Enzymes - Chautauqua Lake Central SD
... Enzymes aren’t used up • Enzymes are not changed by the reaction – used only temporarily – re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules – very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions substrate active site ...
... Enzymes aren’t used up • Enzymes are not changed by the reaction – used only temporarily – re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules – very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions substrate active site ...
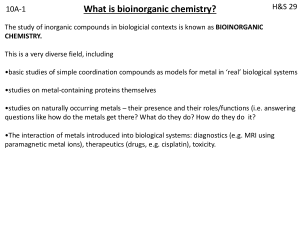
bioinorganic 1
... Hemoglobin’s active sites (all 4 of them) without the O2 is known as deoxyhemoglobin. The active site contains five-coordinate, pseudo-square planar Fe(+2). The fifth donor site is an imidazole ring from a histidine residue in the polypeptide chain. In deoxyhemoglobin the iron lies above the protopo ...
... Hemoglobin’s active sites (all 4 of them) without the O2 is known as deoxyhemoglobin. The active site contains five-coordinate, pseudo-square planar Fe(+2). The fifth donor site is an imidazole ring from a histidine residue in the polypeptide chain. In deoxyhemoglobin the iron lies above the protopo ...
Organic Chemistry
... Organic Chemistry: What is it? • 1780: Organic compounds are very complex and only obtained from living sources (vitalism 生机说) • Vitalism: Belief that a "magic" vital force, present in plants and animals, is necessary for the synthesis of organic compounds • 1789: Antoine Laurent Lavoisier observed ...
... Organic Chemistry: What is it? • 1780: Organic compounds are very complex and only obtained from living sources (vitalism 生机说) • Vitalism: Belief that a "magic" vital force, present in plants and animals, is necessary for the synthesis of organic compounds • 1789: Antoine Laurent Lavoisier observed ...
Chemistry Of The Human Body
... macromolecules. • Functions of proteins. • A polymer composed of many monomers (amino acids) • Peptides are short or incomplete proteins. ...
... macromolecules. • Functions of proteins. • A polymer composed of many monomers (amino acids) • Peptides are short or incomplete proteins. ...
Chemistry Of The Human Body
... macromolecules. • Functions of proteins. • A polymer composed of many monomers (amino acids) • Peptides are short or incomplete proteins. ...
... macromolecules. • Functions of proteins. • A polymer composed of many monomers (amino acids) • Peptides are short or incomplete proteins. ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry Fourth Edition David L. Nelson
... found on the Earth today. About four billion years ago, ...
... found on the Earth today. About four billion years ago, ...
I Preparation of Metaphase Chromosomes
... 1.Primers (short DNA fragments) containing sequences complementary to the target region along with a DNA polymerase (after which the method is named) are key components to enable selective and repeated amplification. 2.Almost all PCR applications employ a heat-stable DNA polymerase, such as Taq poly ...
... 1.Primers (short DNA fragments) containing sequences complementary to the target region along with a DNA polymerase (after which the method is named) are key components to enable selective and repeated amplification. 2.Almost all PCR applications employ a heat-stable DNA polymerase, such as Taq poly ...
B - DHSTAKS
... Saltwater fish remove extra salt from their body by active transport through the gills. What is the result of this activity? A The salt becomes more chemically active. B Water balance is maintained in the blood. C The rate of energy production is decreased. D The cell membrane becomes less permeabl ...
... Saltwater fish remove extra salt from their body by active transport through the gills. What is the result of this activity? A The salt becomes more chemically active. B Water balance is maintained in the blood. C The rate of energy production is decreased. D The cell membrane becomes less permeabl ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... It can’t be touched, but can be felt. It can’t be opened, but can be gone into. Those who seek it always find it under ...
... It can’t be touched, but can be felt. It can’t be opened, but can be gone into. Those who seek it always find it under ...
1) Which of the following correctly lists the levels of organization
... Cells are surrounded by water, and cells themselves are about 70-95% water. As a result, _____. a. the temperature of living things tends to change relatively slowly b. a variety of nutrient molecules are readily available as dissolved solutes c. waste products produced by cell metabolism can be eas ...
... Cells are surrounded by water, and cells themselves are about 70-95% water. As a result, _____. a. the temperature of living things tends to change relatively slowly b. a variety of nutrient molecules are readily available as dissolved solutes c. waste products produced by cell metabolism can be eas ...
