Newton*s Second Law
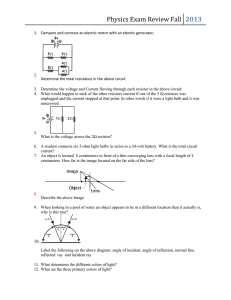
... 4. Two forces of 6 N and 3 N act upon an object in opposite directions. What is the net force acting on the object? (See image below) a. 3 N to the left b. 3 N to the right c. 9 N to the left d. 9 N to the right ...
... 4. Two forces of 6 N and 3 N act upon an object in opposite directions. What is the net force acting on the object? (See image below) a. 3 N to the left b. 3 N to the right c. 9 N to the left d. 9 N to the right ...
OLE11_SCIIPC_TX_04D_TB_1
... 2010 TEKS 4D falls under science concept statement 4: The student knows concepts of force and motion evident in everyday life. In this context, students will come to understand how to describe and measure the motion of an object. In addition, students will learn how an object’s motion is affected by ...
... 2010 TEKS 4D falls under science concept statement 4: The student knows concepts of force and motion evident in everyday life. In this context, students will come to understand how to describe and measure the motion of an object. In addition, students will learn how an object’s motion is affected by ...
Document
... d) Students should use their experiment and Newton’s 2nd law to base their prediction. The prediction should be quantitative. e) Newton’s 2nd law is the hypothesis mathematically it states: a = ΣF/m . The prediction should be qualitative or quantitative based on the experiment if Newton’s 2nd law is ...
... d) Students should use their experiment and Newton’s 2nd law to base their prediction. The prediction should be quantitative. e) Newton’s 2nd law is the hypothesis mathematically it states: a = ΣF/m . The prediction should be qualitative or quantitative based on the experiment if Newton’s 2nd law is ...
4.2.2 Newton`s Laws - Renton School District
... 2. If the force remains constant and the mass changes, what happens to the acceleration? ...
... 2. If the force remains constant and the mass changes, what happens to the acceleration? ...
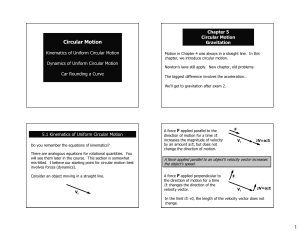
Circular Motion
... The force that accelerates the ball is the tension in the string to which it is attached. The centripetal force due to the string gives rise to a centripetal (also called radial) acceleration. If the ball moves uniformly in a circle, both the force and acceleration continually change direction, so ...
... The force that accelerates the ball is the tension in the string to which it is attached. The centripetal force due to the string gives rise to a centripetal (also called radial) acceleration. If the ball moves uniformly in a circle, both the force and acceleration continually change direction, so ...
Forces and motion
... experiences. For instance, calculating the force acting between the floor of a lift and their feet when the lift is moving upwards and decelerating lets them interpret the ‘light’ feeling they have all experienced in that situation. Good diagrams are always helpful (and often essential) so students ...
... experiences. For instance, calculating the force acting between the floor of a lift and their feet when the lift is moving upwards and decelerating lets them interpret the ‘light’ feeling they have all experienced in that situation. Good diagrams are always helpful (and often essential) so students ...
(field forces: magnetic force, gravitational force).
... the Earth attracts the body. Weight (a vector quantity) is different from mass (a scalar quantity). The weight of a body varies with its location near the Earth (or other astronomical body), whereas its mass is the same everywhere in the universe. The weight of a body is the force that causes it to ...
... the Earth attracts the body. Weight (a vector quantity) is different from mass (a scalar quantity). The weight of a body varies with its location near the Earth (or other astronomical body), whereas its mass is the same everywhere in the universe. The weight of a body is the force that causes it to ...
Slide 1
... The net force Fnet acting on a body is equal to the product of the body mass m and its acceleration a Fnet = ma; a= Fnet / m Acceleration component along a given axis is caused only by sum of forces component along that axis ax = Fnet,x /m ; ay = Fnet,y /m ; az = Fnet,z /m SI unit of force New ...
... The net force Fnet acting on a body is equal to the product of the body mass m and its acceleration a Fnet = ma; a= Fnet / m Acceleration component along a given axis is caused only by sum of forces component along that axis ax = Fnet,x /m ; ay = Fnet,y /m ; az = Fnet,z /m SI unit of force New ...
