Strata Soil Reinforcement Solutions for Slopes and Walls
... Embankments represent a special class of slopes or walls where soil reinforcement is used to stabilize and construct a fill structure having a smaller footprint than what could be constructed with the soil alone. Embankment stabilization is common when constructing roadways or other structures over ...
... Embankments represent a special class of slopes or walls where soil reinforcement is used to stabilize and construct a fill structure having a smaller footprint than what could be constructed with the soil alone. Embankment stabilization is common when constructing roadways or other structures over ...
The study on sensitivity analysis method of slope stability based on
... eliminated the crude assumptions made on the conventional approach. The advantage of this analytical method is both the safety factor and the sensitivity ratio can be computed simultaneously, for slopes with any given slip surface. The authors of this paper believed that, the findings of this paper ...
... eliminated the crude assumptions made on the conventional approach. The advantage of this analytical method is both the safety factor and the sensitivity ratio can be computed simultaneously, for slopes with any given slip surface. The authors of this paper believed that, the findings of this paper ...
Engineers - Bearsden Academy
... They must be able to still stand, even if there is natural disasters like, floodings, earthquakes and much more. Also bridges and buildings must be able to bear a very large amount of weight, because if they can’t then they would not be safe for people to go on. ...
... They must be able to still stand, even if there is natural disasters like, floodings, earthquakes and much more. Also bridges and buildings must be able to bear a very large amount of weight, because if they can’t then they would not be safe for people to go on. ...
CE 251 Civil Engineering Systems
... 5. Given the relatively low-cost associated with porosity measurements, use the Hazen formula and the linear regression derived in step 3 to develop the relationship between the soil D15 and porosity n; what distribution do you expect the soil D15 to satisfy? 6. Using the linear regression equation ...
... 5. Given the relatively low-cost associated with porosity measurements, use the Hazen formula and the linear regression derived in step 3 to develop the relationship between the soil D15 and porosity n; what distribution do you expect the soil D15 to satisfy? 6. Using the linear regression equation ...
Chapter2 permeability and stress in soil
... ♦ The importance of the forces transmitted through the soil skeleton from particle to particle was recognized in 1923 when Terzaghi presented the principle of effective stress, an intuitive relationship based on experimental data. The principle applies only to fully saturated soils and relates the f ...
... ♦ The importance of the forces transmitted through the soil skeleton from particle to particle was recognized in 1923 when Terzaghi presented the principle of effective stress, an intuitive relationship based on experimental data. The principle applies only to fully saturated soils and relates the f ...
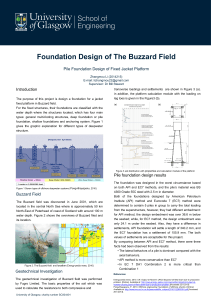
Foundation Design of The Buzzard Field
... Energy-pedia news, 2010. UK: Output at Nexen's UKCS Buzzard oil field down due to production problem. [Online] Available at: http://www.energy-pedia.com/news/united-kingdom/output-atnexens-ukcs-buzzard-oil-field-down-due-to-production-problem [Accessed 22 8 2013] Pongvithayapanu, P., 2010. Offshore ...
... Energy-pedia news, 2010. UK: Output at Nexen's UKCS Buzzard oil field down due to production problem. [Online] Available at: http://www.energy-pedia.com/news/united-kingdom/output-atnexens-ukcs-buzzard-oil-field-down-due-to-production-problem [Accessed 22 8 2013] Pongvithayapanu, P., 2010. Offshore ...
Key_Personnel_files/Corsair Resume
... back, soil nail and MSE walls on the project. The proximity of the US 54 bridge to the tie back walls required that spread footings used to support the existing US 54 bridge be underpinned with micro piling. Mr. Galvan designed the footing underpinning details and provided construction phasing detai ...
... back, soil nail and MSE walls on the project. The proximity of the US 54 bridge to the tie back walls required that spread footings used to support the existing US 54 bridge be underpinned with micro piling. Mr. Galvan designed the footing underpinning details and provided construction phasing detai ...
Rec #: 152981BR Entry-Level Structural Project Engineer for
... Apply the latest design methodologies and theories to novel problem solving situations not readily resolved through accepted conventional methods Contribute and affect the content, interpretation, or development of design policies concerning varied design and construction projects Minimum Requiremen ...
... Apply the latest design methodologies and theories to novel problem solving situations not readily resolved through accepted conventional methods Contribute and affect the content, interpretation, or development of design policies concerning varied design and construction projects Minimum Requiremen ...
Manuscript Preparation for International Conference on Problematic
... Mehmet Inanc ONUR Anadolu University, Department of Civil Engineering, Eskisehir- Turkey [email protected] ...
... Mehmet Inanc ONUR Anadolu University, Department of Civil Engineering, Eskisehir- Turkey [email protected] ...
Presentation
... A tunnel is an underground passageway, completely enclosed except for openings for entrance and exit, commonly at each end. A tunnel may be for foot or vehicular road traffic, for rail traffic, or for a canal. There are three basic types of tunnel construction in common use: • Cut-and-cover tunnels, ...
... A tunnel is an underground passageway, completely enclosed except for openings for entrance and exit, commonly at each end. A tunnel may be for foot or vehicular road traffic, for rail traffic, or for a canal. There are three basic types of tunnel construction in common use: • Cut-and-cover tunnels, ...
standard penetration test
... are used up to 6 meter depth and the mechanically operated augers are used for greater depth up to 15 meter. The auger is vertically driven into the ground by roating its handle and is pressed down during the process of rotation. At every 30 cm. depth of penetration, the aiger is drawn out and the ...
... are used up to 6 meter depth and the mechanically operated augers are used for greater depth up to 15 meter. The auger is vertically driven into the ground by roating its handle and is pressed down during the process of rotation. At every 30 cm. depth of penetration, the aiger is drawn out and the ...
