PAN Shen Quan
... • Molecular basis for bacterial pathogenesis • Protein engineering • DNA and protein delivery systems • Vectors for gene therapy and DNA vaccines As a natural genetic engineer of plants, Agrobacterium tumefaciens can deliver T-DNA into different eukaryotes, including plant, yeast, fungal and human c ...
... • Molecular basis for bacterial pathogenesis • Protein engineering • DNA and protein delivery systems • Vectors for gene therapy and DNA vaccines As a natural genetic engineer of plants, Agrobacterium tumefaciens can deliver T-DNA into different eukaryotes, including plant, yeast, fungal and human c ...
word - Mr Idea Hamster
... 3. Understand and observe postulated evolution of proteins/genes. 4. Understand and observe the interconnectedness of genetic diseases, gene alleles, proteins booboos, protein functions, amino acid sequences, and nucleotide sequences. 5. Study an amalgamation of disease/gene/protein using the NCBI w ...
... 3. Understand and observe postulated evolution of proteins/genes. 4. Understand and observe the interconnectedness of genetic diseases, gene alleles, proteins booboos, protein functions, amino acid sequences, and nucleotide sequences. 5. Study an amalgamation of disease/gene/protein using the NCBI w ...
Receptor Protein
... Receptor proteins are proteins imbedded in the cell membrane (Check out the picture below). These proteins span across the membrane, so part of it is sticking out of the cell and part of it is inside of the cell. These receptor proteins, like the transport proteins we learned about earlier, are spec ...
... Receptor proteins are proteins imbedded in the cell membrane (Check out the picture below). These proteins span across the membrane, so part of it is sticking out of the cell and part of it is inside of the cell. These receptor proteins, like the transport proteins we learned about earlier, are spec ...
PATHOLOGY NEW YORK UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
... Yet, not everyone expected this family of orphan proteins to wield power over so many important cellular processes. Pagano's research group has revealed that F-box proteins help control cell proliferation, DNA-damage checkpoints, chromosomal stability, ribosomal biogenesis, protein synthesis, apopto ...
... Yet, not everyone expected this family of orphan proteins to wield power over so many important cellular processes. Pagano's research group has revealed that F-box proteins help control cell proliferation, DNA-damage checkpoints, chromosomal stability, ribosomal biogenesis, protein synthesis, apopto ...
Leukaemia Section t(5;12)(q33;q24) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... and GIT2 belong to the family of ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating proteins (ARF-GAP). GIT1 and GIT2 form homodimers and heterodimers which bind in oligomeric complex to the p21-activated kinase-interacting exchange factor proteins ARHGEF6 and ARHGEF7, to regulate the small GTP-binding prote ...
... and GIT2 belong to the family of ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating proteins (ARF-GAP). GIT1 and GIT2 form homodimers and heterodimers which bind in oligomeric complex to the p21-activated kinase-interacting exchange factor proteins ARHGEF6 and ARHGEF7, to regulate the small GTP-binding prote ...
Title
... [email protected] Protein conformational diseases such as Huntington’s Disease and spinocerebellar ataxias (SCA) are characterised by mutations of wild type genes leading to the expression of proteins that have expanded poly-glutamine domains. The expression of poly-Q mutant proteins res ...
... [email protected] Protein conformational diseases such as Huntington’s Disease and spinocerebellar ataxias (SCA) are characterised by mutations of wild type genes leading to the expression of proteins that have expanded poly-glutamine domains. The expression of poly-Q mutant proteins res ...
中文題目:
... sequences of these promoters are various, they all contain almost the same cis-acting elements, such as W-box and GCC-box. Therefore, the expression pattern of each gene member may be quite similar. Our previous data demonstrated that a sporamin promoter : SP1 (PROSPOA) is wound-induced in the trans ...
... sequences of these promoters are various, they all contain almost the same cis-acting elements, such as W-box and GCC-box. Therefore, the expression pattern of each gene member may be quite similar. Our previous data demonstrated that a sporamin promoter : SP1 (PROSPOA) is wound-induced in the trans ...
Molecules of life 2.4 - Madison County Schools
... a. A variety of bonds (covalent, ionic, hydrogen) between distant amino acids causes large folds in the protein. These help provide stability to the folded protein. 4. Quaternary Structure (4’ ) “Quarter” means “fourth” a. This is when two or more polypeptides are woven together. b. Hemoglobin (Red ...
... a. A variety of bonds (covalent, ionic, hydrogen) between distant amino acids causes large folds in the protein. These help provide stability to the folded protein. 4. Quaternary Structure (4’ ) “Quarter” means “fourth” a. This is when two or more polypeptides are woven together. b. Hemoglobin (Red ...
Campbell Greg fruit fly wing genetics Sci Proj 2010
... Dp protein is very large and is found on the outside of cells Do dp mutants change the shape of nw mutant wings like the Df? ...
... Dp protein is very large and is found on the outside of cells Do dp mutants change the shape of nw mutant wings like the Df? ...
Nutrition - Eden High School
... - raise LDL and lower HDL cholesterol levels.! found in: commercially packaged foods, commercially fried food- French Fries, ...
... - raise LDL and lower HDL cholesterol levels.! found in: commercially packaged foods, commercially fried food- French Fries, ...
biochemical composition presentation
... and traits that are best fit for the environment are passed on. ...
... and traits that are best fit for the environment are passed on. ...
The American Journal of Human Genetics
... exon in spliced transcripts could be modulated by regulation of the expression levels of H3-K36 methyltransferases. Additional experiments by Luco et al. support a model in which the chromatin binding protein MRG15 binds to H3-K36me3, and this in turn recruits the splice regulator PTB to FGFR2. The ...
