Hormonal Control of Glucose Metabolism
... humans, plasma glucose concentrations throughout a 24-hour period average 90 mg/ dl, with maximum values 60-90 minutes after meals, usually not exceeding 140 mg/ dl, and values during a moderate fast or exercise usually remaining above 50 mg/dl. This relative stability contrasts with the situation f ...
... humans, plasma glucose concentrations throughout a 24-hour period average 90 mg/ dl, with maximum values 60-90 minutes after meals, usually not exceeding 140 mg/ dl, and values during a moderate fast or exercise usually remaining above 50 mg/dl. This relative stability contrasts with the situation f ...
Fatty liver index and mortality: The cremona study in the 15th year of
... inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, markers of subclinical cardiovascular risk, and a higher prevalence of clinically manifesting CVD.6 Some studies have also reported a higher incidence of major outcomes,7-10 such as nonfatal CVD events,7 deaths due to CVD,8,9 revascularization procedures,9 and a ...
... inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, markers of subclinical cardiovascular risk, and a higher prevalence of clinically manifesting CVD.6 Some studies have also reported a higher incidence of major outcomes,7-10 such as nonfatal CVD events,7 deaths due to CVD,8,9 revascularization procedures,9 and a ...
Carbohydrate Counting - Clinical Diabetes
... greater flexibility this management approach provides in controlling blood glucose. This is an issue that should be raised with patients before they begin ...
... greater flexibility this management approach provides in controlling blood glucose. This is an issue that should be raised with patients before they begin ...
Exploring the world mythology of diabetes
... A link also exists in the mythology between insulin and death. It is believed that insulin is an addictive narcotic, and that once a person starts taking insulin it becomes impossible for them to stop. However, insulin is not addictive, nor is it a narcotic. Insulin is a hormone which occurs natural ...
... A link also exists in the mythology between insulin and death. It is believed that insulin is an addictive narcotic, and that once a person starts taking insulin it becomes impossible for them to stop. However, insulin is not addictive, nor is it a narcotic. Insulin is a hormone which occurs natural ...
glucose
... glucose into cells and storage as glycogen in the liver and muscles. Insulin also s8mulates the conversion of excess glucose into fat for storage. ...
... glucose into cells and storage as glycogen in the liver and muscles. Insulin also s8mulates the conversion of excess glucose into fat for storage. ...
Mutations in the Insulin Gene Can Cause MODY and Autoantibody
... MODY criteria, while 30 were categorized as “suspected MODY.” None of the probands had mutations in HNF1A (14). Moreover, 57 of the probands had a phenotype clinically evaluated as MODY2-like. GCK mutations had therefore been excluded in them. Standard oral glucose tolerance testing was performed, a ...
... MODY criteria, while 30 were categorized as “suspected MODY.” None of the probands had mutations in HNF1A (14). Moreover, 57 of the probands had a phenotype clinically evaluated as MODY2-like. GCK mutations had therefore been excluded in them. Standard oral glucose tolerance testing was performed, a ...
A review on antidiabetic action of Asanadi gana
... methanol extract showed more significant antidiabetic activity as compared to aqueous extract.11 The possible mechanism by which Ougeinia oojeinensis brings about its hypoglycemic action in diabetic rat may be by potentiating the insulin effect of plasma by increasing either the pancreatic secretion ...
... methanol extract showed more significant antidiabetic activity as compared to aqueous extract.11 The possible mechanism by which Ougeinia oojeinensis brings about its hypoglycemic action in diabetic rat may be by potentiating the insulin effect of plasma by increasing either the pancreatic secretion ...
METABOLIC AND ENDOCRINE ADAPTATIONS TO HEAT STRESS
... confounding factors result from differentiated feed intakes, showed that HS increased circulating insulin and decreased plasma non-esterified fatty acid (NEFA) in lactating cow, the opposite responses typical of PF cohorts. Therefore, the present studies were performed in order to elucidate the mech ...
... confounding factors result from differentiated feed intakes, showed that HS increased circulating insulin and decreased plasma non-esterified fatty acid (NEFA) in lactating cow, the opposite responses typical of PF cohorts. Therefore, the present studies were performed in order to elucidate the mech ...
