Optical Properties of Materials Optical Properties of Materials
... (1) Rubies are red because of the absorption of light by Cr3+ ions. The color of emeralds also has the same origin in absorption of light light by Cr3+ ions. Explain whether the crystal field experienced by Cr3+ is less in emerald or in ruby. (2) How do the host lattices influence the energy level s ...
... (1) Rubies are red because of the absorption of light by Cr3+ ions. The color of emeralds also has the same origin in absorption of light light by Cr3+ ions. Explain whether the crystal field experienced by Cr3+ is less in emerald or in ruby. (2) How do the host lattices influence the energy level s ...
Light and Color
... A Photon is a discrete packet of energy. The visible spectrum is the range of wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation which stimulate the human retina (4 x 10-7 m < λ < 7.5 x 10-7 m). White light is a combination of all colors of the visible spectrum, while black is the absence of all colors. White ...
... A Photon is a discrete packet of energy. The visible spectrum is the range of wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation which stimulate the human retina (4 x 10-7 m < λ < 7.5 x 10-7 m). White light is a combination of all colors of the visible spectrum, while black is the absence of all colors. White ...
chapter 3 – sensation and perception
... 2. Switching in 3. Some go to the centers – 4. Others throught the reticular 5. Most of the auditory sections in the 6. 4 levels of D. Theories of Hearing 1. Place Theory – Helmholtz a. Place on Basilar 2. Frequency Theory a. Basilar membrane as a b. Volley principle – 3. Neither explains IV. ...
... 2. Switching in 3. Some go to the centers – 4. Others throught the reticular 5. Most of the auditory sections in the 6. 4 levels of D. Theories of Hearing 1. Place Theory – Helmholtz a. Place on Basilar 2. Frequency Theory a. Basilar membrane as a b. Volley principle – 3. Neither explains IV. ...
669790507205MyersMod_LG_12
... 4. Explain the Young-Helmholtz and opponent-process theories of color vision. The Young-Helmholtz trichromatic (three-color) theory states that the retina has three types of color receptors, each especially sensitive to red, green, or blue. When we stimulate combinations of these cones, we see other ...
... 4. Explain the Young-Helmholtz and opponent-process theories of color vision. The Young-Helmholtz trichromatic (three-color) theory states that the retina has three types of color receptors, each especially sensitive to red, green, or blue. When we stimulate combinations of these cones, we see other ...
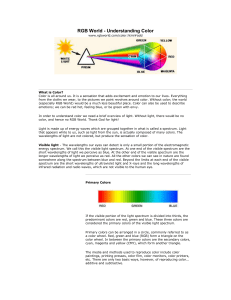
04 RGB World (print in color).
... (especially RGB World) would be a much less beautiful place. Color can also be used to describe emotions; we can be red hot, feeling blue, or be green with envy. In order to understand color we need a brief overview of light. Without light, there would be no color, and hence no RGB World. Thank God ...
... (especially RGB World) would be a much less beautiful place. Color can also be used to describe emotions; we can be red hot, feeling blue, or be green with envy. In order to understand color we need a brief overview of light. Without light, there would be no color, and hence no RGB World. Thank God ...
Psychology (9th Edition) David Myers
... change the size of the opening (pupil) for light. 3. Lens: Focuses the light rays on the retina. 4. Retina: Contains sensory receptors that process visual information and sends it to the brain. ...
... change the size of the opening (pupil) for light. 3. Lens: Focuses the light rays on the retina. 4. Retina: Contains sensory receptors that process visual information and sends it to the brain. ...
Practice Sheet 2 Color Light Pigments
... 3. Of the colors red and blue, which has the longest wavelength? 4. Of the colors orange and violet, which has the shortest wavelength? 5. Suppose you add green and blue light together. What color will result? 6. If you wanted to make the color green, what paints (pigments) should you mix together? ...
... 3. Of the colors red and blue, which has the longest wavelength? 4. Of the colors orange and violet, which has the shortest wavelength? 5. Suppose you add green and blue light together. What color will result? 6. If you wanted to make the color green, what paints (pigments) should you mix together? ...
document
... who see all colors called trichromats (from the Greek term meaning “three colors” Smaller number of people see only two colors = dichromats ...
... who see all colors called trichromats (from the Greek term meaning “three colors” Smaller number of people see only two colors = dichromats ...
1. Accommodation Accommodation of the eye refers to its ability to a
... Accommodation of the eye refers to its ability to a. focus on both nearby and distant objects. b. move in the eye socket to look in different directions. c. see on both the brightest days and in the dimmest light. d. see both in air and while under water. 2. Resolution The fundamental resolution of ...
... Accommodation of the eye refers to its ability to a. focus on both nearby and distant objects. b. move in the eye socket to look in different directions. c. see on both the brightest days and in the dimmest light. d. see both in air and while under water. 2. Resolution The fundamental resolution of ...
Color

Color, or colour—see spelling differences—is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, blue, yellow, etc. Color derives from the spectrum of light (distribution of light power versus wavelength) interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors. Color categories and physical specifications of color are also associated with objects or materials based on their physical properties such as light absorption, reflection, or emission spectra. By defining a color space colors can be identified numerically by their coordinates.Because perception of color stems from the varying spectral sensitivity of different types of cone cells in the retina to different parts of the spectrum, colors may be defined and quantified by the degree to which they stimulate these cells. These physical or physiological quantifications of color, however, do not fully explain the psychophysical perception of color appearance.The science of color is sometimes called chromatics, colorimetry, or simply color science. It includes the perception of color by the human eye and brain, the origin of color in materials, color theory in art, and the physics of electromagnetic radiation in the visible range (that is, what we commonly refer to simply as light).