Newton`s Laws and Motion Air resistance
... 1. What acceleration will result when a 12 N net force applied to a 3 kg object? 12 N = 3 kg x 4 m/s/s 2. A net force of 16 N causes a mass to accelerate at a rate of 5 m/s2. Determine the mass. 16 N = 3.2 kg x 5 m/s/s 3. How much force is needed to accelerate a 66 kg skier 1 m/sec/sec? 66 kg-m/sec/ ...
... 1. What acceleration will result when a 12 N net force applied to a 3 kg object? 12 N = 3 kg x 4 m/s/s 2. A net force of 16 N causes a mass to accelerate at a rate of 5 m/s2. Determine the mass. 16 N = 3.2 kg x 5 m/s/s 3. How much force is needed to accelerate a 66 kg skier 1 m/sec/sec? 66 kg-m/sec/ ...
Section 7
... Objects with masses of 200 kg and 500 kg are separated by 0.400 m. (a) Find the net gravitational force exerted by these objects on a 50.0-kg object placed midway between them. (b) At what position (other than infinitely remote ones) can the 50.0-kg object be placed so as to experience a net force o ...
... Objects with masses of 200 kg and 500 kg are separated by 0.400 m. (a) Find the net gravitational force exerted by these objects on a 50.0-kg object placed midway between them. (b) At what position (other than infinitely remote ones) can the 50.0-kg object be placed so as to experience a net force o ...
Content Area: Newtonian Mechanics Unit: 5 Topic (s): Circular
... 1) The Amazing Rando (m=85kg) is swinging through the air with the greatest of ease on a flying trapeze that has a string length of 3.1m. (a) What is the period of Rando's oscillation? (b) If the Amazing Rando was to sit on a seat that was attached to a spring, what would the spring constant need to ...
... 1) The Amazing Rando (m=85kg) is swinging through the air with the greatest of ease on a flying trapeze that has a string length of 3.1m. (a) What is the period of Rando's oscillation? (b) If the Amazing Rando was to sit on a seat that was attached to a spring, what would the spring constant need to ...
Forces Weight and Normal Force
... • 3. A force of 40 Nt applied horizontally is required to push a 20 kg box at constant velocity across the floor. What is the coefficient of friction between the box and the floor? • 4. A 100 Nt box is moving on a horizontal surface. A force of 10 Nt applied parallel to the surface is required to ke ...
... • 3. A force of 40 Nt applied horizontally is required to push a 20 kg box at constant velocity across the floor. What is the coefficient of friction between the box and the floor? • 4. A 100 Nt box is moving on a horizontal surface. A force of 10 Nt applied parallel to the surface is required to ke ...
Vector Applications
... Draw a figure to solve each of the following problems on a inclined plane. 5. What is the weight of a car sitting on a 14 slope if the force required to push the car up the hill is 750 pounds.? 6. What is the force required to push a 40 pound lawn mower up a hill inclined at 8? 7. A 3000 pound car ...
... Draw a figure to solve each of the following problems on a inclined plane. 5. What is the weight of a car sitting on a 14 slope if the force required to push the car up the hill is 750 pounds.? 6. What is the force required to push a 40 pound lawn mower up a hill inclined at 8? 7. A 3000 pound car ...
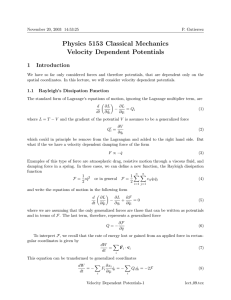
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics Velocity Dependent Potentials
... A potential that satisfies this condition, also allows the Lagrange equations to be put into the same form as Eq. 11 ...
... A potential that satisfies this condition, also allows the Lagrange equations to be put into the same form as Eq. 11 ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... • Newton’s law of universal gravitation describes the gravitational attraction between bodies with mass, the earth and moon for example. • Newton’s three laws of motion relate the forces acting on a body to its motion. The first is the law of inertia, it states that ‘every object in motion will stay ...
... • Newton’s law of universal gravitation describes the gravitational attraction between bodies with mass, the earth and moon for example. • Newton’s three laws of motion relate the forces acting on a body to its motion. The first is the law of inertia, it states that ‘every object in motion will stay ...
