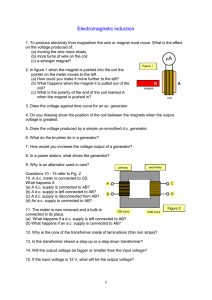
Electromagnetic induction
... 16. If you use a step-up transformer, how does the current in the secondary compare with the current in the primary? 17. If you wanted to repeat the nail melting experiment and your transformer had 600 turns on the primary, suggest how many turns there might be on the secondary. 18. Using the same ...
... 16. If you use a step-up transformer, how does the current in the secondary compare with the current in the primary? 17. If you wanted to repeat the nail melting experiment and your transformer had 600 turns on the primary, suggest how many turns there might be on the secondary. 18. Using the same ...
Electrical circuits wyklad 6
... Transformers On the mutual inductance bases the transformer operation. The transformer is constructed of two coils, the flux generated in one of the coils induced voltage across the second coil. The source coil is called primary coil and the coil to which the load is applied is called secondary. ...
... Transformers On the mutual inductance bases the transformer operation. The transformer is constructed of two coils, the flux generated in one of the coils induced voltage across the second coil. The source coil is called primary coil and the coil to which the load is applied is called secondary. ...
SPH3U Physics 11 Magnetism Quiz 2 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE
... many turns should be present in the coil to provide a maximum induced ...
... many turns should be present in the coil to provide a maximum induced ...
Chapter 6 - Topic 11 - Electromagnetic induction – AHL.
... Essential idea: Generation and transmission of alternating current (ac) electricity has transformed the world. 11.2 – Power generation and transmission Nature of science 3.5 Bias: In the late 19th century Edison was a proponent of direct current electrical energy transmission while Westinghouse and ...
... Essential idea: Generation and transmission of alternating current (ac) electricity has transformed the world. 11.2 – Power generation and transmission Nature of science 3.5 Bias: In the late 19th century Edison was a proponent of direct current electrical energy transmission while Westinghouse and ...
Generators and Transformers
... The good news is you are going on a trip to France. The bad news is that in France the outlets have 240 volts. You remember from Phy1152 that you need a transformer, so you wrap 100 turns around the primary. How many turns should you wrap around the secondary if you need 120 volts ...
... The good news is you are going on a trip to France. The bad news is that in France the outlets have 240 volts. You remember from Phy1152 that you need a transformer, so you wrap 100 turns around the primary. How many turns should you wrap around the secondary if you need 120 volts ...
Electric Power Distribution
... The Power Distribution Process 1. A generator at a power station produces AC electricity at V = 25,000 volts, flowing at 8,000 A. 2. A step-up transformer raises V 16x to 400,000 volts (decreases current by 16x to 500 A) ...
... The Power Distribution Process 1. A generator at a power station produces AC electricity at V = 25,000 volts, flowing at 8,000 A. 2. A step-up transformer raises V 16x to 400,000 volts (decreases current by 16x to 500 A) ...
Transformers - Purdue Physics
... second coil The coils are connected indirectly through the magnetic flux The effect is called mutual inductance Section 21.4 ...
... second coil The coils are connected indirectly through the magnetic flux The effect is called mutual inductance Section 21.4 ...
Transcutaneous Energy Transfer System for Powering Implantable
... High power implantable biomedical devices such as cardiac assist devices and artificial heart pumps require electrical energy for operation. Presently this energy is provided by percutaneous leads from the implant to an external power supply [1]. This method of power delivery has the potential risk ...
... High power implantable biomedical devices such as cardiac assist devices and artificial heart pumps require electrical energy for operation. Presently this energy is provided by percutaneous leads from the implant to an external power supply [1]. This method of power delivery has the potential risk ...
Resonant inductive coupling
Resonant inductive coupling or electrodynamic induction is the near field wireless transmission of electrical energy between two magnetically coupled coils that are part of resonant circuits tuned to resonate at the same frequency. This process occurs in a resonant transformer, an electrical component which consists of two high Q coils wound on the same core with capacitors connected across the windings to make two coupled LC circuits. Resonant transformers are widely used in radio circuits as bandpass filters, and in switching power supplies. Resonant inductive coupling is also being used in wireless power systems. Here the two LC circuits are in different devices; a transmitter coil in one device transmits electric power across an intervening space to a resonant receiver coil in another device. This technology is being developed for powering and charging portable devices such as cellphones and tablet computers at a distance, without being tethered to an outlet.Resonant transfer works by making a coil ring with an oscillating current. This generates an oscillating magnetic field. Because the coil is highly resonant, any energy placed in the coil dies away relatively slowly over very many cycles; but if a second coil is brought near it, the coil can pick up most of the energy before it is lost, even if it is some distance away. The fields used are predominately non-radiative, near fields (sometimes called evanescent waves), as all hardware is kept well within the 1/4 wavelength distance they radiate little energy from the transmitter to infinity.One of the applications of the resonant transformer is for the CCFL inverter. Another application of the resonant transformer is to couple between stages of a superheterodyne receiver, where the selectivity of the receiver is provided by tuned transformers in the intermediate-frequency amplifiers. The Tesla coil is a resonant transformer circuit used to generate very high voltages, and is able to provide much higher current than high voltage electrostatic machines such as the Van de Graaff generator. Resonant energy transfer is the operating principle behind proposed short range (up to 2 metre) wireless electricity systems such as WiTricity or Rezence and systems that have already been deployed, such as Qi power transfer, passive RFID tags and contactless smart cards.