Hemolytic disease of the newborn - Easymed.club
... fetomaternal haemorrhage (FMH) at the time of delivery. • The mother immune system reacts and form anti-D antibodies for many years. • Second pregnancy: Maternal IgG anti-D crosses the placenta and sensitizes the D+ fetal cells. ...
... fetomaternal haemorrhage (FMH) at the time of delivery. • The mother immune system reacts and form anti-D antibodies for many years. • Second pregnancy: Maternal IgG anti-D crosses the placenta and sensitizes the D+ fetal cells. ...
X Std Biology Chapter 2 Question answers
... individual artificially, (produced in some other animal and extracted) it is called Artificial Passive Acquired Immunity. This immunity is not permanent. 42. Describe the life-cycle of plasmodium in man. Ans : Life cycle of malarial parasite – Plasmodium: 1.The sexual stage of Plasmodium takes place ...
... individual artificially, (produced in some other animal and extracted) it is called Artificial Passive Acquired Immunity. This immunity is not permanent. 42. Describe the life-cycle of plasmodium in man. Ans : Life cycle of malarial parasite – Plasmodium: 1.The sexual stage of Plasmodium takes place ...
Ans - St.Paul`s Mat. Hr. Sec. School Welcomes You
... individual artificially, (produced in some other animal and extracted) it is called Artificial Passive Acquired Immunity. This immunity is not permanent. 42. Describe the life-cycle of plasmodium in man. Ans : Life cycle of malarial parasite – Plasmodium: 1.The sexual stage of Plasmodium takes place ...
... individual artificially, (produced in some other animal and extracted) it is called Artificial Passive Acquired Immunity. This immunity is not permanent. 42. Describe the life-cycle of plasmodium in man. Ans : Life cycle of malarial parasite – Plasmodium: 1.The sexual stage of Plasmodium takes place ...
GENETICS OF SUSCEPTIBILITY TO HUMAN INFECTIOUS DISEASE
... P. falciparum infection (FIG. 1). From this followed the hypothesis of J. B. S. Haldane8,9, in which he proposed that red-blood-cell disorders, such as thalassaemia, might protect an individual from life-threatening infection with malaria. Individuals that are homozygous for the HbS variant of haemo ...
... P. falciparum infection (FIG. 1). From this followed the hypothesis of J. B. S. Haldane8,9, in which he proposed that red-blood-cell disorders, such as thalassaemia, might protect an individual from life-threatening infection with malaria. Individuals that are homozygous for the HbS variant of haemo ...
Lesson Plans
... are extremely infectious. This causes pneumonic plague (an infection of the lungs), which is extremely virulent and spreads quickly. Plague, like many diseases, has an animal reservoir—the black rat, in which it does not cause serious illness. The rat flea must be present to act as a vector, transmi ...
... are extremely infectious. This causes pneumonic plague (an infection of the lungs), which is extremely virulent and spreads quickly. Plague, like many diseases, has an animal reservoir—the black rat, in which it does not cause serious illness. The rat flea must be present to act as a vector, transmi ...
Mapping the Aetiology of Non-Malarial Febrile Illness in
... pathogens, particularly rickettsioses, is very limited outside of Thailand, with very little published data available retrievable in English from Myanmar and Yunnan (Figure 8). Other bacteria and other viral pathogens not specifically targeted in the literature review are grouped in Figures 10 and 1 ...
... pathogens, particularly rickettsioses, is very limited outside of Thailand, with very little published data available retrievable in English from Myanmar and Yunnan (Figure 8). Other bacteria and other viral pathogens not specifically targeted in the literature review are grouped in Figures 10 and 1 ...
Prevalence of Transfusion Transmitted Infections among Blood Donors
... have low level viremia and may not have detectable HBs Ag level, so some centers have started testing antibodies against HBV core protein (anti HBc)6. Syphilis is caused by infection with Treponema pallidum. It is spread primarily through sexual contact. T. Pallidum can also be transmitted by vertic ...
... have low level viremia and may not have detectable HBs Ag level, so some centers have started testing antibodies against HBV core protein (anti HBc)6. Syphilis is caused by infection with Treponema pallidum. It is spread primarily through sexual contact. T. Pallidum can also be transmitted by vertic ...
hVIVO notes the initiation of a Phase
... cycle. Scientists suspect that the mosquitoes who take a blood meal from ASG-v-vaccinated participants may have altered behavior that could lead to early death or a reduced ability to reproduce. This would indicate that the experimental vaccine could also hinder disease transmission by controlling t ...
