Chapter 13 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Q19 Four equal masses, 2.0 kg each, are placed at the four corners of a square of side 10 cm as shown in Fig 7. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force on one of the masses due to the other three? A1 5.1 * 10**-8 N Q20 The escape speed from a certain planet for an empty spaceship of mass M ...
... Q19 Four equal masses, 2.0 kg each, are placed at the four corners of a square of side 10 cm as shown in Fig 7. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force on one of the masses due to the other three? A1 5.1 * 10**-8 N Q20 The escape speed from a certain planet for an empty spaceship of mass M ...
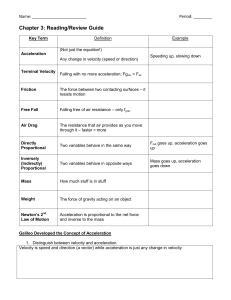
the particle was on Earth`s surface
... 14-2 Newton's Law of Gravitation Nowton published the law of gravitation In 1687. It may be stated as follows: Every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directely proportional to the product of the masses of the particles and inversely proportinal to the squa ...
... 14-2 Newton's Law of Gravitation Nowton published the law of gravitation In 1687. It may be stated as follows: Every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directely proportional to the product of the masses of the particles and inversely proportinal to the squa ...
Forces Review Powerpoint
... objects in orbit. Newton hypothesized gravity pulls objects to the ground also pulls the Moon around the Earth. You can think of an object orbiting Earth as an object that is falling around Earth rather than falling to the ...
... objects in orbit. Newton hypothesized gravity pulls objects to the ground also pulls the Moon around the Earth. You can think of an object orbiting Earth as an object that is falling around Earth rather than falling to the ...
G481 Mechanics
... (a) Derive the equations of motion for constant acceleration in a straight line from a velocity against time graph; (b) Select and use the equations of motion for constant acceleration in a straight line: (c) Apply the equations for constant acceleration in a straight line, including the motion of b ...
... (a) Derive the equations of motion for constant acceleration in a straight line from a velocity against time graph; (b) Select and use the equations of motion for constant acceleration in a straight line: (c) Apply the equations for constant acceleration in a straight line, including the motion of b ...
Discover - Astronomy Magazine
... attack that could steer them toward an ultimate theory of everything. Simply put, the equivalence principle holds that all bodies under the influence of the same gravitational field experience the same acceleration, regardless of their mass or composition. One advantage of this strategy is that, so ...
... attack that could steer them toward an ultimate theory of everything. Simply put, the equivalence principle holds that all bodies under the influence of the same gravitational field experience the same acceleration, regardless of their mass or composition. One advantage of this strategy is that, so ...
Gravitation and Inverse Squared
... Newton went further and created his Law of Universal Gravitation, shown below. Mass is a property of matter (stuff). Anything that has mass has inertia. Anything that has mass also has gravity. The more mass an object has, the more gravity it has (just like it has more inertia).* All objects are att ...
... Newton went further and created his Law of Universal Gravitation, shown below. Mass is a property of matter (stuff). Anything that has mass has inertia. Anything that has mass also has gravity. The more mass an object has, the more gravity it has (just like it has more inertia).* All objects are att ...
Universal Gravitation
... • Newton proposed that an attraction between bodies is universal. • Gravitational force is extremely weak between ordinary objects. • Objects with enormous mass have significant gravitational force. Creates orbits Creates tides Is known as weight for objects on the surface. ...
... • Newton proposed that an attraction between bodies is universal. • Gravitational force is extremely weak between ordinary objects. • Objects with enormous mass have significant gravitational force. Creates orbits Creates tides Is known as weight for objects on the surface. ...
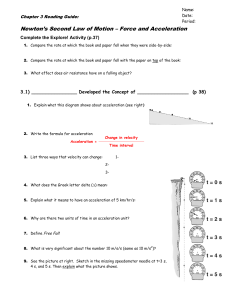
Chapter 3 activity 1 instructions, summarizing questions
... Step 2: Now have a group member stand with both their arms stretched out horizontally, palms upward. Place the 100 g mass on one palm, and the 1000 g mass on the other. Q4. Does it requir ...
