PS02H - willisworldbio
... • If you are sitting in a chair reading this sentence, you are _______. • You are not moving relative to your desk or your school building, but you are moving relative to the other _______ in the solar system and the Sun. ...
... • If you are sitting in a chair reading this sentence, you are _______. • You are not moving relative to your desk or your school building, but you are moving relative to the other _______ in the solar system and the Sun. ...
Solutions - CSUN.edu
... Strategy: Determine the effective force constants of the two springs connected in the arrangements shown in the figure. Then use the relationship between the period and the force constant to predict the effect upon T. Solution: 1. (a) Twice as much force is required to stretch two springs connected ...
... Strategy: Determine the effective force constants of the two springs connected in the arrangements shown in the figure. Then use the relationship between the period and the force constant to predict the effect upon T. Solution: 1. (a) Twice as much force is required to stretch two springs connected ...
Energy - Madison County Schools
... property of a moving object that depends on the object’s mass and velocity in other words: more momentum an object has the harder it is to stop the object Conservation (constant) of momentum That is, the momentum lost by object 1 is equal to the momentum gained by object 2 ...
... property of a moving object that depends on the object’s mass and velocity in other words: more momentum an object has the harder it is to stop the object Conservation (constant) of momentum That is, the momentum lost by object 1 is equal to the momentum gained by object 2 ...
reading – motion and forces review – innovation lab
... As this equation shows, weight is directly related to mass. As an object’s mass increases, so does its weight. For example, if mass doubles, weight doubles as well. You can learn more about weight and acceleration at this Helpful Hints The equation for calculating weight (F=m×a) works only when the ...
... As this equation shows, weight is directly related to mass. As an object’s mass increases, so does its weight. For example, if mass doubles, weight doubles as well. You can learn more about weight and acceleration at this Helpful Hints The equation for calculating weight (F=m×a) works only when the ...
Chapter 8
... A 60.0-kg woman stands at the rim of a horizontal turntable having a moment of inertia of 500 kg ∙ m2 and a radius of 2.00 m. The turntable is initially at rest and is free to rotate about a frictionless, vertical axle through its center. The woman then starts walking around the rim clockwise (as vi ...
... A 60.0-kg woman stands at the rim of a horizontal turntable having a moment of inertia of 500 kg ∙ m2 and a radius of 2.00 m. The turntable is initially at rest and is free to rotate about a frictionless, vertical axle through its center. The woman then starts walking around the rim clockwise (as vi ...
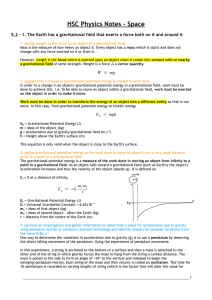
HSC Physics Notes - Space
... To reduce the effect that g-forces have on the astronauts, they are made to lie down in specialised seats which minimise the effect of the feeling of g-forces. By lying down, the force is spread out across the body and also prevents the eye balls of astronauts popping under the intense stress. The ...
... To reduce the effect that g-forces have on the astronauts, they are made to lie down in specialised seats which minimise the effect of the feeling of g-forces. By lying down, the force is spread out across the body and also prevents the eye balls of astronauts popping under the intense stress. The ...
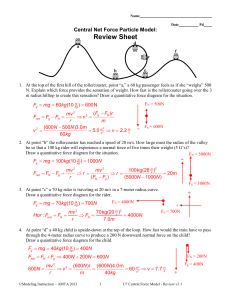
Central Net Force Particle Model:
... 8. Here is the data for the space shuttle in its orbit around earth: Shuttle mass in orbit = 94,802 kg mass of the earth = 6 x 1024 kg shuttle orbital height above the earth = 2.76 x 105m radius of the earth = 6.38 x106 m shuttle tangential velocity when in orbit = 7823 m/sec a. Use the principles ...
... 8. Here is the data for the space shuttle in its orbit around earth: Shuttle mass in orbit = 94,802 kg mass of the earth = 6 x 1024 kg shuttle orbital height above the earth = 2.76 x 105m radius of the earth = 6.38 x106 m shuttle tangential velocity when in orbit = 7823 m/sec a. Use the principles ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... the force related to something else? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with t ...
... the force related to something else? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with t ...
PHYS140 - Ch4.pptx
... An object’s mass is a measure of its inertia. The more mass, the more force is required to obtain a given acceleration. The net force is just the vector sum of all of the forces acting on the body, often wri]en as ΣF. If a = 0, then ΣF = 0. ...
... An object’s mass is a measure of its inertia. The more mass, the more force is required to obtain a given acceleration. The net force is just the vector sum of all of the forces acting on the body, often wri]en as ΣF. If a = 0, then ΣF = 0. ...
Glossary
... Shear modulus: The ratio of shear stress divided by the corresponding shear strain in a linear elastic material. Stability: Stability is best defined as the opposite of instability, which is the occurrence of large structural deformations which are not the result of material failure. Static equilibr ...
... Shear modulus: The ratio of shear stress divided by the corresponding shear strain in a linear elastic material. Stability: Stability is best defined as the opposite of instability, which is the occurrence of large structural deformations which are not the result of material failure. Static equilibr ...
Work and Kinetic Energy
... Worked Example: Work Done by Several Forces A block of mass m slides along a horizontal table with speed v0. At x = 0 it hits a spring with spring constant k and begins to experience a friction force. The coefficient of kinetic friction is given by m. How far did the spring compress when the block ...
... Worked Example: Work Done by Several Forces A block of mass m slides along a horizontal table with speed v0. At x = 0 it hits a spring with spring constant k and begins to experience a friction force. The coefficient of kinetic friction is given by m. How far did the spring compress when the block ...
day 2 newtons laws review - Appoquinimink High School
... (C) move with constant velocity down the ramp. (D) Not move. (E) cannot be determined from the information given. 6) If all the forces acting on an object balance so that the net force is zero, then (A) the object must be at rest. (B) the object’s speed will decrease. (C) the object will follow a pa ...
... (C) move with constant velocity down the ramp. (D) Not move. (E) cannot be determined from the information given. 6) If all the forces acting on an object balance so that the net force is zero, then (A) the object must be at rest. (B) the object’s speed will decrease. (C) the object will follow a pa ...