Full-Text PDF
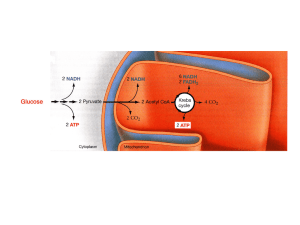
... of G3P is glucose via glycolysis, since the activity of glycerokinase (GK), the enzyme that transforms glycerol into G3P, is low. This process is stimulated by insulin that promotes the uptake of glucose into the cell but also the transformation of dihydroxyacetone-3P (DHAP) into G3P by glycerophosp ...
... of G3P is glucose via glycolysis, since the activity of glycerokinase (GK), the enzyme that transforms glycerol into G3P, is low. This process is stimulated by insulin that promotes the uptake of glucose into the cell but also the transformation of dihydroxyacetone-3P (DHAP) into G3P by glycerophosp ...
The Perfect World for Diabetes Educators Your patients
... Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Effect of intensive diabetes treatment on the development and progression of long-term complications in adolescents with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. The Journal of ...
... Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Effect of intensive diabetes treatment on the development and progression of long-term complications in adolescents with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. The Journal of ...
The Perfect World for Diabetes Educators Your patients
... Table 2—Criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes ...
... Table 2—Criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... which stimulates glycogen synthesis. – This is accomplished through a complex highly regulated signal transduction pathway. • Remember: Glycogen metabolism in liver regulates blood glucose levels. ...
... which stimulates glycogen synthesis. – This is accomplished through a complex highly regulated signal transduction pathway. • Remember: Glycogen metabolism in liver regulates blood glucose levels. ...
Carbohydrate Storage and Synthesis in Liver and Muscle: Glycogen
... Carbohydrate Metabolism Signal Transduction Regulation Mechanism 1. Glucagon binds hepatic membrane receptor: activates cascade reactions. 2. G‐protein‐GDP in resting state: releases GDP, ‐ subunit binds GTP. 3. G‐protein‐GTP: conformation change, releases ‐ ...
... Carbohydrate Metabolism Signal Transduction Regulation Mechanism 1. Glucagon binds hepatic membrane receptor: activates cascade reactions. 2. G‐protein‐GDP in resting state: releases GDP, ‐ subunit binds GTP. 3. G‐protein‐GTP: conformation change, releases ‐ ...
Review of Diabetes and Diabetic Retinopathy
... normally. Additionally, the body may not respond properly to the insulin being produced and therefore glucose cannot be taken up efficiently by the cells of the body. The reasons for this insulin resistance are not always clear. ...
... normally. Additionally, the body may not respond properly to the insulin being produced and therefore glucose cannot be taken up efficiently by the cells of the body. The reasons for this insulin resistance are not always clear. ...
Management of the Athlete With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
... guidelines for avoiding exercise during periods of hyperglycemia (Appendix 3). 8. Athletes with type 1 diabetes who experience hyperglycemia during short-term, intense, and stressful periods of exercise should consult with their physicians concerning an increased basal rate or the use of small insul ...
... guidelines for avoiding exercise during periods of hyperglycemia (Appendix 3). 8. Athletes with type 1 diabetes who experience hyperglycemia during short-term, intense, and stressful periods of exercise should consult with their physicians concerning an increased basal rate or the use of small insul ...
Branched-chain amino acids improve glucose
... Preparation of plasma and intracellular membranes from skeletal muscle tissue. Plasma membranes from stock samples of soleus and gastrocnemius muscles (6 g weight) of several CCl4 rats, obtained 30 min after compulsory oral administration of 1.5 g/kg of each BCAA (leucine, isoleucine, valine) or BCA ...
... Preparation of plasma and intracellular membranes from skeletal muscle tissue. Plasma membranes from stock samples of soleus and gastrocnemius muscles (6 g weight) of several CCl4 rats, obtained 30 min after compulsory oral administration of 1.5 g/kg of each BCAA (leucine, isoleucine, valine) or BCA ...
Excess portal venous long-chain fatty acids induce syndrome X via
... is associated with a higher incidence of the symptoms of syndrome X than is lower body obesity (4, 22, 32, 49). This is primarily related to the amount of visceral fat rather than to the amount of subcutaneous fat (2–4). Visceral adipose tissue has metabolic characteristics that are unique in compar ...
... is associated with a higher incidence of the symptoms of syndrome X than is lower body obesity (4, 22, 32, 49). This is primarily related to the amount of visceral fat rather than to the amount of subcutaneous fat (2–4). Visceral adipose tissue has metabolic characteristics that are unique in compar ...