Structure of an Atom
... fl Store and process information on the molecular level within living cells. fl Two classes of nucleic acid molecules: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). fl DNA in our cells determine inherited characteristics (eye and hair color, blood type, etc.). fl DNA molecules encode infor ...
... fl Store and process information on the molecular level within living cells. fl Two classes of nucleic acid molecules: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). fl DNA in our cells determine inherited characteristics (eye and hair color, blood type, etc.). fl DNA molecules encode infor ...
BIO 15 SM 2016 FINAL EXAM 135 Q 160804.1rac
... Cells are surrounded by water, and cells themselves are about 70-95% water. As a result, _____. a. the temperature of living things tends to change relatively slowly b. a variety of nutrient molecules are readily available as dissolved solutes c. waste products produced by cell metabolism can be eas ...
... Cells are surrounded by water, and cells themselves are about 70-95% water. As a result, _____. a. the temperature of living things tends to change relatively slowly b. a variety of nutrient molecules are readily available as dissolved solutes c. waste products produced by cell metabolism can be eas ...
Learning Outcomes
... It is expected that students will: D1. name the four bases in DNA and describe the structure of DNA using the following terms: nucleotide (sugar, phosphate, base) complementary base pairing double helix hydrogen bonding D2. describe DNA replication with reference to three basic steps ...
... It is expected that students will: D1. name the four bases in DNA and describe the structure of DNA using the following terms: nucleotide (sugar, phosphate, base) complementary base pairing double helix hydrogen bonding D2. describe DNA replication with reference to three basic steps ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... E. The set of coded DNA instructions for each protein is called a gene, and the entire collection of genes is called the genome of an organism. F. James D. Watson and Francis H. C. Crick discovered the structure of DNA in 1953. 12-17. Origin of Life A. Hypotheses about the origin of life on earth in ...
... E. The set of coded DNA instructions for each protein is called a gene, and the entire collection of genes is called the genome of an organism. F. James D. Watson and Francis H. C. Crick discovered the structure of DNA in 1953. 12-17. Origin of Life A. Hypotheses about the origin of life on earth in ...
2007-2008 AP Biology
... reproduction internal fertilization internal development in uterus nourishment through placenta birth live young mammary glands make milk ...
... reproduction internal fertilization internal development in uterus nourishment through placenta birth live young mammary glands make milk ...
The Chemistry of Living Systems
... carbon dioxide may be responsible for the warming of Earth by several degrees over the past 200 years. Can you think of ways to stabilize ...
... carbon dioxide may be responsible for the warming of Earth by several degrees over the past 200 years. Can you think of ways to stabilize ...
Synthesis of RNA - Stamm revision
... Protocol 1: Incorporation of modified phosphoramidites during solid-phase synthesis The coupling conditions for modified phosphoramidite building blocks may require alterations of the standard RNA synthesis protocols, as usually specified in the accompanying product sheets. In general, the modified ...
... Protocol 1: Incorporation of modified phosphoramidites during solid-phase synthesis The coupling conditions for modified phosphoramidite building blocks may require alterations of the standard RNA synthesis protocols, as usually specified in the accompanying product sheets. In general, the modified ...
AP BIOLOGY Reading Guide 42.1 NAME_____________________
... 3. Examine the graph below and answer the questions that follow: ...
... 3. Examine the graph below and answer the questions that follow: ...
AP Biology
... By using the radioactive isotopes present in rocks, and understanding the rates at which these isotopes decay, scientists can determine approximate age of the rocks. Atoms of the same element with differing atomic weights can be naturally found in the environment, and are called isotopes. ...
... By using the radioactive isotopes present in rocks, and understanding the rates at which these isotopes decay, scientists can determine approximate age of the rocks. Atoms of the same element with differing atomic weights can be naturally found in the environment, and are called isotopes. ...
Lipids
... A protein consists of one or more polypeptide chains folded into a highly specific 3D shape. There are up to four levels of structure in a protein: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Each of these play an important role in the overall structure and function of the protein. 22 of 12 ...
... A protein consists of one or more polypeptide chains folded into a highly specific 3D shape. There are up to four levels of structure in a protein: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Each of these play an important role in the overall structure and function of the protein. 22 of 12 ...