... exon in spliced transcripts could be modulated by regulation of the expression levels of H3-K36 methyltransferases. Additional experiments by Luco et al. support a model in which the chromatin binding protein MRG15 binds to H3-K36me3, and this in turn recruits the splice regulator PTB to FGFR2. The ...
Macromolecules Quiz 1
... created by Brandon Dunson [email protected] Fall 2010 for future students of Dr Orr’s Bio1406 ...
... created by Brandon Dunson [email protected] Fall 2010 for future students of Dr Orr’s Bio1406 ...
Virtual Issue: Structure Characterization of Biomolecules
... have complex but rather well-defined lowest-energy structures, it became increasingly apparent in recent years that many of them have not. Especially for proteins, but also for RNA, it has been shown that they can instead feature a number of significantly different yet similarly stable structures, o ...
... have complex but rather well-defined lowest-energy structures, it became increasingly apparent in recent years that many of them have not. Especially for proteins, but also for RNA, it has been shown that they can instead feature a number of significantly different yet similarly stable structures, o ...
Slide 1
... flank two selectable marker genes is inserted into the chloroplast genome through homologous recombination, thereby transforming the native plastome into a TRANSPLASTOME (a). One of the selectable genes (aadA) is designed for exclusive expression in the chloroplast and incorporation of this marker c ...
... flank two selectable marker genes is inserted into the chloroplast genome through homologous recombination, thereby transforming the native plastome into a TRANSPLASTOME (a). One of the selectable genes (aadA) is designed for exclusive expression in the chloroplast and incorporation of this marker c ...
The Stochastic Nature of Gene Expression Revealed at the Single-Molecule Level
... amplification. a) The enzyme β‑gal cleaves FDG to create fluorescein and two galactose molecules. b) Schematic diagram of a single-cell, single-chamber apparatus for β‑gal measurements. Each cell was treated withβ‑lactam antibiotics to increase the permeability of its membrane. This treatment enable ...
... amplification. a) The enzyme β‑gal cleaves FDG to create fluorescein and two galactose molecules. b) Schematic diagram of a single-cell, single-chamber apparatus for β‑gal measurements. Each cell was treated withβ‑lactam antibiotics to increase the permeability of its membrane. This treatment enable ...
Team Publications
... Invasion across tissue boundaries by metastatic tumor cells depends on the proteolytic degradation of the extracellular matrix, initiated by the formation of invadopodia, actindriven membrane protrusions with matrix-degradative activity. Yet, mechanisms underlying invadopodia formation remain largel ...
... Invasion across tissue boundaries by metastatic tumor cells depends on the proteolytic degradation of the extracellular matrix, initiated by the formation of invadopodia, actindriven membrane protrusions with matrix-degradative activity. Yet, mechanisms underlying invadopodia formation remain largel ...
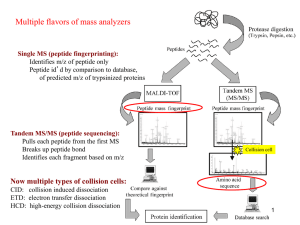
Proteomics2_2012
... Often focus on proteins identified by at least 2 different PSMs (or proteins with single PSMs of very high posterior probability) ...
... Often focus on proteins identified by at least 2 different PSMs (or proteins with single PSMs of very high posterior probability) ...
Gene Section NSD1 (Nuclear receptor-binding, su(var), enhancer-of-zeste and trithorax domain-containing protein 1
... (NR)-interaction domains (NID-L, NID+L). Human NSD1 shows 86% identity to the murine Nsd1 at the nucleotide level and 83% at the amino acid level, retaining the nuclear interaction domains (NID) as well as the SET/SAC and PHD finger domains. ...
... (NR)-interaction domains (NID-L, NID+L). Human NSD1 shows 86% identity to the murine Nsd1 at the nucleotide level and 83% at the amino acid level, retaining the nuclear interaction domains (NID) as well as the SET/SAC and PHD finger domains. ...
Fig. 4.3 - glenbrook s hs
... allows some substances to pass through, but blocks the passgae of other substances • Membranes enclose and maintain the specific chemical environment • Every membrane carries out its specific functions ...
... allows some substances to pass through, but blocks the passgae of other substances • Membranes enclose and maintain the specific chemical environment • Every membrane carries out its specific functions ...
Chapter 2 - Regulation of protein activities
... subunit. There is substantial diversity in these individual subunits, with 16 different α, 5 β and 11 γ isoforms present in mammalian tissues. Thus, via various different combinations, it is possible to generate hundreds of different types of G-proteins. G-proteins exist in either an inactive or an ...
... subunit. There is substantial diversity in these individual subunits, with 16 different α, 5 β and 11 γ isoforms present in mammalian tissues. Thus, via various different combinations, it is possible to generate hundreds of different types of G-proteins. G-proteins exist in either an inactive or an ...
Chapter 16
... in length. siRNA plays many roles, but it is most notable in the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, where it interferes with the expression of specific genes with complementary nucleotide sequences. siRNA functions by causing mRNA to be broken down after transcription, resulting in no translation. ...
... in length. siRNA plays many roles, but it is most notable in the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, where it interferes with the expression of specific genes with complementary nucleotide sequences. siRNA functions by causing mRNA to be broken down after transcription, resulting in no translation. ...
DNA sequence of Exenatide to be prepared using Phosphoramidite
... Size Exclusion Chromatography (Gel Filtration Chromatography) – The fusion protein must be applied onto a gel filtration column which allows for fractionation of proteins based on their size. Larger proteins travel faster in the column since smaller proteins get trapped in porous beads and are ther ...
... Size Exclusion Chromatography (Gel Filtration Chromatography) – The fusion protein must be applied onto a gel filtration column which allows for fractionation of proteins based on their size. Larger proteins travel faster in the column since smaller proteins get trapped in porous beads and are ther ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.