Newton`s 2nd Law
... For example, weight (force of gravity) for 1 kg is ( 9.8 Newtons ) = ( 1 kg ) X ( 9.8 m/s2 ) ...
... For example, weight (force of gravity) for 1 kg is ( 9.8 Newtons ) = ( 1 kg ) X ( 9.8 m/s2 ) ...
document
... "The net force is always the important thing. If the net force is zero, then Newton's Second Law (and Newton's First Law, too) says that the acceleration of the wagon must be zero." "Yes, I remember Newton's Second Law very well, Old Dobbin.", says Farmer Brown, hopefully. "This physics discussion i ...
... "The net force is always the important thing. If the net force is zero, then Newton's Second Law (and Newton's First Law, too) says that the acceleration of the wagon must be zero." "Yes, I remember Newton's Second Law very well, Old Dobbin.", says Farmer Brown, hopefully. "This physics discussion i ...
centripetal force
... Second Law says that if an object is accelerating, there must be a net force on it. For an object moving in a circle, this is called the centripetal force. centripetal force points toward the center of the circle. ...
... Second Law says that if an object is accelerating, there must be a net force on it. For an object moving in a circle, this is called the centripetal force. centripetal force points toward the center of the circle. ...
General Physics I (PHYS 203) Fall 2006 Name: Exam 3: November
... direction points vertically upward. Determine the initial kinetic energy of the ball. Determine the work done by air resistance. ...
... direction points vertically upward. Determine the initial kinetic energy of the ball. Determine the work done by air resistance. ...
the File
... A. The force of gravity is the pulling force of every object on every other object. B. You can’t see the force of gravity but you can see what it does. 1. The force of gravity affects all objects, because all objects have mass. ...
... A. The force of gravity is the pulling force of every object on every other object. B. You can’t see the force of gravity but you can see what it does. 1. The force of gravity affects all objects, because all objects have mass. ...
The First Law of Motion
... An object will always have the same MASS (amount of matter) no matter where that object is….Translation: __________ STAYS THE ____________! An object’s WEIGHT (mass + force of gravity) may be different in different places in the universe because of different forces of ...
... An object will always have the same MASS (amount of matter) no matter where that object is….Translation: __________ STAYS THE ____________! An object’s WEIGHT (mass + force of gravity) may be different in different places in the universe because of different forces of ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... • A force is what we call a push or a pull, or any action that has the ability to change motion of an object. • The metric unit used to describe force is called the Newton (N). One Newton is equal to: 1 Kg x 1 m/s/s Thus, one Newton of force causes a one kilogram object to accelerate at a rate of on ...
... • A force is what we call a push or a pull, or any action that has the ability to change motion of an object. • The metric unit used to describe force is called the Newton (N). One Newton is equal to: 1 Kg x 1 m/s/s Thus, one Newton of force causes a one kilogram object to accelerate at a rate of on ...
5-4 Forces and Circular Motion
... 5-2 Friction •Kinetic frictional force is somewhat smaller than static, so that when object begins to move it accelerates if force stays constant. • Otherwise can lessen force to maintain constant speed. ...
... 5-2 Friction •Kinetic frictional force is somewhat smaller than static, so that when object begins to move it accelerates if force stays constant. • Otherwise can lessen force to maintain constant speed. ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion
... Two teams are playing tug of war. They are both exerting equal force on the rope in opposite directions. This balanced force results in no change of motion. ...
... Two teams are playing tug of war. They are both exerting equal force on the rope in opposite directions. This balanced force results in no change of motion. ...
m/s
... A group of animals are playing tug-of-war. The elephants pull the rope with a force of 100N to the left. The donkeys pull the rope with a force of 105N to the right. Which way will the rope accelerate? To the RIGHT ...
... A group of animals are playing tug-of-war. The elephants pull the rope with a force of 100N to the left. The donkeys pull the rope with a force of 105N to the right. Which way will the rope accelerate? To the RIGHT ...
Newton`s Laws
... An English Mathematician and Physicist that formulated the three laws of motion, law of universal gravitation and invented calculus before the age of 30 Newton’s discoveries helped to answer many questions such as: what causes tides, how do the planets move and why do objects of different masses fal ...
... An English Mathematician and Physicist that formulated the three laws of motion, law of universal gravitation and invented calculus before the age of 30 Newton’s discoveries helped to answer many questions such as: what causes tides, how do the planets move and why do objects of different masses fal ...
Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Balanced Forces But what
... Since these two forces are of equal magnitude and in opposite directions, they balance each other. The book is said to be at equilibrium. There is no unbalanced force acting upon the book and thus the book maintains its state of motion. When all the forces acting upon an object balance each other, t ...
... Since these two forces are of equal magnitude and in opposite directions, they balance each other. The book is said to be at equilibrium. There is no unbalanced force acting upon the book and thus the book maintains its state of motion. When all the forces acting upon an object balance each other, t ...
Name of Model
... c. Is the car accelerating? What direction is the car's acceleration? (Explain how you know.) ...
... c. Is the car accelerating? What direction is the car's acceleration? (Explain how you know.) ...
Physics_Chapter_5
... How much force is required to move a 4000 kg mass 2 m/s²? A) 2000 N B) 4000 N C) 8000 N D) 16,000 N ...
... How much force is required to move a 4000 kg mass 2 m/s²? A) 2000 N B) 4000 N C) 8000 N D) 16,000 N ...
Teaching Forces - Education Scotland
... NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION 1. An object will stay at rest, or move at a constant speed, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
... NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION 1. An object will stay at rest, or move at a constant speed, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
Circular
... 9. A rock is tied to a string and swung in a clockwise, vertical circle. When the rock is at the position shown, which of the following indicates the direction of vT (tangential velocity), aC (centripetal acceleration), and/or FW (weight)? Which represents the greatest centripetal acceleration? ...
... 9. A rock is tied to a string and swung in a clockwise, vertical circle. When the rock is at the position shown, which of the following indicates the direction of vT (tangential velocity), aC (centripetal acceleration), and/or FW (weight)? Which represents the greatest centripetal acceleration? ...
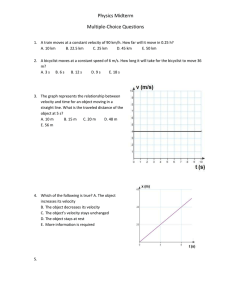
Honors Physics: Practice Problems for Midterm
... is 12.0 m/s, how far from the cliff edge does the stone land? e) What is the initial velocity of the stone? 5. A 15 g ball is released from rest 50. m above the Earth’s surface. What is its velocity just before it hits the ground? 6. A 110.0 kg crate is pulled at constant speed along a horizontal pl ...
... is 12.0 m/s, how far from the cliff edge does the stone land? e) What is the initial velocity of the stone? 5. A 15 g ball is released from rest 50. m above the Earth’s surface. What is its velocity just before it hits the ground? 6. A 110.0 kg crate is pulled at constant speed along a horizontal pl ...