Chapter 12 Test Study Guide: Simple Machines WORK A force
... An ideal machine would have an efficiency of 100 percent. SIMPLE MACHINES The wedge, screw, and lever are all examples of simple machines. Pulleys change the direction over which a force is exerted. A wedge is a simple machine that might be thought of as an inclined plane that moves. A ramp is an ex ...
... An ideal machine would have an efficiency of 100 percent. SIMPLE MACHINES The wedge, screw, and lever are all examples of simple machines. Pulleys change the direction over which a force is exerted. A wedge is a simple machine that might be thought of as an inclined plane that moves. A ramp is an ex ...
Using Machines
... Conservation of energy states that energy can never be created or destroyed, therefore the machine can never create extra energy Machine can never give more energy then it receives ...
... Conservation of energy states that energy can never be created or destroyed, therefore the machine can never create extra energy Machine can never give more energy then it receives ...
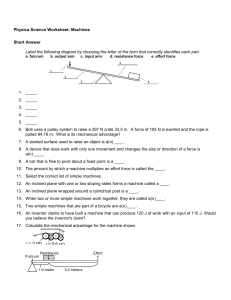
Physica Science Worksheet: Machines Short Answer Label the
... 8. A device that does work with only one movement and changes the size or direction of a force is a(n) ____. 9. A bar that is free to pivot about a fixed point is a ____. 10. The amount by which a machine multiplies an effort force is called the ____. 11. Select the correct list of simple machines. ...
... 8. A device that does work with only one movement and changes the size or direction of a force is a(n) ____. 9. A bar that is free to pivot about a fixed point is a ____. 10. The amount by which a machine multiplies an effort force is called the ____. 11. Select the correct list of simple machines. ...
Section 9.1
... 9.1 Using Machines The input includes everything you do to make the machine accomplish a task, like pushing on the bicycle pedals. The output is what the machine does for you, like going fast or climbing a steep hill. ...
... 9.1 Using Machines The input includes everything you do to make the machine accomplish a task, like pushing on the bicycle pedals. The output is what the machine does for you, like going fast or climbing a steep hill. ...
PSCh5GR - TeacherPage.com
... Where is energy lost in a machine and in what form does it come out? ...
... Where is energy lost in a machine and in what form does it come out? ...
Chapter 14 - Work and Power – Physical Science Study Guide What
... 9. A machine is a device that can multiply __________. 10. When a machine does work it can not increase a force and _______________________. 11. How can a machine make work easier for you? 12. How can you make the work output of a machine greater than the work input? 13. The actual mechanical advant ...
... 9. A machine is a device that can multiply __________. 10. When a machine does work it can not increase a force and _______________________. 11. How can a machine make work easier for you? 12. How can you make the work output of a machine greater than the work input? 13. The actual mechanical advant ...
Machine tool

A machine tool is a machine for shaping or machining metal or other rigid materials, usually by cutting, boring, grinding, shearing, or other forms of deformation. Machine tools employ some sort of tool that does the cutting or shaping. All machine tools have some means of constraining the workpiece and provide a guided movement of the parts of the machine. Thus the relative movement between the workpiece and the cutting tool (which is called the toolpath) is controlled or constrained by the machine to at least some extent, rather than being entirely ""offhand"" or ""freehand"".The precise definition of the term machine tool varies among users, as discussed below. While all machine tools are ""machines that help people to make things"", not all factory machines are machine tools.Today machine tools are typically powered other than by human muscle (e.g., electrically, hydraulically, or via line shaft), used to make manufactured parts (components) in various ways that include cutting or certain other kinds of deformation.With their inherent precision, machine tools enabled the economical production of interchangeable parts.