Motion in Two Dimensions
... A net torque would produce an angular acceleration. An object spinning at a constant rate will accelerate if the mass is redistributed farther or closer to the axis of rotation. Rotational Inertia is the resistance of a rotating object to changes in its rotational velocity-- it depends on mass, dist ...
... A net torque would produce an angular acceleration. An object spinning at a constant rate will accelerate if the mass is redistributed farther or closer to the axis of rotation. Rotational Inertia is the resistance of a rotating object to changes in its rotational velocity-- it depends on mass, dist ...
Chapter 2
... The extra mass of the heavier object exactly balances the additional gravitational force so they fall at the same rate ...
... The extra mass of the heavier object exactly balances the additional gravitational force so they fall at the same rate ...
Newton’s 3rd Law
... • Momentum- product of mass and velocityinfluences how easily an object can be stopped –P=mxv – P : momentum Units kg*m/s2 – Has direction because velocity has direction – Indicate direction of momentum ...
... • Momentum- product of mass and velocityinfluences how easily an object can be stopped –P=mxv – P : momentum Units kg*m/s2 – Has direction because velocity has direction – Indicate direction of momentum ...
Ch. 12 Review Period: Name: ANSWER KEY Physical Science Date
... of 80kg, while Bob has a mass of 40kg, who will hit the ground first? Murray 12. The two aspects that affect terminal velocity are surface area and mass (or weight) 13. What happens when an object reaches terminal velocity while in falling through an atmosphere in terms of forces and accelerations: ...
... of 80kg, while Bob has a mass of 40kg, who will hit the ground first? Murray 12. The two aspects that affect terminal velocity are surface area and mass (or weight) 13. What happens when an object reaches terminal velocity while in falling through an atmosphere in terms of forces and accelerations: ...
FORCE & MOTION - Boyle County School District
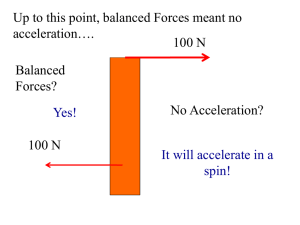
... exerting equal force on the rope in opposite directions. This balanced force results in no change of motion. ...
... exerting equal force on the rope in opposite directions. This balanced force results in no change of motion. ...
Chapter 7: Circular Motion and Gravitation
... made a sharp turn in your vehicle. If you make a sharp turn to your right, you are thrown against the door to the left. • If centripetal force is always toward the center of the circular path, why wouldn’t you be thrown toward the inside of the car rather than the outside? • A popular explanation is ...
... made a sharp turn in your vehicle. If you make a sharp turn to your right, you are thrown against the door to the left. • If centripetal force is always toward the center of the circular path, why wouldn’t you be thrown toward the inside of the car rather than the outside? • A popular explanation is ...
Review - prettygoodphysics
... Sample Problem – 3rd Law • A tug-of-war team ties a rope to a tree and pulls hard horizontally to create a tension of 30,000 N in the rope. Suppose the team pulls equally hard when, instead of a tree, the other end of the rope is being pulled by another tug-of-war team such that no movement occurs. ...
... Sample Problem – 3rd Law • A tug-of-war team ties a rope to a tree and pulls hard horizontally to create a tension of 30,000 N in the rope. Suppose the team pulls equally hard when, instead of a tree, the other end of the rope is being pulled by another tug-of-war team such that no movement occurs. ...
Newton`s Second Law.
... dt Mathematically, this is just the equation for a harmonic oscillator where u is the displacement from equilibrium, and the angular frequency is given by ...
... dt Mathematically, this is just the equation for a harmonic oscillator where u is the displacement from equilibrium, and the angular frequency is given by ...
Intro to Physics - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 1. Explain the characteristics of force 2. Identify the basic forces (Weight, normal force and friction, spring force, tension, air resistance, applied force) 3. Draw free-body diagrams showing forces acting on an object 4. Explain the cause of acceleration of any object. 5. Explain the difference b ...
... 1. Explain the characteristics of force 2. Identify the basic forces (Weight, normal force and friction, spring force, tension, air resistance, applied force) 3. Draw free-body diagrams showing forces acting on an object 4. Explain the cause of acceleration of any object. 5. Explain the difference b ...
Teachers Guide Second Law Simulation Lab
... accelerations? And how does friction play a role in acceleration? In this experiment you will accelerate various objects. First, you will apply the same force to carts of different masses. Then, you will apply varying forces to the same mass. A relationship between mass and acceleration should be fo ...
... accelerations? And how does friction play a role in acceleration? In this experiment you will accelerate various objects. First, you will apply the same force to carts of different masses. Then, you will apply varying forces to the same mass. A relationship between mass and acceleration should be fo ...
document
... B) there are no forces acting on it at all C) it does move, but too slowly to be seen D) there is no net force on the book E) there is a net force, but the book is too heavy to move ...
... B) there are no forces acting on it at all C) it does move, but too slowly to be seen D) there is no net force on the book E) there is a net force, but the book is too heavy to move ...
Slides - Powerpoint - University of Toronto Physics
... – The direction in which it acts – The point at which it is applied on the object Image by John Zdralek, retrieved Jan.10 2013 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:1980_c1980_Torque_wrench,_140ftlbs_19.36m-kg,_nominally_14-20in,_.5in_socket_drive,_Craftsman_44641_WF,_Sears_dtl.jpg ] ...
... – The direction in which it acts – The point at which it is applied on the object Image by John Zdralek, retrieved Jan.10 2013 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:1980_c1980_Torque_wrench,_140ftlbs_19.36m-kg,_nominally_14-20in,_.5in_socket_drive,_Craftsman_44641_WF,_Sears_dtl.jpg ] ...
Dynamics Notes - Blue Valley Schools
... 52. The carton shown in Fig. 4–55 lies on a plane tilted at an angle 22 .0º to the horizontal, with k 0.12. (a) Determine the acceleration of the carton as it slides down the plane. (b) If the carton starts from rest 9.30 m up the plane from its base, what will be the carton’s speed when it ...
... 52. The carton shown in Fig. 4–55 lies on a plane tilted at an angle 22 .0º to the horizontal, with k 0.12. (a) Determine the acceleration of the carton as it slides down the plane. (b) If the carton starts from rest 9.30 m up the plane from its base, what will be the carton’s speed when it ...
Net force
... can, but not after realizing that you know TC. • Step 6: Determine TC by considering the forces on the block, and requiring that the net force is equal to 0 N. This tells us that TC = mg. ...
... can, but not after realizing that you know TC. • Step 6: Determine TC by considering the forces on the block, and requiring that the net force is equal to 0 N. This tells us that TC = mg. ...