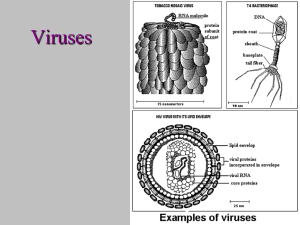
Picornaviruses
... In most cases, no further virus spread occurs, and there is asymptomatic or mild febrile undifferentiated illness, such as fever, malaise, headache, nausea, gastrointestinal disturbances, and sore throat, or combinations of these. In rare cases in which disease progresses to the neurologic phase, th ...
... In most cases, no further virus spread occurs, and there is asymptomatic or mild febrile undifferentiated illness, such as fever, malaise, headache, nausea, gastrointestinal disturbances, and sore throat, or combinations of these. In rare cases in which disease progresses to the neurologic phase, th ...
Childhood
... Pneumococcal is a group of diseases caused by bacteria. The bacteria affect different parts of the body such as the lining of the brain, lungs or blood. These diseases are dangerous and can lead to brain damage, hearing loss, blindness, paralysis, and even death. Symptoms of the disease vary dependi ...
... Pneumococcal is a group of diseases caused by bacteria. The bacteria affect different parts of the body such as the lining of the brain, lungs or blood. These diseases are dangerous and can lead to brain damage, hearing loss, blindness, paralysis, and even death. Symptoms of the disease vary dependi ...
ARTICLE Polio and Smallpox - Progressive Radio Network
... would also explain why these childrens’ tumors contained the SV40 virus present, even though the children themselves did not receive the vaccine. [9] There is a large body of scientific literature detailing the catastrophic consequences of SV40 virus infection. As of 2001, Neil Miller counted 62 pee ...
... would also explain why these childrens’ tumors contained the SV40 virus present, even though the children themselves did not receive the vaccine. [9] There is a large body of scientific literature detailing the catastrophic consequences of SV40 virus infection. As of 2001, Neil Miller counted 62 pee ...
the brochure - Foundation for Biomedical Research
... Prior to the 1960s, kidney disease was almost uniformly fatal and resulted in the death of about 20,000 Americans annually, making it the fourth leading cause of death among young adults. Virtually all of the recent improvements in the care of patients with kidney disease have resulted from basic re ...
... Prior to the 1960s, kidney disease was almost uniformly fatal and resulted in the death of about 20,000 Americans annually, making it the fourth leading cause of death among young adults. Virtually all of the recent improvements in the care of patients with kidney disease have resulted from basic re ...
Vaccine-Preventable Diseases
... Mumps is a viral disease caused by the mumps virus. It is spread through air droplets from the cough or sneeze of an infected person. Symptoms include fever, swelling and pain of the salivary glands, headache, muscle pain, weakness and decreased appetite. Complications of mumps are rare, but can ...
... Mumps is a viral disease caused by the mumps virus. It is spread through air droplets from the cough or sneeze of an infected person. Symptoms include fever, swelling and pain of the salivary glands, headache, muscle pain, weakness and decreased appetite. Complications of mumps are rare, but can ...
Polio programme: let us declare victory and move on
... billion US$ 1 = Rs 50) on polio eradication after the programme started here in 1994 (2). The $2.5 billion spent by India must be seen against $2 billion spent by the United States of America on world-wide polio eradication (3), the $1.3 billion expended by Bill Gates (4), and the $0.8 billion raise ...
... billion US$ 1 = Rs 50) on polio eradication after the programme started here in 1994 (2). The $2.5 billion spent by India must be seen against $2 billion spent by the United States of America on world-wide polio eradication (3), the $1.3 billion expended by Bill Gates (4), and the $0.8 billion raise ...
Vaccines stimulating immunity
... Name the first recombinant DNA vaccine made available in the US. What is the difference between a vaccine made with an attenuated virus and one made with an inactive virus? Can you catch the disease from the vaccine (live or inactive)? What is the purpose of a vaccine? What is the purpose of a vacci ...
... Name the first recombinant DNA vaccine made available in the US. What is the difference between a vaccine made with an attenuated virus and one made with an inactive virus? Can you catch the disease from the vaccine (live or inactive)? What is the purpose of a vaccine? What is the purpose of a vacci ...
immunisations - mededcoventry.com
... 5-in-1 (DTaP/IPV/Hib) vaccine – this single jab contains vaccines to protect against five separate diseases: diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough (pertussis), polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b (known as Hib – a bacterial infection that can cause severe pneumonia or meningitis in young children) ...
... 5-in-1 (DTaP/IPV/Hib) vaccine – this single jab contains vaccines to protect against five separate diseases: diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough (pertussis), polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b (known as Hib – a bacterial infection that can cause severe pneumonia or meningitis in young children) ...
40. RNA Non-enveloped Viruses
... tissue, the virus spreads through the bloodstream to the central nervous system. It can also spread retrograde along nerve axons. In the central nervous system, poliovirus preferentially replicates in the motor neurons located in the anterior horn of the spinal cord. Death of these cells results in ...