Forces & Newton`s Laws
... – Imagine a rocket is being launched from the earth. Hot gases are pushed out from the bottom of the rocket as the rocket is thrust upward. The force of the gases pushing against the surface of the earth is equal and opposite to the force with which the rocket moves upward ...
... – Imagine a rocket is being launched from the earth. Hot gases are pushed out from the bottom of the rocket as the rocket is thrust upward. The force of the gases pushing against the surface of the earth is equal and opposite to the force with which the rocket moves upward ...
Pretest Forces
... ______ 3. Any change in an object’s motion is called a. momentum. c. a force. b. an acceleration. d. velocity. ______ 4. Changes in an object’s motion are caused by a. a balanced force. c. an unbalanced force. b. an acceleration. d. opposing forces. ______ 5. The gravitational force between two obje ...
... ______ 3. Any change in an object’s motion is called a. momentum. c. a force. b. an acceleration. d. velocity. ______ 4. Changes in an object’s motion are caused by a. a balanced force. c. an unbalanced force. b. an acceleration. d. opposing forces. ______ 5. The gravitational force between two obje ...
Force Problems #3
... 12. Refer back to the box in question 11. What is the acceleration of the box? 13. Refer back to the box in question 11. Which of the following could possibly be the velocity of the box? A. 8.5m/s B. 2.2m/s C. 16m/s D. 0m/s 14. What is the mass of a cannon projectile that is accelerated at 220m/s/s ...
... 12. Refer back to the box in question 11. What is the acceleration of the box? 13. Refer back to the box in question 11. Which of the following could possibly be the velocity of the box? A. 8.5m/s B. 2.2m/s C. 16m/s D. 0m/s 14. What is the mass of a cannon projectile that is accelerated at 220m/s/s ...
Circular Motion - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Apparent Weight: This is a consequence of your inertia. When an elevator, jet airplane, rocket, etc. accelerates upward the passenger wants to stay put due to inertia and is pulled down by gravity. The elevator pushes up and you feel heavier. Add the acceleration of the elevator to the acceleration ...
... Apparent Weight: This is a consequence of your inertia. When an elevator, jet airplane, rocket, etc. accelerates upward the passenger wants to stay put due to inertia and is pulled down by gravity. The elevator pushes up and you feel heavier. Add the acceleration of the elevator to the acceleration ...
CP Review Sheet Newton`s Laws
... of the apple is a different story. It may weigh exactly 1.0 N in San Francisco and slightly less in mile-high Denver, Colorado. On the surface of the moon the apple would weigh 0.17 N and far out in outer-space it may have almost no weight at all. The quantity that does not change with location is ( ...
... of the apple is a different story. It may weigh exactly 1.0 N in San Francisco and slightly less in mile-high Denver, Colorado. On the surface of the moon the apple would weigh 0.17 N and far out in outer-space it may have almost no weight at all. The quantity that does not change with location is ( ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide
... 4) Give two examples of centripetal forces. Describe the situation in which they serve as centripetal forces. 5) How do we define the period of an object’s rotation? 6) What are the two things an object wants to do as it moves around a circular path? What will determine which of these two things act ...
... 4) Give two examples of centripetal forces. Describe the situation in which they serve as centripetal forces. 5) How do we define the period of an object’s rotation? 6) What are the two things an object wants to do as it moves around a circular path? What will determine which of these two things act ...
Sections 13.1-13.4 - University of Mary Hardin–Baylor
... force acts on the particle, the equation of motion can be written F = FR = ma where FR is the resultant force, which is a vector summation of all the forces. To illustrate the equation, consider a particle acted on by two forces. First, draw the particle’s free-body diagram, showing all forces acti ...
... force acts on the particle, the equation of motion can be written F = FR = ma where FR is the resultant force, which is a vector summation of all the forces. To illustrate the equation, consider a particle acted on by two forces. First, draw the particle’s free-body diagram, showing all forces acti ...
Newton`s Second Law - Philadelphia University
... force acts on the particle, the equation of motion can be written F = FR = ma where FR is the resultant force, which is a vector summation of all the forces. To illustrate the equation, consider a particle acted on by two forces. First, draw the particle’s free-body diagram, showing all forces acti ...
... force acts on the particle, the equation of motion can be written F = FR = ma where FR is the resultant force, which is a vector summation of all the forces. To illustrate the equation, consider a particle acted on by two forces. First, draw the particle’s free-body diagram, showing all forces acti ...