Deep excavation in Irish glacial deposits
... “hard / firm” secant pile wall with 640 mm diameter structural “male” piles and 900 mm diameter “female”. A single anchor ...
... “hard / firm” secant pile wall with 640 mm diameter structural “male” piles and 900 mm diameter “female”. A single anchor ...
Structure Foundation Considerations
... - The need for pile driving control such as dynamic testing or wave equation analysis. ...
... - The need for pile driving control such as dynamic testing or wave equation analysis. ...
Bearing Capacity Calculation Of Footings On Layered Soil Using
... behaviour of the soil. Von-Mises and Mohr-Coulomb yield ...
... behaviour of the soil. Von-Mises and Mohr-Coulomb yield ...
Foundations
... Calculus methods. Beams under elastic medium. Beam of infinite length. Beam of infinite length loaded with a concentrated moment. Beam of infinite length loaded with a uniform distributed load. Beams and plates calculus under linear deformable semi-infinite space (Gorbunov – Posadov method; Simvulid ...
... Calculus methods. Beams under elastic medium. Beam of infinite length. Beam of infinite length loaded with a concentrated moment. Beam of infinite length loaded with a uniform distributed load. Beams and plates calculus under linear deformable semi-infinite space (Gorbunov – Posadov method; Simvulid ...
Department: Electrical and Electronic Engineering
... Week 1-2 Geotechnical properties of soils. (5 Classes) Week 3-4 Site exploration; borehole drilling and insitu testing methods. (10 classes) Week 5-8 Shallow foundations: Bearing capacity and settlement of single pad foundation, Global Factor of Safety method and Eurocode 7 (20 classes) Week 9 Midte ...
... Week 1-2 Geotechnical properties of soils. (5 Classes) Week 3-4 Site exploration; borehole drilling and insitu testing methods. (10 classes) Week 5-8 Shallow foundations: Bearing capacity and settlement of single pad foundation, Global Factor of Safety method and Eurocode 7 (20 classes) Week 9 Midte ...
Foundations powerpoint
... support a line of loads such as a load bearing wall. They could also be used where the line of column positions are so close that individual pad foundations would be pointless. ...
... support a line of loads such as a load bearing wall. They could also be used where the line of column positions are so close that individual pad foundations would be pointless. ...
The effect of vegetation roots in slope stability, 2nd Civil... Conference on Civil Engineering and Sustainable Development held in Mombasa...
... widespread landslides and floods in various parts of the country. An enormous number of landslides occurred in Central, Western and to the Coast Provinces. This triggered a nation-wide crusade to plant trees in an effort to counter future landslide phenomenon. However, little quantitative research h ...
... widespread landslides and floods in various parts of the country. An enormous number of landslides occurred in Central, Western and to the Coast Provinces. This triggered a nation-wide crusade to plant trees in an effort to counter future landslide phenomenon. However, little quantitative research h ...
What is Geological Engineering?
... What do Geo Engineers Do? • Building structures • Foundations • Dams • Mining • Disposing of Waste • Mitigation of Natural hazards ...
... What do Geo Engineers Do? • Building structures • Foundations • Dams • Mining • Disposing of Waste • Mitigation of Natural hazards ...
Subject - IESL e-Learning System
... Design of centrally and eccentrically loaded footings with vertical and inclined loads; Use of insitu soil test results in shallow foundation design; Settlement estimation of shallow foundations using the theory of beams on elastic medium and the theory of consolidation. ...
... Design of centrally and eccentrically loaded footings with vertical and inclined loads; Use of insitu soil test results in shallow foundation design; Settlement estimation of shallow foundations using the theory of beams on elastic medium and the theory of consolidation. ...
Geotechnical engineering

Geotechnical engineering is the branch of civil engineering concerned with the engineering behavior of earth materials. Geotechnical engineering is important in civil engineering, but also has applications in military, mining, petroleum and other engineering disciplines that are concerned with construction occurring on the surface or within the ground. Geotechnical engineering uses principles of soil mechanics and rock mechanics to investigate subsurface conditions and materials; determine the relevant physical/mechanical and chemical properties of these materials; evaluate stability of natural slopes and man-made soil deposits; assess risks posed by site conditions; design earthworks and structure foundations; and monitor site conditions, earthwork and foundation construction.A typical geotechnical engineering project begins with a review of project needs to define the required material properties. Then follows a site investigation of soil, rock, fault distribution and bedrock properties on and below an area of interest to determine their engineering properties including how they will interact with, on or in a proposed construction. Site investigations are needed to gain an understanding of the area in or on which the engineering will take place. Investigations can include the assessment of the risk to humans, property and the environment from natural hazards such as earthquakes, landslides, sinkholes, soil liquefaction, debris flows and rockfalls.A geotechnical engineer then determines and designs the type of foundations, earthworks, and/or pavement subgrades required for the intended man-made structures to be built. Foundations are designed and constructed for structures of various sizes such as high-rise buildings, bridges, medium to large commercial buildings, and smaller structures where the soil conditions do not allow code-based design.Foundations built for above-ground structures include shallow and deep foundations. Retaining structures include earth-filled dams and retaining walls. Earthworks include embankments, tunnels, dikes and levees, channels, reservoirs, deposition of hazardous waste and sanitary landfills.Geotechnical engineering is also related to coastal and ocean engineering. Coastal engineering can involve the design and construction of wharves, marinas, and jetties. Ocean engineering can involve foundation and anchor systems for offshore structures such as oil platforms.The fields of geotechnical engineering and engineering geology are closely related, and have large areas of overlap. However, the field of geotechnical engineering is a specialty of engineering, where the field of engineering geology is a specialty of geology.