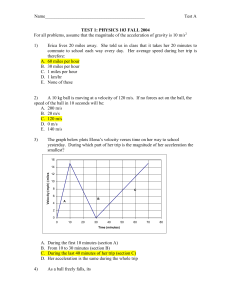
SAMPLE TEST 1: PHYSICS 103
... magnitude 200 N. The elephant moves with a constant forward acceleration. Which statement is most true about the magnitude of the force of kinetic friction acting on the elephant? A. It is greater than 200 N B. It is less than 200 N C. It is equal to 200 N D. None of the above are necessarily true ...
... magnitude 200 N. The elephant moves with a constant forward acceleration. Which statement is most true about the magnitude of the force of kinetic friction acting on the elephant? A. It is greater than 200 N B. It is less than 200 N C. It is equal to 200 N D. None of the above are necessarily true ...
Work PRobs - New Haven Science
... on you by the force of gravity as you ride the elevator from the top floor to the ground floor? 2. In 1985 in San Antonio, Texas, an entire hotel building was moved several blocks on 36 dollies. The mass of the building was about 1.45 *106 kg. Suppose the amount of work done on the building was 100 ...
... on you by the force of gravity as you ride the elevator from the top floor to the ground floor? 2. In 1985 in San Antonio, Texas, an entire hotel building was moved several blocks on 36 dollies. The mass of the building was about 1.45 *106 kg. Suppose the amount of work done on the building was 100 ...
Motion and forces introduction PowerPoint
... An astronaut has less mass on the moon since the moon exerts a weaker gravitational force. ...
... An astronaut has less mass on the moon since the moon exerts a weaker gravitational force. ...
Newton`s 1st Law
... Two teams are playing tug of war. They are both exerting equal force on the rope in opposite directions. This balanced force results in no change of motion. Any change in the balance would mean that there is now an unbalanced force at work! ...
... Two teams are playing tug of war. They are both exerting equal force on the rope in opposite directions. This balanced force results in no change of motion. Any change in the balance would mean that there is now an unbalanced force at work! ...
Newton`s Laws Study Guide
... 25. What is the mass of the object represented in the following graph? ...
... 25. What is the mass of the object represented in the following graph? ...
Honors Physics - Practice Final Exam
... circular path. If the maximum tension that the string can withstand is 350 N, what is the maximum speed of the mass if the string is not to break? A. 700 m/s C. 19 m/s B. 26 m/s D. 13 m/s 54. An object moves in a circular path at a constant speed. Consider the direction of the object’s velocity and ...
... circular path. If the maximum tension that the string can withstand is 350 N, what is the maximum speed of the mass if the string is not to break? A. 700 m/s C. 19 m/s B. 26 m/s D. 13 m/s 54. An object moves in a circular path at a constant speed. Consider the direction of the object’s velocity and ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... 2. Use one of Newton’s laws to explain how the seat belt stopped the driver’s body from moving too far forward. Newton’s third law says that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. The driver’s body exerted an action force on the seat belt. The seat belt exerted a reac ...
... 2. Use one of Newton’s laws to explain how the seat belt stopped the driver’s body from moving too far forward. Newton’s third law says that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. The driver’s body exerted an action force on the seat belt. The seat belt exerted a reac ...
Sects. 6.5 through 6.9
... A particle is attached between two identical springs on a horizontal frictionless table. Both springs have spring constant k and are initially unstressed. (a) The particle is pulled a distance x along a direction perpendicular to the initial configuration of the springs. Show that the force exerted ...
... A particle is attached between two identical springs on a horizontal frictionless table. Both springs have spring constant k and are initially unstressed. (a) The particle is pulled a distance x along a direction perpendicular to the initial configuration of the springs. Show that the force exerted ...
amanda`sGravity and Free Fall
... Orbiting objects are in free fall Why do astronauts appear to “float” in a space shuttle? Is it because they are weightless in space? The gravitational force will be there, though almost undetectable in space, because it is so far away, but nothing can ever be weightless. You would still have mass. ...
... Orbiting objects are in free fall Why do astronauts appear to “float” in a space shuttle? Is it because they are weightless in space? The gravitational force will be there, though almost undetectable in space, because it is so far away, but nothing can ever be weightless. You would still have mass. ...
Dag Force and Terminal Speed
... – and are generally proportional to the square of the speed of the object •So, as falling object accelerates, drag force gets bigger and bigger, until it is equal to accelerating force •At this point, the net force on the object is zero, and it moves at a constant velocity from then on; this is call ...
... – and are generally proportional to the square of the speed of the object •So, as falling object accelerates, drag force gets bigger and bigger, until it is equal to accelerating force •At this point, the net force on the object is zero, and it moves at a constant velocity from then on; this is call ...