... Step 2: Now have a group member stand with both their arms stretched out horizontally, palms upward. Place the 100 g mass on one palm, and the 1000 g mass on the other. Q4. Does it requir ...
Unit 1 Cycle 2: Interactions and Energy
... Instructions: Read the Scientist Ideas, paying careful attention to each key idea. When you read, try to think about how the key ideas relate to the evidence you collected in the activity. Gravitational force is from the Earth idea: The Earth exerts a gravitational force on all objects. This force i ...
... Instructions: Read the Scientist Ideas, paying careful attention to each key idea. When you read, try to think about how the key ideas relate to the evidence you collected in the activity. Gravitational force is from the Earth idea: The Earth exerts a gravitational force on all objects. This force i ...
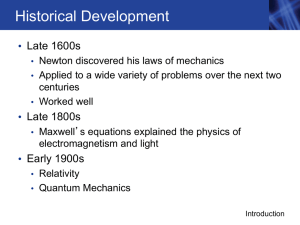
relative - Purdue Physics
... • Special relativity • Concerned with objects and observers moving at a constant velocity • Topic of this chapter • General relativity • Applies to situations when the object or the observer is accelerated • Gravitational fields also are a form of acceleration (take g, for example) • GR is the world ...
... • Special relativity • Concerned with objects and observers moving at a constant velocity • Topic of this chapter • General relativity • Applies to situations when the object or the observer is accelerated • Gravitational fields also are a form of acceleration (take g, for example) • GR is the world ...
the full article here
... gravitational waves would be so weak that only astrophysical events with fast‐moving star‐sized masses would offer a chance of making waves strong enough to detect. Very compact massive objects, such as neutron stars, orbiting each other very fast, would be the most likely ...
... gravitational waves would be so weak that only astrophysical events with fast‐moving star‐sized masses would offer a chance of making waves strong enough to detect. Very compact massive objects, such as neutron stars, orbiting each other very fast, would be the most likely ...
an analogy between solutions of electrostatic and
... The purpose of this paper is to relate the solutions of a conducting shell with uniform charge density to that of hollow earth of uniform mass density. Both problems involve the use of vector superposition within the empty space within each shell. The mathematical form, as a function of densities, p ...
... The purpose of this paper is to relate the solutions of a conducting shell with uniform charge density to that of hollow earth of uniform mass density. Both problems involve the use of vector superposition within the empty space within each shell. The mathematical form, as a function of densities, p ...
General relativity and Its applications - UoN Repository
... are caused by external forces acting on a body in accordance with Newton's second law of motion, which states that the net force acting on a body is equal to that body's (inertial) mass multiplied by its acceleration, ...
... are caused by external forces acting on a body in accordance with Newton's second law of motion, which states that the net force acting on a body is equal to that body's (inertial) mass multiplied by its acceleration, ...
rEVIEW CHAPTER 6
... 11. The gravitational constant, G, near the Moon is different than G near Earth. (6.1) K/U 12. The gravitational field around Earth at a fixed distance from its centre would be the same if Earth had half the radius but the same mass. (6.1) K/U 13. A book is surrounded by its own gravitationa ...
... 11. The gravitational constant, G, near the Moon is different than G near Earth. (6.1) K/U 12. The gravitational field around Earth at a fixed distance from its centre would be the same if Earth had half the radius but the same mass. (6.1) K/U 13. A book is surrounded by its own gravitationa ...
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory
... Einstein theorized that smaller masses travel toward larger masses, not because they are "attracted" by a mysterious force, but because the smaller objects travel through space that is warped by the larger object. ...
... Einstein theorized that smaller masses travel toward larger masses, not because they are "attracted" by a mysterious force, but because the smaller objects travel through space that is warped by the larger object. ...