
Presentation - ScienceScene
... 1. Observing Forces (using the “Gizmo”) . . . . . . . . . 14 2. Finding The Forces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 3. Types of Force. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 4. Forces in a Collision . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 ...
... 1. Observing Forces (using the “Gizmo”) . . . . . . . . . 14 2. Finding The Forces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 3. Types of Force. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 4. Forces in a Collision . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 ...
Chapter 12
... • All matter is affected by gravity • Gravitational force increases with mass OR decreases with distance ...
... • All matter is affected by gravity • Gravitational force increases with mass OR decreases with distance ...
II. Describing Motion
... direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram is shows the magnitude of the force. The direction of the arrow reveals the direction in which the force acts. ...
... direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram is shows the magnitude of the force. The direction of the arrow reveals the direction in which the force acts. ...
Lecture-07-09
... of about 2.5 m/s2 upward e) experiencing a constant acceleration of about 2.5 m/s2 downward ...
... of about 2.5 m/s2 upward e) experiencing a constant acceleration of about 2.5 m/s2 downward ...
PHYSICS I FALL FINAL REVIEW Use the graph above to answer the
... plane. What is the speed of the plane relative to the ground? 9. An athlete attempting a long jump runs down the track at 40km/hr before launching himself vertically into the air. What is his speed in the air if he launches himself with a vertical velocity of 20 km/hr? 10. A bullet leaves a rifle wi ...
... plane. What is the speed of the plane relative to the ground? 9. An athlete attempting a long jump runs down the track at 40km/hr before launching himself vertically into the air. What is his speed in the air if he launches himself with a vertical velocity of 20 km/hr? 10. A bullet leaves a rifle wi ...
Class XI-Physics 2016-17
... (b) Why does a cricket player lower his hands while catching a ball? 17. Define conservative force. Show that the total mechanical energy of a freely falling body remains constant throughout its fall. 18. A railway carriage of mass 9000 kg moving with a speed of 36 kmh-1 collides with a stationary c ...
... (b) Why does a cricket player lower his hands while catching a ball? 17. Define conservative force. Show that the total mechanical energy of a freely falling body remains constant throughout its fall. 18. A railway carriage of mass 9000 kg moving with a speed of 36 kmh-1 collides with a stationary c ...
Force and acceleration Chapter_3_Lesson_1
... Mass and Acceleration • If you throw a softball and a baseball as hard as you can, why don’t they have the same speed? • The difference is due to their masses. • If it takes the same amount of time to throw both balls, the softball would have less. • Force, mass, acceleration and acceleration are r ...
... Mass and Acceleration • If you throw a softball and a baseball as hard as you can, why don’t they have the same speed? • The difference is due to their masses. • If it takes the same amount of time to throw both balls, the softball would have less. • Force, mass, acceleration and acceleration are r ...
ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS
... There are friction forces at both contact surfaces—between the hand and the book on top, and between the book and the table underneath. If the friction force between the hand and the book is larger than that between the table and the book, the book will be dragged along by the hand. In this case sta ...
... There are friction forces at both contact surfaces—between the hand and the book on top, and between the book and the table underneath. If the friction force between the hand and the book is larger than that between the table and the book, the book will be dragged along by the hand. In this case sta ...
Document
... These relationships will be valuable when we study the kinetic energy of rotating objects. ...
... These relationships will be valuable when we study the kinetic energy of rotating objects. ...
File
... • Momentum is transferred. • When a moving object hits a second object, some or all of the momentum of the first object is transferred to the second object. • Momentum can be transferred in collisions, but the total momentum before and after a collision is the same. • A semi and a car collide… W ...
... • Momentum is transferred. • When a moving object hits a second object, some or all of the momentum of the first object is transferred to the second object. • Momentum can be transferred in collisions, but the total momentum before and after a collision is the same. • A semi and a car collide… W ...
What is a Force?
... On Mars 220 lbs. would weigh 82.9 lbs. What’s “Your Weight On Other Worlds?” http://www.exploratorium.edu/ronh/weight/ ...
... On Mars 220 lbs. would weigh 82.9 lbs. What’s “Your Weight On Other Worlds?” http://www.exploratorium.edu/ronh/weight/ ...
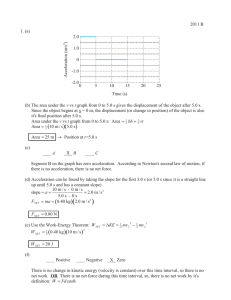
2011 B 1. (a) 2.0 0
... Since the object begins at x = 0 m, the displacement (or change in position) of the object is also it's final position after 5.0 s. Area under the v vs t graph from 0 to 5.0 s: Area = 12 bh = 12 vt Area = 12 (10 m / s)(5.0 s) Area = 25 m ® Position at t=5.0 s (c) ____ A ...
... Since the object begins at x = 0 m, the displacement (or change in position) of the object is also it's final position after 5.0 s. Area under the v vs t graph from 0 to 5.0 s: Area = 12 bh = 12 vt Area = 12 (10 m / s)(5.0 s) Area = 25 m ® Position at t=5.0 s (c) ____ A ...
PowerPoint Newton`s 2nd Law
... that is perfectly horizontal. In this case, the marble will neither slow down nor speed up. In fact, it should keep rolling. Forever. ...
... that is perfectly horizontal. In this case, the marble will neither slow down nor speed up. In fact, it should keep rolling. Forever. ...
Amusement Park Ride Project
... A bicyclist is coasting downhill and puts on the brakes. He has to stop in 1.5 seconds to avoid a suddenly stopped car. If his wheel is rotating at an angular velocity of 20 rad/s, how many revolutions does his wheel make before he comes to a stop? ...
... A bicyclist is coasting downhill and puts on the brakes. He has to stop in 1.5 seconds to avoid a suddenly stopped car. If his wheel is rotating at an angular velocity of 20 rad/s, how many revolutions does his wheel make before he comes to a stop? ...
F r i c t i o n - Southgate Community School District
... • When an object falls, is the force of gravity, the only force acting on the object? • NO! Air resistance, a form of friction, is acting in OPPOSITE direction of force of gravity ...
... • When an object falls, is the force of gravity, the only force acting on the object? • NO! Air resistance, a form of friction, is acting in OPPOSITE direction of force of gravity ...
Ch. 4
... • Downward force is weight. • a = weight/mass • but an object with twice the mass will have twice the weight… • so the accelerations are the same… • We call this acceleration “g”. • g is about 10m/s/s downward. ...
... • Downward force is weight. • a = weight/mass • but an object with twice the mass will have twice the weight… • so the accelerations are the same… • We call this acceleration “g”. • g is about 10m/s/s downward. ...

















![PhysRozz Midterm 2012 [via06-07] Version 18](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014722455_1-33f5b15b25beb94441904fea997b655c-300x300.png)



