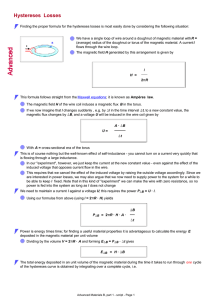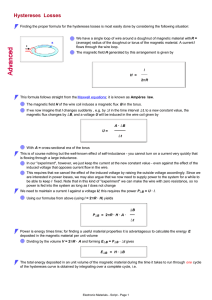
16.202: Magnetically Coupled Circuits: Mutual Inductance
... that consists of two components φ11 : Links only L1 φ12 : Links both coils. φ1 = φ11 + φ12 ...
... that consists of two components φ11 : Links only L1 φ12 : Links both coils. φ1 = φ11 + φ12 ...
Transformers
... friction causes the wire to get hot. The more current passing through the wire the hotter it gets. • A transformer that has ‘stepped up’ the voltage will also have ‘stepped down’ the current. ...
... friction causes the wire to get hot. The more current passing through the wire the hotter it gets. • A transformer that has ‘stepped up’ the voltage will also have ‘stepped down’ the current. ...
what is alternating current (ac)?
... do so with stepped-up voltages and stepped-down currents (smaller-diameter wire with less resistive power losses), then step the voltage back down and the current back up for industry, business, or consumer use use. ...
... do so with stepped-up voltages and stepped-down currents (smaller-diameter wire with less resistive power losses), then step the voltage back down and the current back up for industry, business, or consumer use use. ...
PPT - LSU Physics
... Transforming DC power from one voltage to another was difficult and expensive due to the need for a large spinning rotary converter or motorgenerator set, whereas with AC the voltage changes can be done with simple and efficient transformer coils that have no moving parts and require no maintenance. ...
... Transforming DC power from one voltage to another was difficult and expensive due to the need for a large spinning rotary converter or motorgenerator set, whereas with AC the voltage changes can be done with simple and efficient transformer coils that have no moving parts and require no maintenance. ...
How could we CHANGE the flux over a period of time?
... Faraday learned that if you change any part of the flux over time you could induce a current in a conductor and thus create a source of EMF (voltage, potential difference). Since we are dealing with time here were a talking about the RATE of CHANGE of FLUX, which is called Faraday’s Law. ...
... Faraday learned that if you change any part of the flux over time you could induce a current in a conductor and thus create a source of EMF (voltage, potential difference). Since we are dealing with time here were a talking about the RATE of CHANGE of FLUX, which is called Faraday’s Law. ...
Force, Energy & Communication
... The input voltage is lower than the output voltage. e.g. transformers used to convert USA voltage to UK voltage ...
... The input voltage is lower than the output voltage. e.g. transformers used to convert USA voltage to UK voltage ...
The Rules of Electromagnetism
... Some main electric motor types 1. The d.c. motor Basically simple .. the magnetic field is supplied either by a permanent magnet (small motors) or by a current-carrying coil as above. The rotating assembly (known as the Armature) is supplied with current via the Commutator and the Brushes which mak ...
... Some main electric motor types 1. The d.c. motor Basically simple .. the magnetic field is supplied either by a permanent magnet (small motors) or by a current-carrying coil as above. The rotating assembly (known as the Armature) is supplied with current via the Commutator and the Brushes which mak ...
Transformers - Purdue Physics
... The string passes near a pickup coil wound around a permanent magnet As the string vibrates, it produces a changing magnetic flux The resulting emf is sent to an amplifier and the ...
... The string passes near a pickup coil wound around a permanent magnet As the string vibrates, it produces a changing magnetic flux The resulting emf is sent to an amplifier and the ...
Transformers Electrical transformers are used to transform voltage or
... capacitor. The diode allows current to flow in one direction only so the bottom of the sine wave voltage function is chopped off. A diode is like a one-way valve. The solid line of the current versus time graph at left would be the output of the transformer with only a diode (no capacitor). The capa ...
... capacitor. The diode allows current to flow in one direction only so the bottom of the sine wave voltage function is chopped off. A diode is like a one-way valve. The solid line of the current versus time graph at left would be the output of the transformer with only a diode (no capacitor). The capa ...
Resonant inductive coupling
Resonant inductive coupling or electrodynamic induction is the near field wireless transmission of electrical energy between two magnetically coupled coils that are part of resonant circuits tuned to resonate at the same frequency. This process occurs in a resonant transformer, an electrical component which consists of two high Q coils wound on the same core with capacitors connected across the windings to make two coupled LC circuits. Resonant transformers are widely used in radio circuits as bandpass filters, and in switching power supplies. Resonant inductive coupling is also being used in wireless power systems. Here the two LC circuits are in different devices; a transmitter coil in one device transmits electric power across an intervening space to a resonant receiver coil in another device. This technology is being developed for powering and charging portable devices such as cellphones and tablet computers at a distance, without being tethered to an outlet.Resonant transfer works by making a coil ring with an oscillating current. This generates an oscillating magnetic field. Because the coil is highly resonant, any energy placed in the coil dies away relatively slowly over very many cycles; but if a second coil is brought near it, the coil can pick up most of the energy before it is lost, even if it is some distance away. The fields used are predominately non-radiative, near fields (sometimes called evanescent waves), as all hardware is kept well within the 1/4 wavelength distance they radiate little energy from the transmitter to infinity.One of the applications of the resonant transformer is for the CCFL inverter. Another application of the resonant transformer is to couple between stages of a superheterodyne receiver, where the selectivity of the receiver is provided by tuned transformers in the intermediate-frequency amplifiers. The Tesla coil is a resonant transformer circuit used to generate very high voltages, and is able to provide much higher current than high voltage electrostatic machines such as the Van de Graaff generator. Resonant energy transfer is the operating principle behind proposed short range (up to 2 metre) wireless electricity systems such as WiTricity or Rezence and systems that have already been deployed, such as Qi power transfer, passive RFID tags and contactless smart cards.