Diabetes Superfoods - CCG of South Florida, LLC
... 1. Eat lots of vegetables and fruits. Preferably, those which contain less sugar. 2. Eat non-starchy vegetables such as spinach, carrots, broccoli or green beans with meals. 3. Choose whole grain foods over processed grain products. Try brown rice with your stir fry or whole wheat spaghetti with you ...
... 1. Eat lots of vegetables and fruits. Preferably, those which contain less sugar. 2. Eat non-starchy vegetables such as spinach, carrots, broccoli or green beans with meals. 3. Choose whole grain foods over processed grain products. Try brown rice with your stir fry or whole wheat spaghetti with you ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... Glycogenin initiates glycogen synthesis. • Glycogenin is an enzyme that catalyzes attachment of a glucose molecule to one of its own tyrosine residues. • Glycogenin is a dimer, and evidence indicates that the 2 copies of the enzyme glucosylate one another. ...
... Glycogenin initiates glycogen synthesis. • Glycogenin is an enzyme that catalyzes attachment of a glucose molecule to one of its own tyrosine residues. • Glycogenin is a dimer, and evidence indicates that the 2 copies of the enzyme glucosylate one another. ...
Diabetes in the Work Place - Wilmington Regional Safety and Health
... progression, so monitoring with dilated eye exams, urine tests, and foot exams is essential. Because the risk of cardiovascular disease is increased in diabetes and prediabetes, blood pressure and lipid management, along with smoking cessation, are especially important. By working together, people w ...
... progression, so monitoring with dilated eye exams, urine tests, and foot exams is essential. Because the risk of cardiovascular disease is increased in diabetes and prediabetes, blood pressure and lipid management, along with smoking cessation, are especially important. By working together, people w ...
PowerPoint slides - North Dakota Diabetes Control Program
... Gestational Diabetes-Medications • Patients who do not meet metabolic goals within one week or show signs of excessive fetal growth • Insulin has been the usual first choice • Sulfonylureas (glyburide) may be used in select patients • Other diabetes medications not recommended in GDM Summary and Re ...
... Gestational Diabetes-Medications • Patients who do not meet metabolic goals within one week or show signs of excessive fetal growth • Insulin has been the usual first choice • Sulfonylureas (glyburide) may be used in select patients • Other diabetes medications not recommended in GDM Summary and Re ...
Gymnema sylvestre – A Key for Diabetes Management
... will come after 6 to 12 months of continuous use. It is also prescribed in tablet form; in this case 8 to 12 g per day of leaf equivalent is recommended. 8.2. Pediatric dose: In this case, there is insufficient evidence about its uses for pediatric population, so it cannot be recommended for them [3 ...
... will come after 6 to 12 months of continuous use. It is also prescribed in tablet form; in this case 8 to 12 g per day of leaf equivalent is recommended. 8.2. Pediatric dose: In this case, there is insufficient evidence about its uses for pediatric population, so it cannot be recommended for them [3 ...
Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion
... consistent with equipotent insulinotropic effects of the two peptides [39]. Both VIP and PACAP stimulate insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner accompanied by increased action of adenylate cyclase with increased formation of cAMP [47, 48]. The latter also has other signalling actions in ins ...
... consistent with equipotent insulinotropic effects of the two peptides [39]. Both VIP and PACAP stimulate insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner accompanied by increased action of adenylate cyclase with increased formation of cAMP [47, 48]. The latter also has other signalling actions in ins ...
Insulin-Dependent Diabetes
... beta cells in the pancreas and destroys them. The pancreas then produces little or no insulin. Someone with IDDM needs daily injections of insulin to live. At present, scientists do not know exactly what causes the body's immune system to attack the beta cells, but they believe that both genetic fac ...
... beta cells in the pancreas and destroys them. The pancreas then produces little or no insulin. Someone with IDDM needs daily injections of insulin to live. At present, scientists do not know exactly what causes the body's immune system to attack the beta cells, but they believe that both genetic fac ...
Dietary Branched-chain Amino Acids Suppress the Expression of
... Amino acids (AA) have many physiological functions.1–7) Recent studies have shown that some AA, especially branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), directly promote protein synthesis in pancreatic B cells2–4) and muscles5–7) by activation the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and also stimulate secreti ...
... Amino acids (AA) have many physiological functions.1–7) Recent studies have shown that some AA, especially branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), directly promote protein synthesis in pancreatic B cells2–4) and muscles5–7) by activation the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and also stimulate secreti ...