Forces and Motion
... the positive protons from repelling each other and destroying the atom – Strong nuclear force acts only on neutrons and protons in a nucleus – holds them together. Acts at a longer range than weak nuclear forces. – Weak nuclear force acts only over a short range ...
... the positive protons from repelling each other and destroying the atom – Strong nuclear force acts only on neutrons and protons in a nucleus – holds them together. Acts at a longer range than weak nuclear forces. – Weak nuclear force acts only over a short range ...
PY1052 Problem Set 3 – Autumn 2004 Solutions
... mass of 4.5 kg. The coefficient of static friction between A and the table is µs = 0.20, and the corresponding coefficient of kinetic friction is µ k = 0.15. (a) Does the block move? What is the friction force felt by the block? Now a force F2 = 25 N is exerted horizontally on block A. (b) What is t ...
... mass of 4.5 kg. The coefficient of static friction between A and the table is µs = 0.20, and the corresponding coefficient of kinetic friction is µ k = 0.15. (a) Does the block move? What is the friction force felt by the block? Now a force F2 = 25 N is exerted horizontally on block A. (b) What is t ...
Unit 2 Section 4 Notes Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Astronauts in space appear to be “weightless”. This statement is NOT true because gravity exists everywhere in the universe; it is the force of attraction between 2 objects due to mass. Astronauts in orbit experience apparent weightlessness because they are in free fall. The astronauts and vehicle ...
... Astronauts in space appear to be “weightless”. This statement is NOT true because gravity exists everywhere in the universe; it is the force of attraction between 2 objects due to mass. Astronauts in orbit experience apparent weightlessness because they are in free fall. The astronauts and vehicle ...
physics_11_review_be.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
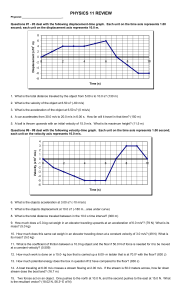
... 16. A 3.0- kg mass is accelerated from rest at a rate of 3.0 m/s2. After 20.0 meters how much kinetic energy does the mass have? (180 J) 18. A water wave passes a raft. If the distance between 2 crests is 10.0 meters, and it takes the wave 20.0 seconds to travel 15.0 meters. What is the frequency of ...
... 16. A 3.0- kg mass is accelerated from rest at a rate of 3.0 m/s2. After 20.0 meters how much kinetic energy does the mass have? (180 J) 18. A water wave passes a raft. If the distance between 2 crests is 10.0 meters, and it takes the wave 20.0 seconds to travel 15.0 meters. What is the frequency of ...
chp. 8
... a falling object, when the force of air resistance becomes equal to the gravitational force on the object it stops ...
... a falling object, when the force of air resistance becomes equal to the gravitational force on the object it stops ...
Glossary of Terms Handout
... on the imaginary "mean sun," which averages out the effects on the length of the solar day caused by Earth's slightly non-circular orbit about the sun. UT is not updated with leap seconds as is UTC. UV -- Ultraviolet (meaning "above violet") radiation. Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood o ...
... on the imaginary "mean sun," which averages out the effects on the length of the solar day caused by Earth's slightly non-circular orbit about the sun. UT is not updated with leap seconds as is UTC. UV -- Ultraviolet (meaning "above violet") radiation. Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood o ...
Forces and The Laws of Motion
... • Bodies at rest will stay at rest and bodies in motion will stay in straight-line motion at a constant speed if no net force is present ...
... • Bodies at rest will stay at rest and bodies in motion will stay in straight-line motion at a constant speed if no net force is present ...
Unit A: Kinematics Exam
... When talking about vertical circular motion we often refer to scenarios dealing with roller coasters or a bucket swinging Things to remember: - Gravity will always act downwards at the same force - Normal force will always be perpendicular from its surface - Tension will always be towards the center ...
... When talking about vertical circular motion we often refer to scenarios dealing with roller coasters or a bucket swinging Things to remember: - Gravity will always act downwards at the same force - Normal force will always be perpendicular from its surface - Tension will always be towards the center ...
Goal: To understand how Galileo and Newton used experimentation
... More concepts • You are in a space craft which is over a trillion miles from the closest star (so that means there is very little gravity on you) traveling at a speed of 2 miles per second. • If you run out of “gas” so to speak, what will happen to your spacecraft and why? • How far do you think yo ...
... More concepts • You are in a space craft which is over a trillion miles from the closest star (so that means there is very little gravity on you) traveling at a speed of 2 miles per second. • If you run out of “gas” so to speak, what will happen to your spacecraft and why? • How far do you think yo ...
Chapter 2 - Forces In Motion
... All forces act in pairs called action-reaction force pairs If a force is exerted, another force occurs that is equal in size and opposite in direction to the first. ...
... All forces act in pairs called action-reaction force pairs If a force is exerted, another force occurs that is equal in size and opposite in direction to the first. ...
5. Universal Laws of Motion
... • As objects fall, they accelerate. • The acceleration due to Earth’s gravity is 10 m/s each second, or g = 10 m/s2. • The higher you drop the ball, the greater its velocity will be at impact. ...
... • As objects fall, they accelerate. • The acceleration due to Earth’s gravity is 10 m/s each second, or g = 10 m/s2. • The higher you drop the ball, the greater its velocity will be at impact. ...
South Pasadena · AP Chemistry
... The speed of an object dropped in air will continue to increase without limit until it strikes the ground. Explain why this statement is true or why it is false. ...
... The speed of an object dropped in air will continue to increase without limit until it strikes the ground. Explain why this statement is true or why it is false. ...
Bell Work 2/23/10
... Inertia depends on an object’s mass. The more mass an object has, the more inertia an object has. ...
... Inertia depends on an object’s mass. The more mass an object has, the more inertia an object has. ...