Geography Pre Ch. 1 Grade 7
... 2.) Identify Key States, Capitals, and Physical Landforms throughout the United States . ...
... 2.) Identify Key States, Capitals, and Physical Landforms throughout the United States . ...
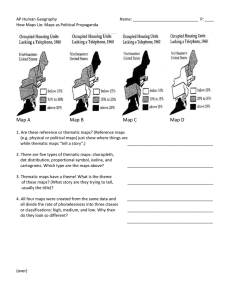
12 Choropleths as Propaganda WS
... each map might logically draw from that map. PLEASE don’t just guess or copy these from someone else. Read through them carefully and match the descriptions with the maps. _________: Since the states in the white low “phonelessness” category (MA, RI, CT, NJ, PA) are all high urban (have lots of big ...
... each map might logically draw from that map. PLEASE don’t just guess or copy these from someone else. Read through them carefully and match the descriptions with the maps. _________: Since the states in the white low “phonelessness” category (MA, RI, CT, NJ, PA) are all high urban (have lots of big ...
Using Thematic Maps
... form.lines (isolines) to show the shape & elevation of an area (shape of the Earth’s surface) -Lines close together indicate steep terrain -Lines far apart indicate flat terrain. EX:? ...
... form.lines (isolines) to show the shape & elevation of an area (shape of the Earth’s surface) -Lines close together indicate steep terrain -Lines far apart indicate flat terrain. EX:? ...
Map Skills Study Guides
... Road maps show major and minor highways and roads, as well as airports, city locations, and points of interest. Road maps are the most widely used of all maps. Topographic maps use contour lines to show changes in elevation and landscape. The five themes of geography are tools geographers use ...
... Road maps show major and minor highways and roads, as well as airports, city locations, and points of interest. Road maps are the most widely used of all maps. Topographic maps use contour lines to show changes in elevation and landscape. The five themes of geography are tools geographers use ...
Unit I - Maps
... Cartography – science of mapmaking Cartographers must choose: • Types of projections • Levels of simplification • Levels of aggregation • Map scale • Symbols to use ...
... Cartography – science of mapmaking Cartographers must choose: • Types of projections • Levels of simplification • Levels of aggregation • Map scale • Symbols to use ...
First Nine Weeks Review Guide
... 3. What lands were not known to Europeans during the time of Columbus? 4. How do lines of longitude differ from lines of latitude? 5. Giving directions to another person to your house using roads and landmarks is an example of using what type of map? 6. What are the main problems associated with usi ...
... 3. What lands were not known to Europeans during the time of Columbus? 4. How do lines of longitude differ from lines of latitude? 5. Giving directions to another person to your house using roads and landmarks is an example of using what type of map? 6. What are the main problems associated with usi ...
CGC 1D Wusssuuuupppp with Maps??? An Intro to mapping skills
... • they actually are measured as angles, with the centre of each angle at the centre of the globe • Latitude represents the distance north or south of the equator, measured in degrees (eg. Equator is O degrees latitude) ...
... • they actually are measured as angles, with the centre of each angle at the centre of the globe • Latitude represents the distance north or south of the equator, measured in degrees (eg. Equator is O degrees latitude) ...
Map Skills Notes
... There are two types of imaginary lines on a map: latitude and longitude. Latitude lines go across the map from side to side. The equator is a latitude line. Longitude lines run up and down on a map. A state border is usually shown with a thin line. A national border is usually shown with a thick lin ...
... There are two types of imaginary lines on a map: latitude and longitude. Latitude lines go across the map from side to side. The equator is a latitude line. Longitude lines run up and down on a map. A state border is usually shown with a thin line. A national border is usually shown with a thick lin ...
The Tools of the Geographer
... established by different geographers developed by geographers based on observations – Do not always work in all situations – Can be used to compare different areas ...
... established by different geographers developed by geographers based on observations – Do not always work in all situations – Can be used to compare different areas ...
History of cartography

Cartography or mapmaking, has been an integral part of the human history for a long time, possibly up to 8,000 years. From cave paintings to ancient maps of Babylon, Greece, and Asia, through the Age of Exploration, and on into the 21st century, people have created and used maps as essential tools to help them define, explain, and navigate their way through the world. Maps began as two-dimensional drawings but can also adopt three-dimensional shapes (globes, models) and be stored in purely numerical forms.The term cartography is modern, loaned into English from French cartographie in the 1840s, based on Middle Latin carta ""map"".