... cycle. Scientists suspect that the mosquitoes who take a blood meal from ASG-v-vaccinated participants may have altered behavior that could lead to early death or a reduced ability to reproduce. This would indicate that the experimental vaccine could also hinder disease transmission by controlling t ...
Unexplained Benefits of Antibiotics in Childhood
... adding amoxicillin or cefdinir to readyto-use therapeutic food regimens for the outpatient treatment of acute severe malnutrition [5]. Why might the addition of azithromycin to chloroquine reduce gut and respiratory infections? It is possible that the illnesses averted in the azithromycin antibiotic ...
... adding amoxicillin or cefdinir to readyto-use therapeutic food regimens for the outpatient treatment of acute severe malnutrition [5]. Why might the addition of azithromycin to chloroquine reduce gut and respiratory infections? It is possible that the illnesses averted in the azithromycin antibiotic ...
UF Bloodborne Pathogen Training
... Acceptance/Declination statement (http://webfiles.ehs.ufl.edu/TNV.pdf) If you decline, can change mind at any time Post-vaccination testing available but only recommended for those at high risk of an exposure ...
... Acceptance/Declination statement (http://webfiles.ehs.ufl.edu/TNV.pdf) If you decline, can change mind at any time Post-vaccination testing available but only recommended for those at high risk of an exposure ...
Curt Canine, Nursing
... Levamisole/Enrofloxacin (300mg•L-1) (medications given topically as bath). Frogs were in medication-free, fresh water at least 8 days before experiments were initiated. Frogs were pithed cerebrally and true capillaries with no rolling or sticking white blood cells (WBC) were cannulated (10mg•ml-1 pi ...
... Levamisole/Enrofloxacin (300mg•L-1) (medications given topically as bath). Frogs were in medication-free, fresh water at least 8 days before experiments were initiated. Frogs were pithed cerebrally and true capillaries with no rolling or sticking white blood cells (WBC) were cannulated (10mg•ml-1 pi ...
288862-Bloodborne Pathogens PowerPoint
... Is transmitted primarily through "blood to blood" contact Symptoms range from flu-like to none at all No symptoms - person is infectious and can spread the disease. Can survive in dried blood and surfaces for up to seven days Hepatitis infects about 300,000 people in USA annually Can lead ...
... Is transmitted primarily through "blood to blood" contact Symptoms range from flu-like to none at all No symptoms - person is infectious and can spread the disease. Can survive in dried blood and surfaces for up to seven days Hepatitis infects about 300,000 people in USA annually Can lead ...
Chapter 10 - Vascular Physiology
... aplastic = destruction of bone marrow (radiation/toxins) Sickle-cell Anemia (SCA) Genetic defect in hemoglobin molecule (Hb-S) that changes 2 amino acids at low very O2 levels, RBC is deformed by changes in hemoglobin molecule within the RBC sickle-shaped cells rupture easily = causing anemia & clot ...
... aplastic = destruction of bone marrow (radiation/toxins) Sickle-cell Anemia (SCA) Genetic defect in hemoglobin molecule (Hb-S) that changes 2 amino acids at low very O2 levels, RBC is deformed by changes in hemoglobin molecule within the RBC sickle-shaped cells rupture easily = causing anemia & clot ...
B2B LA Heme_Onc talk_FinalNA
... – Genetic defect in β-globin genes – Autosomal recessive – Red cell sickle under stress (low pO2, dehydration, fever, acidosis) • Results in infarction of tissue: spleen, lungs, bone, brain, digits – Functional asplenia • Greatest cause of mortality is infection/sepsis – Acute Chest syndrome – Vaso- ...
... – Genetic defect in β-globin genes – Autosomal recessive – Red cell sickle under stress (low pO2, dehydration, fever, acidosis) • Results in infarction of tissue: spleen, lungs, bone, brain, digits – Functional asplenia • Greatest cause of mortality is infection/sepsis – Acute Chest syndrome – Vaso- ...
Bloodborn Pathogens
... Blood borne pathogens are usually transmitted or passed on when disease organisms enter the body through mucus membranes or through breaks in the skin. While intact skin offers some protection against blood borne pathogens, they maybe transmitted through the skin via accidental injection with needle ...
... Blood borne pathogens are usually transmitted or passed on when disease organisms enter the body through mucus membranes or through breaks in the skin. While intact skin offers some protection against blood borne pathogens, they maybe transmitted through the skin via accidental injection with needle ...
Kemmer_Molecular diagnostics
... Clinical manifestations include elevated IgM levels (caused by the antigenic variability of the protozoa—mentioned later), but this can be observed in non-infectious individuals, so are not conclusive. However, normal IgM levels exempt a patient from a positive diagnosis.xxviii Further diagnosis inv ...
