Acceleration
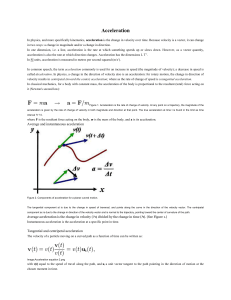
... In physics, and more specifically kinematics, acceleration is the change in velocity over time. Because velocity is a vector, it can change in two ways: a change in magnitude and/or a change in direction. In one dimension, i.e. a line, acceleration is the rate at which something speeds up or slows d ...
... In physics, and more specifically kinematics, acceleration is the change in velocity over time. Because velocity is a vector, it can change in two ways: a change in magnitude and/or a change in direction. In one dimension, i.e. a line, acceleration is the rate at which something speeds up or slows d ...
PHYS2101: General Physics I
... On successful completion of the course, the student will be able to explain physical phenomena based on the general concepts and to use general principles of physics in solving problems in electricity, magnetism and thermal physics. The student will also develop skills to use experimental apparatus ...
... On successful completion of the course, the student will be able to explain physical phenomena based on the general concepts and to use general principles of physics in solving problems in electricity, magnetism and thermal physics. The student will also develop skills to use experimental apparatus ...
05.TE.Newton`s Second Law
... is represented by the equation y = mx. In each case the proportionality constant in the equation is equal to the slope of the line. ...
... is represented by the equation y = mx. In each case the proportionality constant in the equation is equal to the slope of the line. ...
Explanation - Fort Bend ISD
... What will happen if the balls are released from the same height above the floor? ...
... What will happen if the balls are released from the same height above the floor? ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... reaction force on you. This reaction force has the same magnitude as, but is opposite in direction to, your action force. The motion of a rocket illustrates Newton's Third Law. In order to move, the rocket expels gaseous molecules. The rocket exerts a large force backward on the molecules to expel t ...
... reaction force on you. This reaction force has the same magnitude as, but is opposite in direction to, your action force. The motion of a rocket illustrates Newton's Third Law. In order to move, the rocket expels gaseous molecules. The rocket exerts a large force backward on the molecules to expel t ...
Newton`s laws of motion
... • An object will keep a constant velocity (unless there is a non-zero net force acting on it). Examples include: • Ice-skaters (pretty close to zero friction gliding forward) ...
... • An object will keep a constant velocity (unless there is a non-zero net force acting on it). Examples include: • Ice-skaters (pretty close to zero friction gliding forward) ...
AP Physics – The Physics Little AP Test Review Helper
... Try summing forces second. Draw a FBD, identify all the forces, and see if you can come up with a solution in this way. If you see a vector at an angle, resolve it into its x and y components. Last, try kinematics. ...
... Try summing forces second. Draw a FBD, identify all the forces, and see if you can come up with a solution in this way. If you see a vector at an angle, resolve it into its x and y components. Last, try kinematics. ...
Chapter 4 - Newton`s Laws of motion
... – The magnitude w of a body’s weight is directly proportional to its mass m. – The weight of a body is a force, a vector quantity, w = mg ...
... – The magnitude w of a body’s weight is directly proportional to its mass m. – The weight of a body is a force, a vector quantity, w = mg ...
Chapter 10 PowerPoint
... Air Resistance - Objects falling through the air experience a type of fluid friction Terminal velocity – The greatest velocity a falling object reaches ...
... Air Resistance - Objects falling through the air experience a type of fluid friction Terminal velocity – The greatest velocity a falling object reaches ...
Motion and Forces - 7thGradeHillsboro
... The direction of the object is described as whether it is “moving away” from or “moving toward” the reference point. If the object is “moving away” from the reference point, the line will go up (distance increasing) as in position A. If the object is “moving toward” the reference point the line wil ...
... The direction of the object is described as whether it is “moving away” from or “moving toward” the reference point. If the object is “moving away” from the reference point, the line will go up (distance increasing) as in position A. If the object is “moving toward” the reference point the line wil ...























