Monday, Oct. 7, 2002
... A small ball of mass 2.00g is released from rest in a large vessel filled with oil, where it experiences a resistive force proportional to its speed. The ball reaches a terminal speed of 5.00 cm/s. Determine the time constant t and the time it takes the ball to reach 90% of its terminal speed. ...
... A small ball of mass 2.00g is released from rest in a large vessel filled with oil, where it experiences a resistive force proportional to its speed. The ball reaches a terminal speed of 5.00 cm/s. Determine the time constant t and the time it takes the ball to reach 90% of its terminal speed. ...
Lecture Notes for Sections 14.1
... Another equation for working kinetics problems involving particles can be derived by integrating the equation of motion (F = ma) with respect to displacement. By substituting at = v (dv/ds) into Ft = mat, the result is integrated to yield an equation known as the principle of work and energy. This p ...
... Another equation for working kinetics problems involving particles can be derived by integrating the equation of motion (F = ma) with respect to displacement. By substituting at = v (dv/ds) into Ft = mat, the result is integrated to yield an equation known as the principle of work and energy. This p ...
Microsoft Powerpoint
... Equilibrium – an object which has zero acceleration, can be at rest or moving with constant velocity ...
... Equilibrium – an object which has zero acceleration, can be at rest or moving with constant velocity ...
L3N - University of Iowa Physics
... forces: gravity and a drag force (air resistance) due to the air molecules hitting it. For objects that fall to earth from a distance of several feet or meters, the effect of air resistance can usually be neglected. To simplify the discussion of gravity, we will just ignore air resistance for now. ...
... forces: gravity and a drag force (air resistance) due to the air molecules hitting it. For objects that fall to earth from a distance of several feet or meters, the effect of air resistance can usually be neglected. To simplify the discussion of gravity, we will just ignore air resistance for now. ...
Forces and Motion - Catawba County Schools
... A force is a push or pull that acts on an object. * A force can cause a resting object to move * A force can accelerate an object by changing its speed or direction. * Force is measured in Newtons. A Newton is the force that causes a 1-kilogram mass to accelerate at a rate of 1 m/s2. 1 N = 1kg*m/s2 ...
... A force is a push or pull that acts on an object. * A force can cause a resting object to move * A force can accelerate an object by changing its speed or direction. * Force is measured in Newtons. A Newton is the force that causes a 1-kilogram mass to accelerate at a rate of 1 m/s2. 1 N = 1kg*m/s2 ...
newton`s lesson 6 homework
... resistance force to the motion of the cart is 0.720 N, then what is the cart's acceleration? 4. A 72.0-kg skydiver is falling from 10 000.0 feet. After reaching terminal velocity, the skydiver opens his parachute. Shortly thereafter, there is an an instant in time in which the skydiver encounters an ...
... resistance force to the motion of the cart is 0.720 N, then what is the cart's acceleration? 4. A 72.0-kg skydiver is falling from 10 000.0 feet. After reaching terminal velocity, the skydiver opens his parachute. Shortly thereafter, there is an an instant in time in which the skydiver encounters an ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... of your body parts, mostly at a point of contact. If your body is not stretched or compressed, you will feel like you are floating. Gravity ALONE will not stretch or compress your body. Hanging from the board, the board also pulls up on your arms. Newton’s 3rd law! Standing on the ground, the ground ...
... of your body parts, mostly at a point of contact. If your body is not stretched or compressed, you will feel like you are floating. Gravity ALONE will not stretch or compress your body. Hanging from the board, the board also pulls up on your arms. Newton’s 3rd law! Standing on the ground, the ground ...
Dynamics Introduction to Forces Fundamental Forces
... b) if a 20.0 N brick is placed on the block, what force would be required to keep the block and brick moving at a constant velocity? ...
... b) if a 20.0 N brick is placed on the block, what force would be required to keep the block and brick moving at a constant velocity? ...
10_WEP_Summary
... Consider Fig. 1 of Case 1. If the force is the only force acting and the body is at rest initially, then the force is a net force that causes acceleration and a gain in speed. The kinetic energy gained can be shown to be equal to the work done. Try proving it using kinematics equations. ...
... Consider Fig. 1 of Case 1. If the force is the only force acting and the body is at rest initially, then the force is a net force that causes acceleration and a gain in speed. The kinetic energy gained can be shown to be equal to the work done. Try proving it using kinematics equations. ...
Skating - How Everything Works
... Real-world complications are a nuisance Complications can mask simple physics Solution: overwhelm the complications! To demonstrate inertia: – work on level ground (goodbye gravity) – work fast (goodbye friction and air resistance) ...
... Real-world complications are a nuisance Complications can mask simple physics Solution: overwhelm the complications! To demonstrate inertia: – work on level ground (goodbye gravity) – work fast (goodbye friction and air resistance) ...
Chapter 5
... Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relativ ...
... Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relativ ...
Second
... the weight Fg of an object, the magnitude of the force of gravity acting on it, if the acceleration a is the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2. ...
... the weight Fg of an object, the magnitude of the force of gravity acting on it, if the acceleration a is the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2. ...
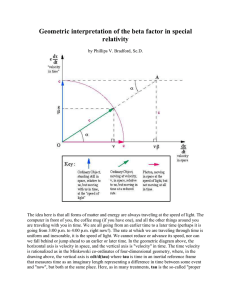
A space-time geometric interpretation of the beta factor in Special
... enormous "hidden" (i.e. atomic) energy in the form of E = mc^2. Another possible significance is that an object in motion seems to rotate its velocity vector in space-time, maintaining a constant magnitude at the speed of light, c, as it changes velocity, v. A rotation in space-time is perfectly smo ...
... enormous "hidden" (i.e. atomic) energy in the form of E = mc^2. Another possible significance is that an object in motion seems to rotate its velocity vector in space-time, maintaining a constant magnitude at the speed of light, c, as it changes velocity, v. A rotation in space-time is perfectly smo ...
Applying Newton`s Third Law of Motion in the Gravitron Ride
... Bobby: Well, first you have to understand the three vector definitions of motion. Joe: What do you mean by “vector”? Bobby: A vector quantity is a quantity that specifies not only a magnitude, which is basically a number, but also a direction, which is usually specified as an angle. Joe: Oh, you mea ...
... Bobby: Well, first you have to understand the three vector definitions of motion. Joe: What do you mean by “vector”? Bobby: A vector quantity is a quantity that specifies not only a magnitude, which is basically a number, but also a direction, which is usually specified as an angle. Joe: Oh, you mea ...