What is a Map?
... natural features such as rivers and mountain ranges) – A dot should be used to locate cities, with the name of the city as close to the dot as possible. ...
... natural features such as rivers and mountain ranges) – A dot should be used to locate cities, with the name of the city as close to the dot as possible. ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... for maps of the poles. Cylindrical Projection – projecting the globe onto a cylinder. Most accurate near the Equator. Shapes and distances are distorted near the poles. Conic Projection – comes from placing a cone over part of a globe. Best sutied for showing limited east-west areas that are not ...
... for maps of the poles. Cylindrical Projection – projecting the globe onto a cylinder. Most accurate near the Equator. Shapes and distances are distorted near the poles. Conic Projection – comes from placing a cone over part of a globe. Best sutied for showing limited east-west areas that are not ...
Map Master Skills Handbook
... can probably figure out that “Geography” is a huge topic to study. When some people hear the word “Geography” they think about studying states and capitals. Although that’s part of Geography, there is so much more! To make the study of Geography a little easier to understand, geographers have divide ...
... can probably figure out that “Geography” is a huge topic to study. When some people hear the word “Geography” they think about studying states and capitals. Although that’s part of Geography, there is so much more! To make the study of Geography a little easier to understand, geographers have divide ...
Chapter 6 - views of Earth PPT
... B. Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each about 15° of longitude wide and exactly one hour different from the zones on either side of it. C. Calendar dates begin and end at midnight; the International Date Line is located at the 180° meridian. ...
... B. Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each about 15° of longitude wide and exactly one hour different from the zones on either side of it. C. Calendar dates begin and end at midnight; the International Date Line is located at the 180° meridian. ...
Maps-PPT-Unit
... one, or at most two, points in any direction or along certain lines. Equidistance is important in maps which are used for analyzing velocity, e.g. ocean currents. Typically, reference lines such as the equator or a meridian are chosen to have equidistance and are termed standard parallels or standar ...
... one, or at most two, points in any direction or along certain lines. Equidistance is important in maps which are used for analyzing velocity, e.g. ocean currents. Typically, reference lines such as the equator or a meridian are chosen to have equidistance and are termed standard parallels or standar ...
unit 1: american geography
... LATITUDE: Lines on a map that measure distance north and south from the Equator. LONGITUDE: Lines on a map that measure distance east and west from the Prime Meridian. Latitude: Lines that run north (above) and south (below) of the equator. They go left to right on the map. ...
... LATITUDE: Lines on a map that measure distance north and south from the Equator. LONGITUDE: Lines on a map that measure distance east and west from the Prime Meridian. Latitude: Lines that run north (above) and south (below) of the equator. They go left to right on the map. ...
World Geography Unit 1 Study Guide
... mountain) into 13 smaller zones? (60 – 63) - It’s not possible to accurately describe all the places within the 6 major climate zones ...
... mountain) into 13 smaller zones? (60 – 63) - It’s not possible to accurately describe all the places within the 6 major climate zones ...
Slide 1
... natural features such as rivers and mountain ranges) – A dot should be used to locate cities, with the name of the city as close to the dot as possible. ...
... natural features such as rivers and mountain ranges) – A dot should be used to locate cities, with the name of the city as close to the dot as possible. ...
Relative distance - Winston-Salem/Forsyth County Schools
... locates places according to longitude and latitude defines a place in terms of how central or isolated it is to other places defines patterns of natural environment helps cartographers to develop more accurate maps illustrates how local, regional and global factors interact within the local-global c ...
... locates places according to longitude and latitude defines a place in terms of how central or isolated it is to other places defines patterns of natural environment helps cartographers to develop more accurate maps illustrates how local, regional and global factors interact within the local-global c ...
here - Crescent School
... are no necessities, but everywhere possibilities; and man, as master of the possibilities, is the judge of their use.” ...
... are no necessities, but everywhere possibilities; and man, as master of the possibilities, is the judge of their use.” ...
Elementary_DL_IntegratingLiteracy_11of15.v1 (new window)
... Some eruptions have been so violent that entire towns have been wiped out, and thousands of people have died. In ancient Rome, a volcanic eruption destroyed the entire city of Pompeii (pahm-PAY) in 79 A.D. The word volcano comes from Vulcan, the Roman god of fire. Volcanoes are found on every contin ...
... Some eruptions have been so violent that entire towns have been wiped out, and thousands of people have died. In ancient Rome, a volcanic eruption destroyed the entire city of Pompeii (pahm-PAY) in 79 A.D. The word volcano comes from Vulcan, the Roman god of fire. Volcanoes are found on every contin ...
Mapping Earth`s Surface
... example, the scale of a map given as a ratio is 1:250,000. At this scale, the distance between two points on the map measures 23.5 cm. How would you find the actual distance? 1. Write the scale as a fraction. ...
... example, the scale of a map given as a ratio is 1:250,000. At this scale, the distance between two points on the map measures 23.5 cm. How would you find the actual distance? 1. Write the scale as a fraction. ...
Mr. Johnson`s Geography
... A hemisphere is half of a sphere, or ball. People use the word to describe one half of earth. Geographers, or people who study earth, have divided the planet into two sets of two hemispheres. These are the Northern and Southern hemispheres and the Eastern and Western hemispheres. The Northern Hemisp ...