... Clinical manifestations include elevated IgM levels (caused by the antigenic variability of the protozoa—mentioned later), but this can be observed in non-infectious individuals, so are not conclusive. However, normal IgM levels exempt a patient from a positive diagnosis.xxviii Further diagnosis inv ...
Agglutination tests:
... similar to the venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test. In this test the reagent contains carbon in addition to cardiolipin to enhance the difference between the negative and the positive reaction. It is a screening test (non specific test) A positive test result may mean you have syp ...
... similar to the venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test. In this test the reagent contains carbon in addition to cardiolipin to enhance the difference between the negative and the positive reaction. It is a screening test (non specific test) A positive test result may mean you have syp ...
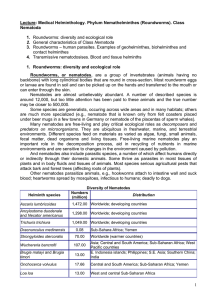
Lecture 13: “Roundworms (Nemathelminthes)
... Life cycle: Infection occurs by ingestion of larvae in poorly cooked meat, which immediately invade intestinal mucosa and sexually differentiate within 18 to 24 hours. The female, after fertilization, burrows deeply in the small intestinal mucosa, whereas the male is dislodged (intestinal stage). O ...
... Life cycle: Infection occurs by ingestion of larvae in poorly cooked meat, which immediately invade intestinal mucosa and sexually differentiate within 18 to 24 hours. The female, after fertilization, burrows deeply in the small intestinal mucosa, whereas the male is dislodged (intestinal stage). O ...
www.leem.org
... most effective solution Pharmaceutical companies increasing its commitment in: ...
... most effective solution Pharmaceutical companies increasing its commitment in: ...
Document
... ¶ Adequate response is anti-HBs 10mIU/mL; inadequate response is anti-HBs<10mIU/mL #The person should be evaluated for antibody response after the vaccine booster dose. For persons who received HBIG, anti-HBs testing should be done when passively acquired antibody from HBIG is no longer detectable ...
... ¶ Adequate response is anti-HBs 10mIU/mL; inadequate response is anti-HBs<10mIU/mL #The person should be evaluated for antibody response after the vaccine booster dose. For persons who received HBIG, anti-HBs testing should be done when passively acquired antibody from HBIG is no longer detectable ...
Infectious mononucleosis
... • Transmitted via contact with body secretions; mainly oropharyngeal secretions (effect is typically on B-cells/lymphocytes). • B-cells spread infection through the entire reticular-endothelial system (lymph, spleen, liver). • B-cells cause a humoral cellular response to the mononucleosis virus (EBV ...
... • Transmitted via contact with body secretions; mainly oropharyngeal secretions (effect is typically on B-cells/lymphocytes). • B-cells spread infection through the entire reticular-endothelial system (lymph, spleen, liver). • B-cells cause a humoral cellular response to the mononucleosis virus (EBV ...
Rh Immune Globulin: Formulations and Indications
... Preventing Rh immunization in an Rh negative recipient of an Rh positive cellular blood component (eg platelets or packed red cells) As little as 100 µl of Rh positive red cells is sufficient to stimulate anti-D in an Rh negative recipient. For women of child bearing age or children, Rh immunization ...
... Preventing Rh immunization in an Rh negative recipient of an Rh positive cellular blood component (eg platelets or packed red cells) As little as 100 µl of Rh positive red cells is sufficient to stimulate anti-D in an Rh negative recipient. For women of child bearing age or children, Rh immunization ...
Bloodborne Pathogens
... 2nd shot is given one month after the 1st 3rd shot follows 5 months after the 2nd. This series gradually builds up the body's immunity to the Hepatitis B virus. ...
... 2nd shot is given one month after the 1st 3rd shot follows 5 months after the 2nd. This series gradually builds up the body's immunity to the Hepatitis B virus. ...
Plasmodium falciparum

Plasmodium falciparum is a protozoan parasite, one of the species of Plasmodium that cause malaria in humans. It is transmitted by the female Anopheles mosquito. Malaria caused by this species (also called malignant or falciparum malaria) is the most dangerous form of malaria, with the highest rates of complications and mortality. As of the latest World Health Organization report in 2014, there were 198 million cases of malaria worldwide in 2013, with an estimated death of 584,000. It is much more prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa than in many other regions of the world; in most African countries, over 75% of cases were due to P. falciparum, whereas in most other countries with malaria transmission, other, less virulent plasmodial species predominate. Almost every malarial death is caused by P. falciparum.