... tissue, the virus spreads through the bloodstream to the central nervous system. It can also spread retrograde along nerve axons. In the central nervous system, poliovirus preferentially replicates in the motor neurons located in the anterior horn of the spinal cord. Death of these cells results in ...
Cholesterol-Lowering Medications and Muscle
... statins, the then newish cholesterol-lowering drugs. There have been no specific studies of cholesterol-lowering drugs in polio survivors, but there seemed to be no reason polio survivors would be more prone to rhabdomyolysis. Only about one-half of 1% of anyone who takes a statin, such as Lipitor, ...
... statins, the then newish cholesterol-lowering drugs. There have been no specific studies of cholesterol-lowering drugs in polio survivors, but there seemed to be no reason polio survivors would be more prone to rhabdomyolysis. Only about one-half of 1% of anyone who takes a statin, such as Lipitor, ...
RNA
... Enteric disease: intestinal disease Enterovirus- refers to oral-fecal transmission, not intestinal disease Sequelae: condition following as a consequence of a disease Frank cases of polio: CNS pathology Encephalitis: inflammation of brain Meningitis: inflammation of the meninges (membrane covering b ...
... Enteric disease: intestinal disease Enterovirus- refers to oral-fecal transmission, not intestinal disease Sequelae: condition following as a consequence of a disease Frank cases of polio: CNS pathology Encephalitis: inflammation of brain Meningitis: inflammation of the meninges (membrane covering b ...
Bacteria/Viruses and Disease - UCO
... • In the first 12 weeks of pregnancy results in birth defects in up to 85 percent of cases • From 13 to 16 weeks of gestation results in birth defects in 54 percent of cases • At the end of the second trimester results in birth defects in 25 percent of cases ...
... • In the first 12 weeks of pregnancy results in birth defects in up to 85 percent of cases • From 13 to 16 weeks of gestation results in birth defects in 54 percent of cases • At the end of the second trimester results in birth defects in 25 percent of cases ...
Vaccination save lives
... Vaccination save lives- The Lives of 3 million children are saved every year thanks to vaccination. ...
... Vaccination save lives- The Lives of 3 million children are saved every year thanks to vaccination. ...
Chapter 22: Infectious Diseases Affecting the Nervous System
... o Viral encephalitis can be a consequence of a primary or secondary infection Some forms of encephalitis are due to herpesviruses Arboviral encephalitis is a result of a primary viral infection – Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain Arboviral encephalitis patients may suffer – pa ...
... o Viral encephalitis can be a consequence of a primary or secondary infection Some forms of encephalitis are due to herpesviruses Arboviral encephalitis is a result of a primary viral infection – Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain Arboviral encephalitis patients may suffer – pa ...
Planet Earth and Its Environment A 5000-million
... Polio, or poliomyelitis, is a viral disease that is transmitted by inhaling infected droplets and by direct contact. It causes fever and headache, speech, swallowing and breathing difficulties, and paralysis. Death occurs in 50% of the cases and nerve damage and paralysis in 50% of sufferers. ...
... Polio, or poliomyelitis, is a viral disease that is transmitted by inhaling infected droplets and by direct contact. It causes fever and headache, speech, swallowing and breathing difficulties, and paralysis. Death occurs in 50% of the cases and nerve damage and paralysis in 50% of sufferers. ...
(Hib) und Hepatitis B auf Englisch
... Possible local and systemic reactions following vaccination After vaccination, redness or a painful swelling may frequently occur at the injection site in addition to the desired immunity and corresponding disease protection. This is the body's normal reaction to the vaccine and usually occurs withi ...
... Possible local and systemic reactions following vaccination After vaccination, redness or a painful swelling may frequently occur at the injection site in addition to the desired immunity and corresponding disease protection. This is the body's normal reaction to the vaccine and usually occurs withi ...
Adenovirus Type 21–Associated Acute Flaccid Paralysis during an
... At follow-up, 4 children were noted to have made full recoveries and 3 had residual flaccid weakness and wasting. Neurophysiological investigation revealed a mixture of axonal and demyelinating features in motor and sensory nerves, with denervation. These findings suggest that Ad21 might cause AFP b ...
... At follow-up, 4 children were noted to have made full recoveries and 3 had residual flaccid weakness and wasting. Neurophysiological investigation revealed a mixture of axonal and demyelinating features in motor and sensory nerves, with denervation. These findings suggest that Ad21 might cause AFP b ...
Polio: the viru s and the vaccine
... fever, which is followed by vomiting, delirium and spreading pain. Within days of ...
... fever, which is followed by vomiting, delirium and spreading pain. Within days of ...
Positive (+) RNA Viruses
... CDC advises that travelers in a SARSaffected area should wash their hands frequently to protect against SARS infection. In addition, CDC advises that travelers may wish to avoid close contact with large numbers of people as much as possible to minimize the possibility of infection. ...
... CDC advises that travelers in a SARSaffected area should wash their hands frequently to protect against SARS infection. In addition, CDC advises that travelers may wish to avoid close contact with large numbers of people as much as possible to minimize the possibility of infection. ...
