Today`s Powerpoint
... Newton’s laws of motion explain how objects interact with the world and with each other. Newton’s first law: An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object will move in a straight line at constant speed if and only if the sum of forces that act on it are balanced. ...
... Newton’s laws of motion explain how objects interact with the world and with each other. Newton’s first law: An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object will move in a straight line at constant speed if and only if the sum of forces that act on it are balanced. ...
CCA Review - Net Start Class
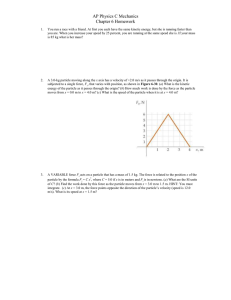
... 13. A crate has a weight of 56 N. What is the mass of the crate? 14. To accelerate at 300 m/s2 what size force has to be applied to a 60 kg rock? 15. An object is acted on with 45N of force to the left and 30N of force to the right. Draw a free body diagram and give the net force on the object. 16. ...
... 13. A crate has a weight of 56 N. What is the mass of the crate? 14. To accelerate at 300 m/s2 what size force has to be applied to a 60 kg rock? 15. An object is acted on with 45N of force to the left and 30N of force to the right. Draw a free body diagram and give the net force on the object. 16. ...
Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion
... constant velocity throughout all three turns. At which turn will there be the greatest centripetal acceleration? If the bobsled moves at 35 m/s throughout the course and turn B has a radius of 20m and turn C is 50m how many G’s of acceleration is the sledder feeling through turns B & C ? ...
... constant velocity throughout all three turns. At which turn will there be the greatest centripetal acceleration? If the bobsled moves at 35 m/s throughout the course and turn B has a radius of 20m and turn C is 50m how many G’s of acceleration is the sledder feeling through turns B & C ? ...
Laws of Motion Notes
... For every action force there is an equal in magnitude but opposite in direction reaction force. - Force pairs, actions and reactions, come from interactions - Interaction: two surfaces come in contact with one another - For example: There is an interaction occurring right now between the chair and y ...
... For every action force there is an equal in magnitude but opposite in direction reaction force. - Force pairs, actions and reactions, come from interactions - Interaction: two surfaces come in contact with one another - For example: There is an interaction occurring right now between the chair and y ...
What are Forces?
... What is the difference between mass and weight? • Mass is the amount of matter in an object. This does not change in an object as it moves away from the earth. • Weight is caused by gravity. Therefore, the greater the distance, the less the force of attraction. The less the distance the greater the ...
... What is the difference between mass and weight? • Mass is the amount of matter in an object. This does not change in an object as it moves away from the earth. • Weight is caused by gravity. Therefore, the greater the distance, the less the force of attraction. The less the distance the greater the ...
Why do things move? - USU Department of Physics
... • ‘I’ is a measure of the resistance of an object to change in its rotational motion. ...
... • ‘I’ is a measure of the resistance of an object to change in its rotational motion. ...
FORCE & MOTION
... force acting on an object the object remains at rest, OR, if the object is already moving, it continues to move in a straight line with constant speed. • A Force does not need to be constantly applied to an object to keep it moving. • The motion of an object does not change until an unbalanced force ...
... force acting on an object the object remains at rest, OR, if the object is already moving, it continues to move in a straight line with constant speed. • A Force does not need to be constantly applied to an object to keep it moving. • The motion of an object does not change until an unbalanced force ...
Problem set 13
... (b) h3i Suppose I1 → I3 so that the symmetric top becomes a spherical top. Based on our study of the spherical top, what do you expect to happen to α? Is this expectation fulfilled by the above formula for α? (c) h3i It can be shown that to take the limit of a rigid rotator (starting from a symmetri ...
... (b) h3i Suppose I1 → I3 so that the symmetric top becomes a spherical top. Based on our study of the spherical top, what do you expect to happen to α? Is this expectation fulfilled by the above formula for α? (c) h3i It can be shown that to take the limit of a rigid rotator (starting from a symmetri ...
Forces and Newton`s 3 Laws of Motion
... Contact Forces • Those types of forces which result when the two interacting objects are perceived to be physically contacting each other. Examples of contact forces include frictional forces, tensional forces, normal forces, air resistance forces, and applied forces. • Contact Forces – Frictional ...
... Contact Forces • Those types of forces which result when the two interacting objects are perceived to be physically contacting each other. Examples of contact forces include frictional forces, tensional forces, normal forces, air resistance forces, and applied forces. • Contact Forces – Frictional ...
Forces and Motion
... usually have less friction than rough surfaces. Friction increases when surfaces are pressed together with greater force. Friction also increases with the weight of an object. ...
... usually have less friction than rough surfaces. Friction increases when surfaces are pressed together with greater force. Friction also increases with the weight of an object. ...
Chapter Eight
... arms have a mass of 5 kg each with the center of mass at 0.4 m from her body. She starts to turn at 0.5 rev/sec on the point of her skate with her arms outstretched. She then pulls her arms inward so that their center of mass is at the axis of her body, r = 0. What will be her speed of rotation? ...
... arms have a mass of 5 kg each with the center of mass at 0.4 m from her body. She starts to turn at 0.5 rev/sec on the point of her skate with her arms outstretched. She then pulls her arms inward so that their center of mass is at the axis of her body, r = 0. What will be her speed of rotation? ...
Chapter 6 Topics - JBHA-Sci-US-tri3
... 16. (6.4)When a cannon is fired, how does the size of the force of the cannon on the cannonball compare with the force of the cannonball on the cannon? How does the acceleration of the cannon compare with that of the cannonball? Explain 17. (6.4) how can a rocket be propelled above the atmosphere wh ...
... 16. (6.4)When a cannon is fired, how does the size of the force of the cannon on the cannonball compare with the force of the cannonball on the cannon? How does the acceleration of the cannon compare with that of the cannonball? Explain 17. (6.4) how can a rocket be propelled above the atmosphere wh ...