... A hemisphere is half of a sphere, or ball. People use the word to describe one half of earth. Geographers, or people who study earth, have divided the planet into two sets of two hemispheres. These are the Northern and Southern hemispheres and the Eastern and Western hemispheres. The Northern Hemisp ...
Geo Bee Jeopardy Level Medium
... How can you use a map scale to help you find actual distances? Answer: 1. Find the map scale. 2. Mark the length of the line segment (usually an inch) shown on a piece of paper. 3. Put the marked paper at one starting point on the map and keep moving it to see how many of those segments fit until y ...
... How can you use a map scale to help you find actual distances? Answer: 1. Find the map scale. 2. Mark the length of the line segment (usually an inch) shown on a piece of paper. 3. Put the marked paper at one starting point on the map and keep moving it to see how many of those segments fit until y ...
Maps
... • Pick a place in the world would like to visit. – What did you see in that place? – What was the landscape like? – What was the weather like? – What were the people like? – What was the vegetation or animals like? ...
... • Pick a place in the world would like to visit. – What did you see in that place? – What was the landscape like? – What was the weather like? – What were the people like? – What was the vegetation or animals like? ...
Name
... 3. Name the projection that shows the whole world except the extreme polar regions? Mercator 4. Where are landmasses distorted on gnomonic projections? ...
... 3. Name the projection that shows the whole world except the extreme polar regions? Mercator 4. Where are landmasses distorted on gnomonic projections? ...
Cartography: Map projejctions
... Another popular equal-area projection (with equally spaced straight lines for the meridians) is the Lambert cylindrical projection given by f (λ, φ) = Rλ g(λ, φ) = R sin(φ) This projection’s perspective is easily visualized by rolling a flexible sheet around the globe and projecting each point hori ...
... Another popular equal-area projection (with equally spaced straight lines for the meridians) is the Lambert cylindrical projection given by f (λ, φ) = Rλ g(λ, φ) = R sin(φ) This projection’s perspective is easily visualized by rolling a flexible sheet around the globe and projecting each point hori ...
Geography - St. Ursula School
... land, population, or history • 1. Nile Valley region – region along Nile River – runs through several countries. • 2. Plains Region of U.S. – united by flat land – covers several states – not whole country ...
... land, population, or history • 1. Nile Valley region – region along Nile River – runs through several countries. • 2. Plains Region of U.S. – united by flat land – covers several states – not whole country ...
Unit Template
... using maps and globes. Students will individually complete a writing prompt evaluating their search and defending their choice for locating information. 9. Students will review intermediate and cardinal directions. Students will view a PowerPoint on the U.S. regions and complete a U.S. map color cod ...
... using maps and globes. Students will individually complete a writing prompt evaluating their search and defending their choice for locating information. 9. Students will review intermediate and cardinal directions. Students will view a PowerPoint on the U.S. regions and complete a U.S. map color cod ...
Maps and Map Projections
... C. tools of geographer - used in any field: 1. maps: cartography, GIS 2. remote sensing: aerial photos, satellite images D. Why study geography E. Region as a concept (Pulsipher pp. 7-10) 1. region: unit of earth’s surface that contains distinct environmental or cultural patterns 2. traits of a regi ...
... C. tools of geographer - used in any field: 1. maps: cartography, GIS 2. remote sensing: aerial photos, satellite images D. Why study geography E. Region as a concept (Pulsipher pp. 7-10) 1. region: unit of earth’s surface that contains distinct environmental or cultural patterns 2. traits of a regi ...
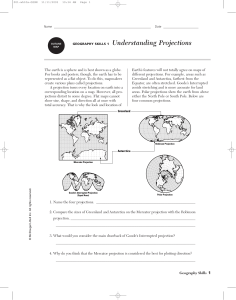
GEOGRAPHY SKILLS 1 Understanding Projections
... The earth is a sphere and is best shown as a globe. For books and posters, though, the earth has to be represented as a flat object. To do this, mapmakers create various plans called projections. A projection turns every location on earth into a corresponding location on a map. However, all projecti ...
... The earth is a sphere and is best shown as a globe. For books and posters, though, the earth has to be represented as a flat object. To do this, mapmakers create various plans called projections. A projection turns every location on earth into a corresponding location on a map. However, all projecti ...
Early world maps
The earliest known world maps date to classical antiquity, the oldest examples of the 6th to 5th centuries BC still based on the flat Earth paradigm.World maps assuming a spherical Earth first appear in the Hellenistic period.The developments of Greek geography during this time, notably by Eratosthenes and Posidonius culminated in the Roman era, with Ptolemy's world map (2nd century AD), which would remain authoritative throughout the Middle Ages.Since Ptolemy, knowledge of the approximate size of the globe allowed cartographers to estimate the extent of their geographical knowledge, and to indicate parts of the globe known to exist but not yet explored as terra incognita.With the Age of Discovery, during the 15th to 18th centuries, world maps became increasingly accurate; exploration of Antarctica and the interior of Africa was left to the 19th and early 20th century.