Dr. B ARM WRESTLING LAB BALANCED, UNBALANCED FORCES
... 3) What future question does this leave you with? Could you do anything to improve your results? ...
... 3) What future question does this leave you with? Could you do anything to improve your results? ...
Newton`s Laws
... So, what happens if you are trying to see how fast a force can accelerate a particular mass?? The equation for acceleration is: a=F m But does the equation make sense?? What happens to the acceleration of a bicycle if the force is ...
... So, what happens if you are trying to see how fast a force can accelerate a particular mass?? The equation for acceleration is: a=F m But does the equation make sense?? What happens to the acceleration of a bicycle if the force is ...
Vectors and Newton`s First and Second Laws of Motion
... Compare the strengths of the two horizontal forces -- the back of the seat pushing her forward and the steering wheel pushing her backward (which one is greater, or are they the same?) when ...
... Compare the strengths of the two horizontal forces -- the back of the seat pushing her forward and the steering wheel pushing her backward (which one is greater, or are they the same?) when ...
Car Push Lab - SchemmScience.com
... Initially you will need two people in the car. One of these individuals will call out regular time intervals (2 sec) for which the second person will drop objects outside the car to demarcate its position in time and space. It is critical this ‘dropper’ has placed a mark at t=0 sec. The timer must c ...
... Initially you will need two people in the car. One of these individuals will call out regular time intervals (2 sec) for which the second person will drop objects outside the car to demarcate its position in time and space. It is critical this ‘dropper’ has placed a mark at t=0 sec. The timer must c ...
Newton`s laws of motion
... • Laws of motion, can be used to analyze motion of ordinary objects. • Not valid for speeds close to the speed of light. Need to use the theory of relativity. • Not valid for atomic sized particles. Need to use quantum mechanics. ...
... • Laws of motion, can be used to analyze motion of ordinary objects. • Not valid for speeds close to the speed of light. Need to use the theory of relativity. • Not valid for atomic sized particles. Need to use quantum mechanics. ...
1) You push your lawnmower (mass = 15 kg) across
... Sum of the forces in the x-direction. What is the value of the frictional force opposing the motion? c. If the frictional force were suddenly reduced to zero, what would happen to the broom? 6) Derive the “a” acceleration system and the Tension (T) in terms of m, g, θ. ...
... Sum of the forces in the x-direction. What is the value of the frictional force opposing the motion? c. If the frictional force were suddenly reduced to zero, what would happen to the broom? 6) Derive the “a” acceleration system and the Tension (T) in terms of m, g, θ. ...
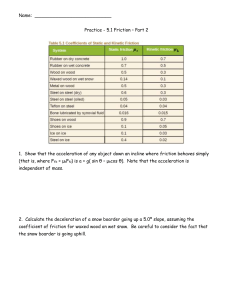
Name: Practice - 5.1 Friction – Part 2 1. Show that the acceleration of
... 2. Calculate the deceleration of a snow boarder going up a 5.0º slope, assuming the coefficient of friction for waxed wood on wet snow. Be careful to consider the fact that the snow boarder is going uphill. ...
... 2. Calculate the deceleration of a snow boarder going up a 5.0º slope, assuming the coefficient of friction for waxed wood on wet snow. Be careful to consider the fact that the snow boarder is going uphill. ...
SESSION 5
... There are 2 external forces acting on the stone. The tension in the string and the weight of the stone. As the stone swings around the direction of the weight force always points down but the direction of the tension changes. We have drawn free-body diagrams for 2 instances, when the stone is at the ...
... There are 2 external forces acting on the stone. The tension in the string and the weight of the stone. As the stone swings around the direction of the weight force always points down but the direction of the tension changes. We have drawn free-body diagrams for 2 instances, when the stone is at the ...
VI. Newton`s Third Law
... forces are equal and opposite but act on different objects they are not “balanced forces” the movement of the horse depends on the forces acting on the horse ...
... forces are equal and opposite but act on different objects they are not “balanced forces” the movement of the horse depends on the forces acting on the horse ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion - Mrs. Robbins Earth Science
... An object that is not moving is said to be at rest. Newton’s 1st Law says that objects will stay at rest unless acted by an unbalanced force. Objects will not start to move until a push or pull is exerted on them. ...
... An object that is not moving is said to be at rest. Newton’s 1st Law says that objects will stay at rest unless acted by an unbalanced force. Objects will not start to move until a push or pull is exerted on them. ...
MidTermReview - Milan Area Schools
... 28. What is an action/reaction pair of forces? 29. Give an example of Newton’s 1st Law 30. Give an example of Newton’s 2nd Law 31. give an example of Newton’s 3rd Law 32. What is the weight of a 10 kg dog? A 75 kg table? 33. What is the normal force on the 10 kg dog? The 75 kg Table? 34. What is the ...
... 28. What is an action/reaction pair of forces? 29. Give an example of Newton’s 1st Law 30. Give an example of Newton’s 2nd Law 31. give an example of Newton’s 3rd Law 32. What is the weight of a 10 kg dog? A 75 kg table? 33. What is the normal force on the 10 kg dog? The 75 kg Table? 34. What is the ...
1st term exam solutions
... plane pointing up the plane. Which of the following statements is true? a. As the magnitude of the applied force increases, the frictional force never changes direction. b. As the magnitude of the applied force increases, the frictional force goes from pointing down to pointing up the plane. c. As t ...
... plane pointing up the plane. Which of the following statements is true? a. As the magnitude of the applied force increases, the frictional force never changes direction. b. As the magnitude of the applied force increases, the frictional force goes from pointing down to pointing up the plane. c. As t ...