Picornaviruse Family
... coxsackie viruses A7, A9, and A24. Fever, malaise, headache, nausea, and abdominal pain are common early symptoms. Signs of meningeal irritation, stiff neck or back, and vomiting may appear 1-2 days later. The disease sometimes progresses to mild muscle weakness suggestive of paralytic poliomyelitis ...
... coxsackie viruses A7, A9, and A24. Fever, malaise, headache, nausea, and abdominal pain are common early symptoms. Signs of meningeal irritation, stiff neck or back, and vomiting may appear 1-2 days later. The disease sometimes progresses to mild muscle weakness suggestive of paralytic poliomyelitis ...
Enteroviruses
... occur 6-9 days after exposure but may occur earlier and persist longer. Major symptoms occur after the viremia, which disseminates infection to target organs. For poliovirus, the incubation period is estimated to be 9-12 days (range: 5-35 days) and 11-17 days (range: 8-36 days) until the onset of pa ...
... occur 6-9 days after exposure but may occur earlier and persist longer. Major symptoms occur after the viremia, which disseminates infection to target organs. For poliovirus, the incubation period is estimated to be 9-12 days (range: 5-35 days) and 11-17 days (range: 8-36 days) until the onset of pa ...
Class Notes
... • Polio is a contagious, historically devastating disease that was virtually eliminated from the Western hemisphere in the second half of the twentieth century. Although polio has plagued humans since ancient times, its most extensive outbreak occurred in the first half of the 1900s before the vacci ...
... • Polio is a contagious, historically devastating disease that was virtually eliminated from the Western hemisphere in the second half of the twentieth century. Although polio has plagued humans since ancient times, its most extensive outbreak occurred in the first half of the 1900s before the vacci ...
Hepatitis B Vaccine
... Protects against Hib disease Polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine Three to four doses are required (at age two, four, six and 12–15 months of age. Route of administration -- intramuscular Efficacy- more than 95% Adverse events- are uncommon. The most common reactions are local reactions at the i ...
... Protects against Hib disease Polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine Three to four doses are required (at age two, four, six and 12–15 months of age. Route of administration -- intramuscular Efficacy- more than 95% Adverse events- are uncommon. The most common reactions are local reactions at the i ...
Science Homework Year 9 B1
... The pioneer in methods of treating infections in hospitals was Ignaz Semmelweiss. He observed that women whose babies were delivered by doctors in hospital had a death rate of 18% from infections caught in the hospital. Women whose babies were delivered by midwives in the hospital had a death rate o ...
... The pioneer in methods of treating infections in hospitals was Ignaz Semmelweiss. He observed that women whose babies were delivered by doctors in hospital had a death rate of 18% from infections caught in the hospital. Women whose babies were delivered by midwives in the hospital had a death rate o ...
Poliomyelitis

Poliomyelitis, often called polio or infantile paralysis, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 90% to 95% of infections cause no symptoms. Another 5 to 10% of people have minor symptoms such as: fever, headache, vomiting, diarrhea, neck stiffness and pains in the arms and legs. These people are usually back to normal within one or two weeks. In about 0.5% of cases there is muscle weakness resulting in an inability to move. This can occur over a few hours to few days. The weakness most often involves the legs but may less commonly involve the muscles of the head, neck and diaphragm. Many but not all people fully recover. In those with muscle weakness about 2% to 5% of children and 15% to 30% of adults die. Years after recovery post-polio syndrome may occur, with a slow development of muscle weakness similar to what the person had during the initial infection.Poliovirus is usually spread from person to person through infected feces entering the mouth. It may also be spread by food or water containing human feces and less commonly from infected saliva. Those who are infected may spread the disease even if no symptoms are present for up to six weeks. The disease may be diagnosed by finding the virus in the feces or detecting antibodies against it in the blood.The disease is preventable with the polio vaccine; however, a number of doses are required for it to be effective. The United States Center for Disease Control recommends polio vaccination boosters for travelers and those who live in countries where the disease is occurring. Once infected there is no specific treatment. In 2013 polio affected 416 people down from 350,000 cases in 1988. In 2014 the disease was only spreading between people in Afghanistan, Nigeria, and Pakistan. In 2015 wild polio was eliminated in Nigeria.Poliomyelitis has existed for thousands of years, with depictions of the disease in ancient art. The disease was first recognized as a distinct condition by Michael Underwood in 1789 and the virus that causes it was first identified in 1908 by Karl Landsteiner. Major outbreaks started to occur in the late 19th century in Europe and the United States. In the 20th century it became one of the most worrying childhood diseases in these areas. The first polio vaccine was developed in the 1950s by Jonas Salk. It is hoped that vaccination efforts and early detection of cases will result in global eradication of the disease by 2018. In 2013; however, there were reports of new cases in Syria and in May 2014, the World Health Organization declared a public health emergency of international concern due to outbreaks of the disease in Asia, Africa and the Middle East. The disease does not naturally occur in any other animals.