Archimedes` Principle
... when it is submerged, but the net force does, we must be observing the action of a second force on the object. This force is called the Buoyant Force. The force on the submerged object is the resultant of the vector addition of the force of gravity and the buoyant force ...
... when it is submerged, but the net force does, we must be observing the action of a second force on the object. This force is called the Buoyant Force. The force on the submerged object is the resultant of the vector addition of the force of gravity and the buoyant force ...
gravity - Northside Middle School
... mass an object has, the higher its terminal velocity will be. More massive objects have a greater gravitational pull toward the earth. A more massive object will also take longer to reach its terminal velocity. This is due to the object needing more time to reach a higher terminal velocity than a ...
... mass an object has, the higher its terminal velocity will be. More massive objects have a greater gravitational pull toward the earth. A more massive object will also take longer to reach its terminal velocity. This is due to the object needing more time to reach a higher terminal velocity than a ...
Static Equilibrium (print version)
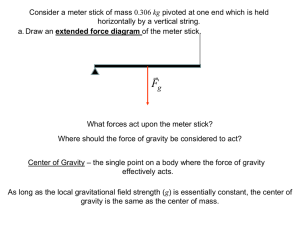
... Where should the force of gravity be considered to act? Center of Gravity – the single point on a body where the force of gravity effectively acts. As long as the local gravitational field strength (g) is essentially constant, the center of gravity is the same as the center of mass. ...
... Where should the force of gravity be considered to act? Center of Gravity – the single point on a body where the force of gravity effectively acts. As long as the local gravitational field strength (g) is essentially constant, the center of gravity is the same as the center of mass. ...
Chapter 4: Making Sense of the Universe
... A. Gravity from the Moon pulling on water B. Gravity from the Moon pulling more strongly on one side of Earth than the other C. Gravity from the Moon or the Sun is stronger on one side of Earth than the other ...
... A. Gravity from the Moon pulling on water B. Gravity from the Moon pulling more strongly on one side of Earth than the other C. Gravity from the Moon or the Sun is stronger on one side of Earth than the other ...
2-GW_MEPhI_2016_bisnovatyi
... and the ringdown of the resulting single black hole. The signal was observed with a matchedfilter signal-to-noise ratio of 24 and a false alarm rate estimated to be less than 1 event per 203 000 years, equivalent to a significance greater than 5.1σ. The source lies at a luminosity distance of 410 (+ ...
... and the ringdown of the resulting single black hole. The signal was observed with a matchedfilter signal-to-noise ratio of 24 and a false alarm rate estimated to be less than 1 event per 203 000 years, equivalent to a significance greater than 5.1σ. The source lies at a luminosity distance of 410 (+ ...
8th Ed【CH13】
... (a) At r = 1.5 m, all of Mtotal is at a smaller radius and thus all contributes to the force: ...
... (a) At r = 1.5 m, all of Mtotal is at a smaller radius and thus all contributes to the force: ...
Conservation of Momentum
... We have only two differential equations for three unknown functions, namely r; P; and %. Obviously we can solve this mechanical problem only if we can express one of them in terms of the others, for example, the density % as a function of P . In general, this will not be the case. But there are some ...
... We have only two differential equations for three unknown functions, namely r; P; and %. Obviously we can solve this mechanical problem only if we can express one of them in terms of the others, for example, the density % as a function of P . In general, this will not be the case. But there are some ...
Chapter 5 Matter in Motion
... • Earth’s gravitational force is large. – Compared to all other objects around you, Earth has the largest mass. – Earth’s gravitational force pulls everything toward the center of the Earth. • That is why objects in this room stay in place, and why dropped objects fall to the Earth rather than movin ...
... • Earth’s gravitational force is large. – Compared to all other objects around you, Earth has the largest mass. – Earth’s gravitational force pulls everything toward the center of the Earth. • That is why objects in this room stay in place, and why dropped objects fall to the Earth rather than movin ...
Understanding Gravity - johndistefano.com.au
... triangles, circles and other geometrical figures, without the means of which it is humanly impossible to understand a word; without these philosophy is a confused wandering in a dark labyrinth. Galileo, The Assayer 1623. In 1602, while Kepler was looking up at the heavens and wrestling with the orbi ...
... triangles, circles and other geometrical figures, without the means of which it is humanly impossible to understand a word; without these philosophy is a confused wandering in a dark labyrinth. Galileo, The Assayer 1623. In 1602, while Kepler was looking up at the heavens and wrestling with the orbi ...
Notes with questions - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Question for Thought • What happens to the velocity and acceleration of an object in free fall? A The velocity decreases as the acceleration remains the same. B The velocity increases as the acceleration remains the same. C The velocity increases and the ...
... Question for Thought • What happens to the velocity and acceleration of an object in free fall? A The velocity decreases as the acceleration remains the same. B The velocity increases as the acceleration remains the same. C The velocity increases and the ...
Document
... These materials were produced by Educational Testing Service ® (ETS®), which develops and administers the examinations of the Advanced Placement Program for the College Board. The College Board and Educational Testing Service (ETS) are dedicated to the principle of equal opportunity, and their progr ...
... These materials were produced by Educational Testing Service ® (ETS®), which develops and administers the examinations of the Advanced Placement Program for the College Board. The College Board and Educational Testing Service (ETS) are dedicated to the principle of equal opportunity, and their progr ...
PHY2020 Test 2 November 5, 2014 Name: sin(30) = 1/2 cos(30
... Newton’s Law of gravity Newton’s Gravitational Constant. Acceleration of gravity at the surface of the Earth gravity at the surface of a round planet of mass M and radius R kinetic energy potential energy for gravity at the Earth’s surface potential energy of a stretched spring, with spring constant ...
... Newton’s Law of gravity Newton’s Gravitational Constant. Acceleration of gravity at the surface of the Earth gravity at the surface of a round planet of mass M and radius R kinetic energy potential energy for gravity at the Earth’s surface potential energy of a stretched spring, with spring constant ...