old and those with other health problems. Larger outbreaks known as pandemics are less frequent. In the 20th century three influenza pandemics occurred: Spanish influenza in 1918, Asian influenza in 1958, and Hong Kong influenza in 1968, each resulting in more than a million deaths. The World Health Organization declared an outbreak of a new type of influenza A/H1N1 to be a pandemic in June 2009. Influenza may also affect other animals, including pigs, horses and birds.